Context
In the digital age, the convergence of communication and technology has given rise to a social media that has transcended geographical boundaries and revolutionized political engagement.
Impact of Social Media On Indian Politics
In the context of Indian politics, the impact of social media is both profound and far-reaching.
- According to data from analytics firm Social Blade, infotainment creator Dhruv Rathee gained 2.5 million subscribers on YouTube in April alone.
- Similarly, since January, television journalists turned-digital news influencers such as Ravish Kumar and Abhisar Sharma, have seen a significant bump in monthly views on their channels—a rise of 175% and 115%, respectively.
Enroll now for UPSC Online Course
About Social Media & Its Usage
- Refers: It refers to means of interactions among people in which they create, share, and/or exchange information and ideas in virtual communities and networks.
- Statistics: As per Data Reportal, India was home to 462.0 million social media users in January 2024, equating to 32.2 percent of the total population.
- An Important Tool:
- Connecting with people to share updates about government schemes and flagship programmes.
- Share about upcoming national events.
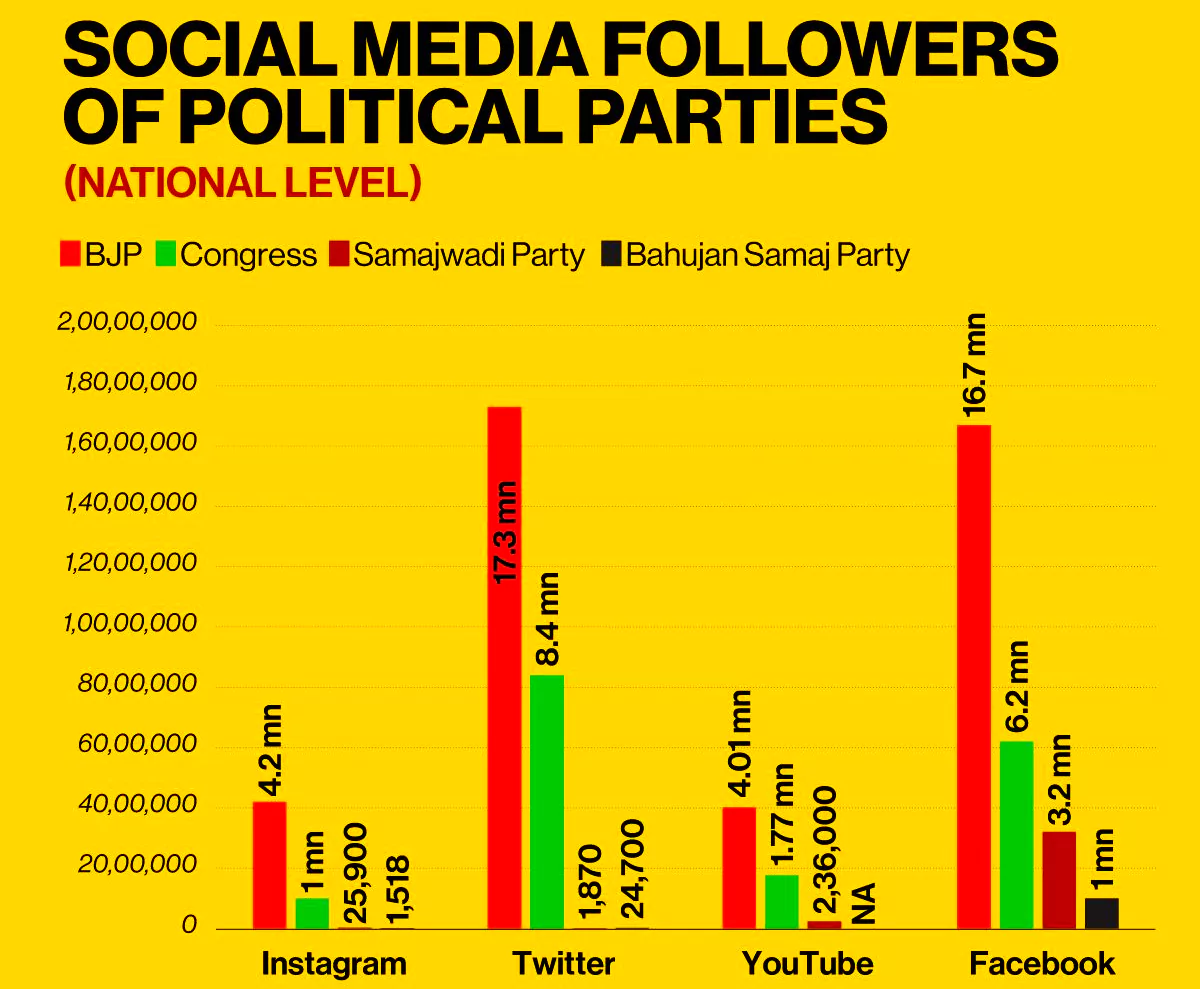 A channel of communication.
