In February 2025, the Union Finance Minister announced the National Manufacturing Mission that aims to boost India’s manufacturing sector.
India’s Industrial Policy Background
- 1957 Industrial Policy: This policy marked the beginning of India’s emphasis on the public sector, where the government played a dominant role in the economy. It aimed to achieve self-reliance and control over key industries.
- As a result, several public sector undertakings (PSUs) like BHEL, ONGC, and SAIL were established to take charge of critical sectors such as power, oil, and steel.
- 1991 Liberalization: The 1991 economic reforms marked a major shift, as the focus moved towards liberalization, privatization, and globalization. The government opened up the economy to private enterprises and foreign direct investment (FDI).
- However, despite these reforms, the Micro, Small, and Medium Enterprises (MSME) sector was largely left behind in the modernization process and continued to face challenges.
- Post-2008 Slowdown: After the global financial crisis of 2008, global trade growth, which had been expanding at a rate of around 20% annually, began to slow down.
- Protectionist policies became more prevalent, as countries started focusing more on safeguarding their own industries in response to economic uncertainties.
- Current Challenges: Today, industries around the world face several new challenges, including global disruptions, technological advancements like AI, and the shift toward green technology.
- Global Politics: Additionally, political changes are influencing industrial policies worldwide. For example, the United States has increasingly adopted protectionist measures, particularly under Donald Trump’s “Make America Great Again” campaign, which aimed to protect American industries from foreign competition.
- China’s Dumping: Another major concern is the practice of “dumping” by China, where it sells goods at prices lower than the market value, which undermines the competitiveness of industries in other countries and causes damage to local businesses.
- Shift Toward Slowbalization: In response to these global disruptions and protectionist tendencies, the world is moving towards a phase of “slowbalization”—a term used to describe the slowing down of globalization. This trend involves reduced global trade integration and a shift towards more localized and protectionist economic policies.
National Manufacturing Mission: Key Highlights
National Manufacturing Mission
- A National Manufacturing Mission was announced to promote Make in India, offering policy support, execution roadmaps, and frameworks for governance and monitoring.
- The mission will also support clean-tech manufacturing in sectors such as solar PV cells, EV batteries, wind turbines, very high voltage transmission equipment and grid-scale batteries.
- The National Manufacturing Mission will lay emphasis on five focal areas;
- Ease and cost of doing business
- Future ready workforce for in-demand jobs
- A vibrant and dynamic MSME sector
- Availability of technology
- Quality products.
|
- Footwear and Leather Sector: A major initiative under the National Manufacturing Mission focuses on India’s footwear and leather industry. This includes a comprehensive support scheme aimed at enhancing design capacity, component manufacturing, and machinery required for producing non-leather quality footwear.
- Job Creation: The scheme is expected to create up to 2.2 million jobs.
- National Action Plan for Toys: Additionally, the initiative includes the establishment of a National Action Plan for Toys. This plan emphasizes cluster development, skill development, and building a manufacturing ecosystem to produce high-quality, innovative toys for both domestic and international markets.
- Cluster Development: The goal is to centralize toy production in a single region, where all related industries, including skilled labor and raw materials, are available in one place.
- Potential: The Indian toy market has the potential to reach a value of ₹15,000 crore, though it is currently dominated by China.
- Food Processing Sector: India, being one of the largest producers of cereals, fruits, vegetables, dairy, and crustaceans, has significant untapped potential in the food processing industry.
- Underdeveloped Procession Industry: However, this sector has been underdeveloped due to low levels of processing, which limits job creation and income generation.
- Addressing the Issue: To address this, the 2025 Budget has proposed the creation of a new National Institute of Food Technology, Entrepreneurship, and Management to be set up in Bihar.
