![]() 19 Feb 2024
19 Feb 2024

This editorial is based on the news “Misplaced priorities: On the scrapping of the Free Movement Regime between India and Myanmar” which was published in the Hindu. Recently, India has decided to scrap the Free Movement Regime (FMR) between India and Myanmar.
| Relevancy for Prelims: Myanmar Crisis, Instability In Myanmar, Smart Border Fencing, Free Movement Regime (FMR), and India’s Northeast Border Tension.
Relevancy for Mains: Removal of Free Movement Regime (FMR) between India and Myanmar. |
|---|
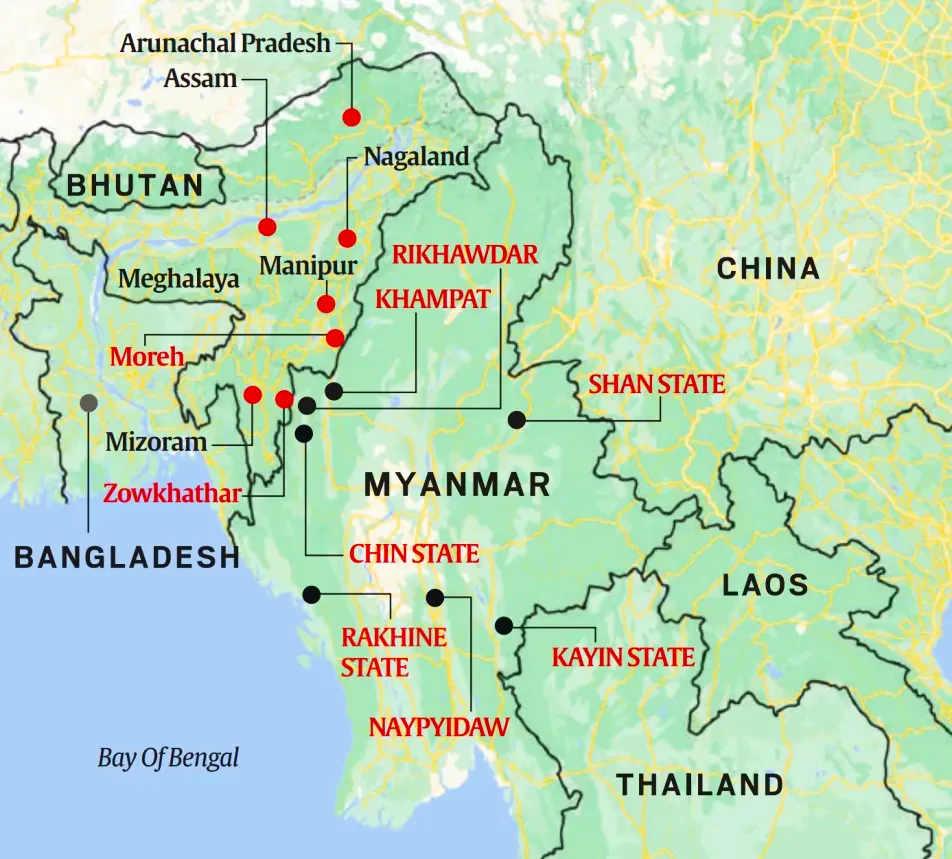
The decision to revoke the Free Movement Regime (FMR) holds immense significance for internal security and demographic integrity of the North Eastern States and to address illegal immigration. However, FMR holds an expression of the will of people of the region who share ethnic relations and the humongous exercise of fencing a border situated in rugged mountains and forests is a case of misplaced priorities and needs reconsideration.
| Prelims PYQ (2016):
Consider the following pairs: Community sometimes mentioned in the news In the affairs of 1. Kurd : Bangladesh 2. Madhesi : Nepal 3. Rohingya : Myanmar Which of the pairs given above is/are correctly matched? (a) 1 and 2 (b) 2 only (c) 2 and 3 (d) 3 only Ans: (c) |
|---|
| Must Read | |
| NCERT Notes For UPSC | UPSC Daily Current Affairs |
| UPSC Blogs | UPSC Daily Editorials |
| Daily Current Affairs Quiz | Daily Main Answer Writing |
| UPSC Mains Previous Year Papers | UPSC Test Series 2024 |
<div class="new-fform">
</div>