A channel of communication.
- During Covid, social media was a boon as people could directly contact for help.
The Rise of Digital Democracy
- Favorable Factors:
- Digital Revolution: In recent years, India has witnessed an exponential growth in internet penetration and smartphone usage, catapulting millions of citizens onto various social media platforms.
Digital Democracy:
- E-democracy, also known as digital democracy or Internet democracy, uses information and communication technology in political and governance processes.
- The term is credited to digital activist Steven Clift.
|
-
- Democratization of Political Discourse: This digital revolution has democratized political discourse, providing individuals from diverse socio-economic backgrounds with a virtual platform to voice their opinions, connect with like-minded individuals, and hold elected representatives accountable.
 Trends Shaping Political Discourse:
Trends Shaping Political Discourse:
- Micro-Targeting and Personalization: Political parties are using data analytics and artificial intelligence to tailor their messages and target specific demographics with precision.
- Influencer Marketing: Influencers and social media personalities wield significant influence over their followers. Political parties are using this phenomenon by collaborating with influencers to amplify their messaging, increase visibility and sway public opinion.
- Real-Time Communication: Using social media platforms, from live streaming rallies to hosting interactive sessions, politicians are leveraging these platforms to cultivate a more authentic and accessible image.

Laws & Regulations on Governing Media
- Information Technology Act (IT), 2000: It seeks to facilitate beneficial uses of cyberspace in India and enhance cyber security through penalising offences related to cyber-crime.
- Section 69-A: It gives the right to the authority to take down any content on the internet against the sovereignty and integrity of India and the security of the states, apart from other reasons.
- The Press Council of India: It is a statutory body that keeps vigil on fake news. It is the self-regulatory watchdog of the press, for the press and by the press, that operates under the Press Council Act of 1978.
- During Conduct of Elections:
- Laws Governing Media Conduct During Elections: During elections, media regulation primarily falls outside the purview of the Election Commission. However, the Commission is tasked with enforcing laws and court directives that may intersect with media activities.
- Section 126 of the Representation of the People Act, 1951: It prohibits the display of any election-related content via cinematograph, television, or similar devices during the 48-hour period leading up to the conclusion of the polls.
- Section 126A of the Representation of the People Act, 1951: It prohibits the conduct of exit polls and the dissemination of their results during specified periods, including the time leading up to the commencement of polls in the first phase and a half-hour after the close of polls for the last phase across all states and union territories.
- Section 127A of the Representation of the People Act, 1951: It governs the printing and publication of election-related materials such as pamphlets and posters, mandating that they bear the names and addresses of the printer and publisher.
- Section 171H of the Indian Penal Code: It prohibits the incurring of expenditures on advertisements and other activities related to elections without the authorization of the contesting candidate.
Enroll now for UPSC Online Classes
Various Initiatives to Regulate Social Media:
- Globally:
- The Digital Services Act of the European Union: It regulates online intermediaries and platforms such as marketplaces, social networks, content-sharing platforms, app stores, and online travel and accommodation platforms. Its main goal is to prevent illegal and harmful activities online and the spread of disinformation.
- The proposed Platform Accountability and Transparency Act (PATA) in the US: It is a law granting academics and researchers broad access to the internal datasets of social media platforms that are covered by the bill’s scope.
- India:
- Fact-checking Websites: Such as Alt News and IndiaSpend’s FactChecker.in attempt to debunk misinformation.
- Other Platforms: Such as Jaano India and Mumbai Votes aim to equip citizens with relevant information on government policies and candidates’ performance.
|
Positive Impact of Social Media on Indian Politics
- Direct Engagement and Personalized Outreach: These social media platforms have facilitated direct and unfiltered communication, enabling politicians to share their policies, perspectives, and visions instantaneously.
- Example: Pariksha Pe Charcha, the event holds interaction between teachers and students who are given an opportunity to meet and communicate with PM Modi.
- Democratization of Information and Participation: Social media empowers citizens with diverse sources of information, fostering political awareness and enabling individuals to form opinions beyond the confines of mainstream media.
- Moreover, it has paved the way for citizen journalism, enabling ordinary individuals to report news and hold those in power accountable.
- Revolutionizing Election Campaigns: Hashtags, live sessions and group chats became indispensable for political parties, enabling them to interact directly with constituents, address concerns, and showcase achievements.
