According to the United Nations Development Programme (UNDP), women and children are 14 times more likely than men to die in a disaster caused due to Climate change.
| Relevance For Prelims: Climate Change In India, Climate Change & Mitigation Strategies, Status Of Women In India, and Women Empowerment And Gender Equality.
Relevance For Mains: Effects of Climate Change on Women. |
|---|
It is necessary to move beyond stereotypes, identify the vulnerabilities of all genders, and employ gender-transformative techniques to ensure a complete and equitable approach to climate adaptation. Instead of being branded as victims, women may take the initiative in climate action.
| Prelims PYQ (2017):
Which of the following gives ‘Global Gender Gap Index’ ranking to the countries of the world? (a) World Economic Forum (b) UN Human Rights Council (c) UN Women (d) World Health Organization Ans: (a) |
|---|
| Mains Question: ‘Climate Change’ is a global problem. How will India be affected by climate change? How Himalayan and coastal states of India will be affected by climate change? (15 M, 250 Words) |
|---|
| Must Read | |
| NCERT Notes For UPSC | UPSC Daily Current Affairs |
| UPSC Blogs | UPSC Daily Editorials |
| Daily Current Affairs Quiz | Daily Main Answer Writing |
| UPSC Mains Previous Year Papers | UPSC Test Series 2024 |
In India, the frequency of human-wildlife interactions is on the rise. Addressing conflicts with wildlife requires solutions beyond reactive capture and relocation.
| Relevance For Prelims: Wildlife Management in India, Wildlife Conservation In India, Rising Human Animal Conflict, Amendments In Wildlife Trade Rules, and WJC Report.
Relevance For Mains: Challenges related to Wildlife Management in India. |
|---|
Enhanced training, habitat restoration, research, and collaboration are critical for negotiating the hazy lines between wildlife “capture” and “rescue,” assuring compassionate and successful management of human-animal conflict in India.
| Prelims PYQ (2022):
With reference to Indian laws about wildlife protection, consider the following statements: 1. Wild animals are the sole property of the government. 2. When a wild animal is declared protected, such animal is entitled for equal protection whether it is found in protected areas or outside. 3. Apprehension of a protected wild animal becoming a danger to human life is sufficient ground for its capture or killing. Which of the statements given above is/are correct? (a) 1 and 2 (b) 2 only (c) 1 and 3 (d) 3 only Ans: (a) |
|---|
| Mains Question: Why is human-wildlife conflict on the rise? What solutions are there to help humans and wildlife coexist? (10 marks, 150 words) |
|---|
| Must Read | |
| NCERT Notes For UPSC | UPSC Daily Current Affairs |
| UPSC Blogs | UPSC Daily Editorials |
| Daily Current Affairs Quiz | Daily Main Answer Writing |
| UPSC Mains Previous Year Papers | UPSC Test Series 2024 |
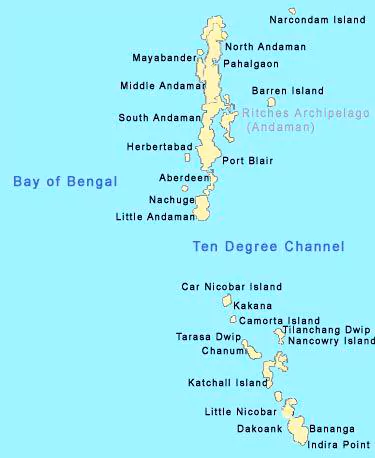
The Strategic Andaman and Nicobar Islands (ANI) are undergoing massive military infrastructure upgrades.
| Relevance For Prelims: Andaman and Nicobar Islands (ANI), The Challenge Of Maritime Security In The Global South, India And Israel Discussed Maritime Safety & Security, Maritime Piracy, Safeguarding India’s Maritime Interests, Exploration Rights In Indian Ocean, 7th Indian Ocean Conference 2024, Indian Ocean Rim Association (IORA), and India’s Response To China’s Naval Expansion
Relevance For Mains: Integrated Theatre Command, Strategic Location and Significance of Andaman and Nicobar islands. |
|---|
 Japanese Occupation: The Japanese conquered the Andaman and Nicobar islands as a potential springboard for an invasion of India following their occupation of Singapore.
Japanese Occupation: The Japanese conquered the Andaman and Nicobar islands as a potential springboard for an invasion of India following their occupation of Singapore.
The Andaman and Nicobar Islands serve as a strategic stronghold in the Indo-Pacific, representing India’s commitment to protecting maritime interests. Strengthening defence capabilities, developing regional collaboration, are critical to sustaining long-term peace and prosperity.
| Prelims PYQ (2014):
Which one of the following pairs of islands is separated from each other by the ‘Ten Degree Channel’? (a) Andman and Nicobar Islands (b) Nicobar and Sumatra (c) Maldives and Lakshadweep (d) Sumatra and Java Ans: (a) |
|---|
| Must Read | |
| NCERT Notes For UPSC | UPSC Daily Current Affairs |
| UPSC Blogs | UPSC Daily Editorials |
| Daily Current Affairs Quiz | Daily Main Answer Writing |
| UPSC Mains Previous Year Papers | UPSC Test Series 2024 |
Scheme for Care and Support to Victims under POCSO...
Addressing the Fatal Consequences of Illegal Hoard...
World Bee Day 2024 and Honey Production in India
SC Verdict on Newsclick Shows Adherence to Due Pro...
Stay Invested: On Chabahar and India-Iran Relation...
Credit Rating Agencies, Impact on India’s De...
<div class="new-fform">
</div>
