![]() 7 Dec 2023
7 Dec 2023
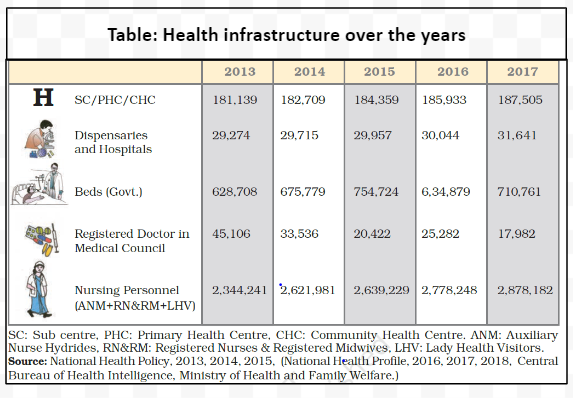
The impact of education, health, and employment on India’s economy is substantial, influencing various aspects of the nation’s Economic Prosperity, productivity, and human capital development.
The quality of a population, which hinges on literacy rates, health (indicated by life expectancy), and skill acquisition, significantly influences a nation’s growth trajectory.
A well-educated and healthy populace is considered an asset.
|
India as a Knowledge Economy
|
|---|
A reflective assessment of the educational landscape in India projects certain future prospects that need to be addressed to enhance literacy and employability, especially among the youth.
|
Glossary
|
|---|
<div class="new-fform">
</div>