- Empowering Grassroots Activism: Social media’s impact transcends traditional politics and extends to the realm of social movements and grassroots activism.
- Examples: Movements like the Anti-Corruption Movement and the Nirbhaya protests found a platform on social media, enabling individuals to express grievances, organize protests, and garner public support.
- Reshaping Campaign Funding: Crowdfunding and micro-donations through social media have democratized the funding process, enabling smaller parties and independent candidates to compete with more established players.
- Reshaping Data Analytics: The advent of data analytics and sentiment-tracking tools has revolutionized election forecasting and public sentiment analysis and offers valuable insights for campaign strategists.
- Bridging the Gap: Social Media has increased the ability for ordinary citizens to take part in the political process and also has been actively used for influencing diplomatic relations between India and other countries.
- Example: The Saksham App of ECI provides a number of features to help PwDs register to vote, find their polling station, and cast their vote.
Arising Challenges that Need to be Tackled
- Fake News and Misinformation: The proliferation of fake news and misinformation poses a significant threat to the integrity of political conversations. The rapid sharing of unverified content can distort facts and manipulate public opinion.
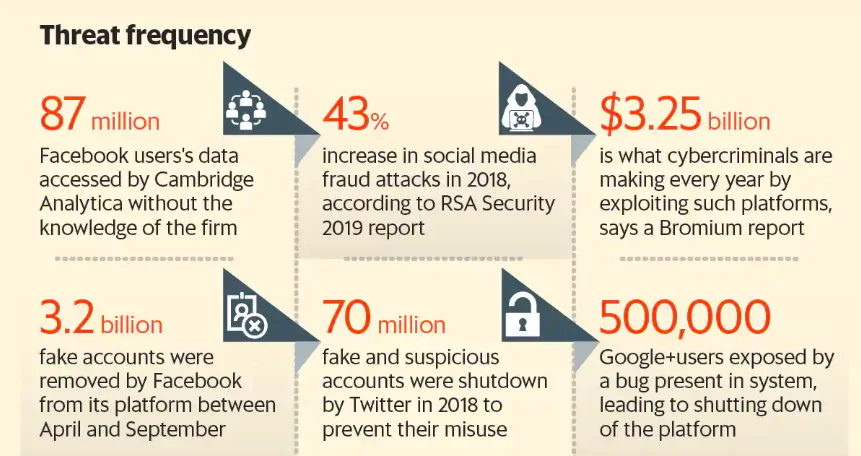 Amplifying Polarization and Echo Chambers: Social media has been criticised by many experts for its contribution to the amplification of ideological polarization. Users are exposed to content that aligns with their existing beliefs, reinforcing echo chambers that hinder healthy political debates.
Amplifying Polarization and Echo Chambers: Social media has been criticised by many experts for its contribution to the amplification of ideological polarization. Users are exposed to content that aligns with their existing beliefs, reinforcing echo chambers that hinder healthy political debates.
- It poses a risk to societal unity and constructive discourse. Moreover, the anonymity granted by social media can foster online harassment and the spread of hate speech.
- Links to Violence: As per various studies in Austria, Sweden and Australia, evidence for an association between increased social media use and online right-wing radicalisation have been found.
- Example: The German study found local outages of Facebook (due to technical faults or internet interruptions, for example) decreased violence in those locations. Also, 50% less anti-refugee sentiment on social media would reduce violent incidents by 12.6%.
- Regulatory Ambiguity: The rapid evolution of social media has outpaced regulatory frameworks, leaving policymakers facing complex issues related to data privacy, online harassment and content moderation.
 The lack of robust regulations and enforcement mechanisms exacerbates the risks associated with online political discourse.
The lack of robust regulations and enforcement mechanisms exacerbates the risks associated with online political discourse.
- Digital Divide: A significant section of the population, particularly in rural and marginalized communities, lack access to digital infrastructure and literacy that exacerbates inequalities in political participation and representation, undermining the democratic ideal of inclusivity.