- Creation of Makhana Board: One notable initiative is the formation of a Makhana Board in Bihar, designed to enhance value addition in the processing of this traditional crop.
| Food Processing
India is a major producer of several agricultural/food items in the world but only less than 10 percent of that is processed. However, in countries like the USA this is around 50 percent. |
- Support for MSMEs: The Budget has introduced significant changes to support the Micro, Small, and Medium Enterprises (MSMEs). Key measures include:
- Doubling of Investment and Turnover Criteria: The criteria for defining MSMEs have been revised, doubling the limits for investment and turnover.
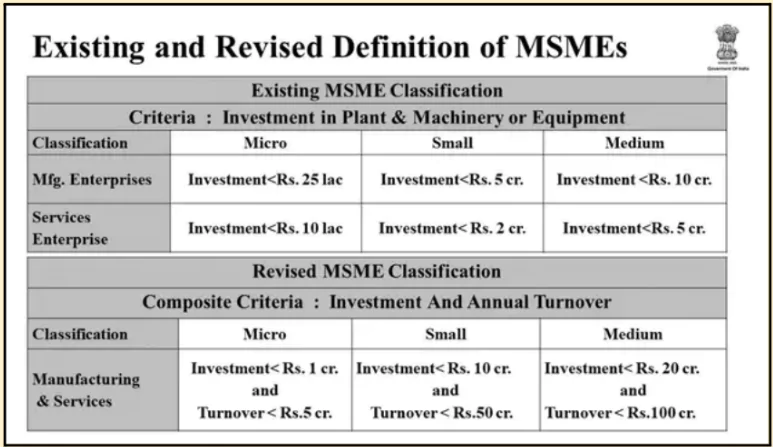
-
- Enhanced Credit Guarantee: The credit guarantee cover has been increased from ₹5 crore to ₹10 crore (₹20 crore for exporting firms).
- Credit Cards for Micro-Enterprises: A new initiative will provide a ₹5 lakh credit card to micro-enterprises, addressing their daily credit needs and reducing reliance on informal lenders and microfinance companies.
- Fund of Funds for Start-ups: To foster innovation and entrepreneurship, a new Fund of Funds with a fresh contribution of ₹10,000 crore has been established.
- Focusing on Green Industries: As part of the National Manufacturing Mission, India will push for green industries that promote clean energy solutions. These sectors—such as solar energy, electric vehicles, and wind power—are poised for rapid growth.
- This will align with India’s pledge to reach net zero emissions by 2070.
Challenges
- Outsourcing: Many established players in traditional industries are increasingly outsourcing production of even low-tech, labor-intensive goods, such as garments, artificial flowers, crockery, plastic ware, and furniture. These items are often sold under Indian brand names.
- Impact: This outsourcing trend has a significant downside: it is destroying millions of jobs, particularly in the MSME sector, which is crucial for India’s employment landscape.
Need for a New Industrial Policy
- Advocating for Accelerated Industrialization: In light of these challenges, the India Industrial Development Report 2024-25, prepared by the Institute for Studies in Industrial Development (ISID), makes a compelling case for a new industrial policy.
- Key Principles for the New Policy: The proposed new policy should be guided by several broad principles:
- Primacy of Localization: Emphasizing job creation and value addition within the country.
- Entrepreneurship Development: Promoting local entrepreneurship and technological capabilities. For instance, the government can launch Make in India 2.0
- Technological Self-Reliance: Building a foundation for locally anchored innovations and capabilities.
- Coordination Between Centre and States: A high-powered institutional framework will be necessary for the coordinated implementation of this new policy in an ever-evolving global and domestic context.
- Benefit: A robust manufacturing sector has the potential to create up to 100 million jobs
- It can increase the share of manufacturing in India’s GDP from 17% to 25% or more.
- Expanding the manufacturing sector will also bolster India’s global trade position.
Conclusion
Manufacturing plays a crucial role in driving economic growth. For India to achieve its goal of becoming a developed nation—Viksit Bharat by 2047—it is essential to have 25% of the total GDP contributed by the manufacturing sector. If the National Manufacturing Mission is implemented properly India can become the ‘Factor of the World’.
![]() 15 Mar 2025
15 Mar 2025

