![]() 5 Dec 2023
5 Dec 2023
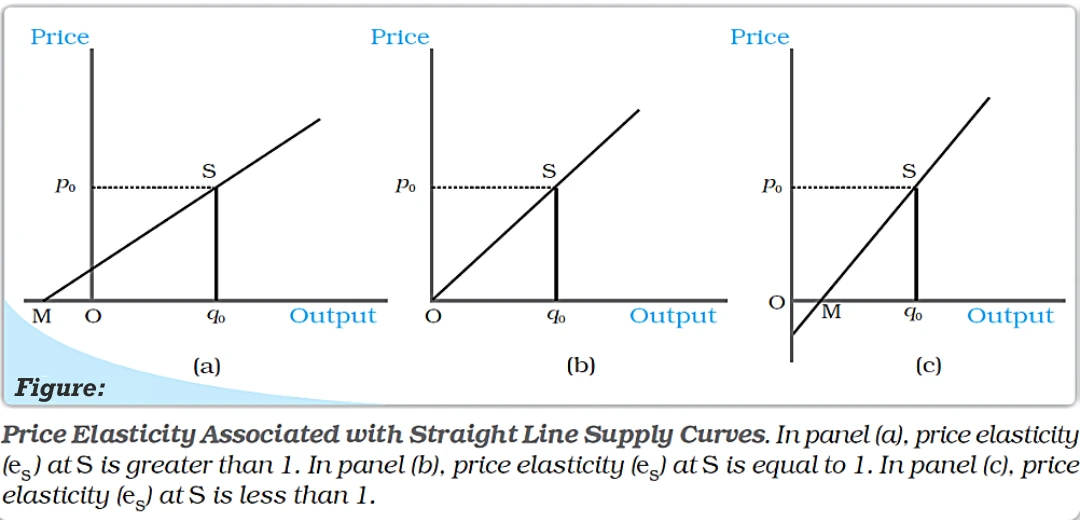
Price Elasticity of Supply refers to the responsiveness of the quantity supplied of a good or service to changes in its price. It measures the degree to which the quantity supplied responds to changes in price, indicating how sensitive producers are to price changes in the market.
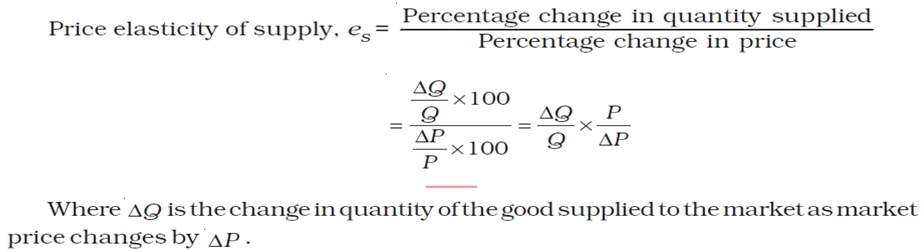
Glossary
|
|---|
<div class="new-fform">
</div>