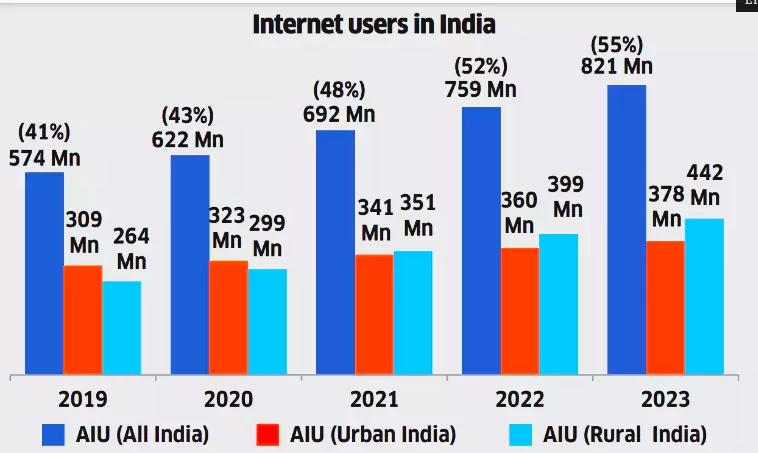
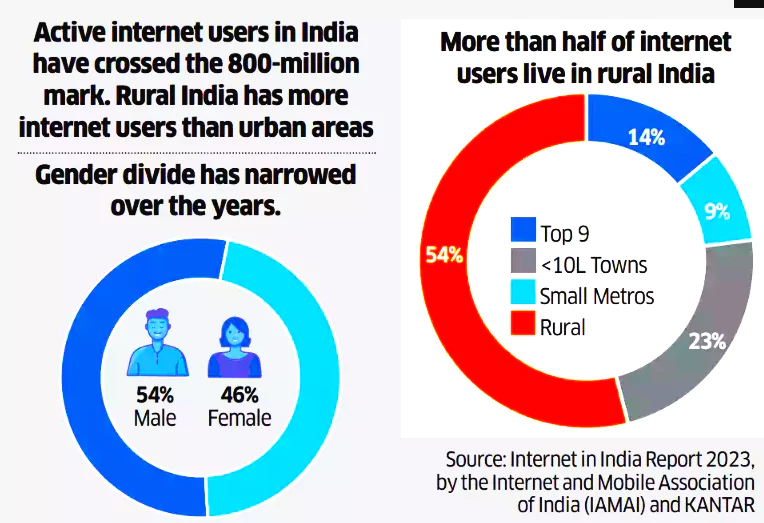
- Example: India has over 820 million active internet users, with more coming from rural areas. The number of non-active internet users is declining. Women lag behind men in internet usage.
- Unequal Participation: Social media distorts policymakers’ perception of public opinion as it is believed that these social media platforms tend to represent every walk of life, but not everyone’s voice is heard equally.
- Disparity: The distribution of effects around the world was also striking. Positive effects on political participation and information consumption were most pronounced in emerging democracies in South America, Africa and Asia. Negative effects were more evident in established democracies in Europe and the United States.
Way Forward
- Media Literacy: There is a need for investing in media literacy programs to equip citizens with the critical thinking skills necessary to identify fact from fiction and navigate the digital landscape responsibly.
- Transparency and Accountability: Political parties and social media platforms must adopt transparency and accountability measures to combat misinformation, protect user data, and uphold ethical standards.
- Regulatory Reform: Policymakers must collaborate with industry stakeholders to develop robust regulatory frameworks that balance the imperatives of free expression with the need to safeguard democratic values and public welfare.
- Maintaining a balance between freedom of the press and addressing misinformation or fake news is required.
- Digital Inclusion: Bridging the digital divide through targeted interventions aimed at expanding access to digital infrastructure, promoting digital literacy, and fostering inclusive online spaces for political engagement.
- Role by Election Commission of India (ECI): The ECI must ensure parity of treatment between political advertising on social media and traditional media and should strictly enforce model code of conduct and should increase vigilance on cyber activities of political parties.
Enroll now for UPSC Online Course
Conclusion
The symbiotic relationship between social media and Indian politics is a double-edged sword, replete with opportunities and challenges. As technology evolves, it is imperative for policymakers, tech companies, and society at large to collaboratively navigate this terrain, harnessing the benefits of social media while mitigating its potential pitfalls.
![]() 16 May 2024
16 May 2024

 A channel of communication.
A channel of communication.
 Trends Shaping Political Discourse:
Trends Shaping Political Discourse:

 Amplifying Polarization and Echo Chambers: Social media has been criticised by many experts for its contribution to the amplification of ideological polarization. Users are exposed to content that aligns with their existing beliefs, reinforcing echo chambers that hinder healthy political debates.
Amplifying Polarization and Echo Chambers: Social media has been criticised by many experts for its contribution to the amplification of ideological polarization. Users are exposed to content that aligns with their existing beliefs, reinforcing echo chambers that hinder healthy political debates.
 The lack of robust regulations and enforcement mechanisms exacerbates the risks associated with online political discourse.
The lack of robust regulations and enforcement mechanisms exacerbates the risks associated with online political discourse.