It is wonderful to watch the sky after sunset. One would see the shining objects – some are bright, others dim. They all appear to be twinkling. Along with these bright objects, one may also see the moon. In this chapter, we will learn how these “twinkling little stars” were formed, the story of origin and evolution of the earth. With that we will eventually read about our solar system.
A large number of hypotheses were given by different philosophers and scientists regarding the origin of the earth.
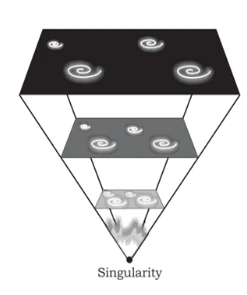
From Singularity to Expansion: Exploring the Big Bang and the Evolution of the Universe
Do You Know?
|
<div class="new-fform">
</div>
