Profit maximization means increasing profits by business firms using a proper strategy to equal marginal revenue and marginal cost.
This strategy is not only about revenue generation but also the efficient allocation of resources, essential for a firm’s longevity and success in a competitive market landscape.
Profit maximization: Breaking down the concept into key points
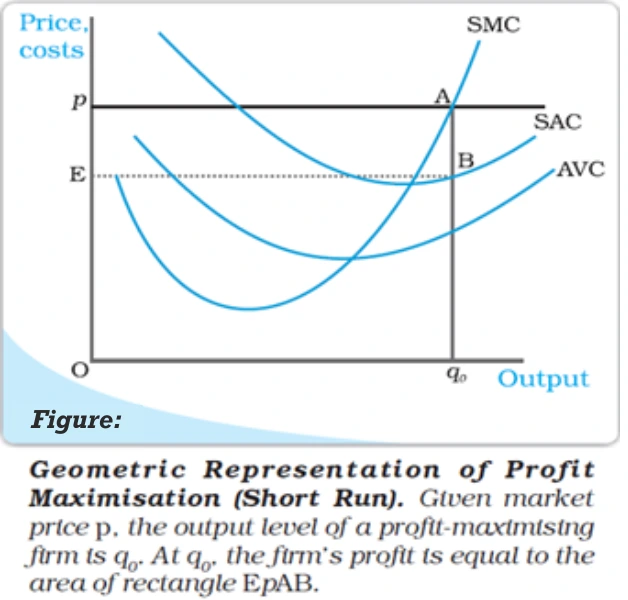
Three cardinal conditions must be satisfied at q0 to achieve profit maximization:
Profit maximization is defined as the difference between total revenue and total cost.
Relation Between Output, Revenue, and Cost: Maximizing Profits Insightfully
Profit Maximization Condition: Balancing Marginal Revenue and Cost
Perfect Competition Scenario: Equating Price and Marginal Cost
The second condition for profit maximization is that the output level is positive. The focus is on the slope of the marginal cost curve at the Profit maximization output level.
Marginal Cost Curve Slope Significance
Drawing from the argument in Condition 1, it’s inferred that the firm’s profit at an output level in Condition 2 slightly smaller than q1 surpasses the profit at output level q1.
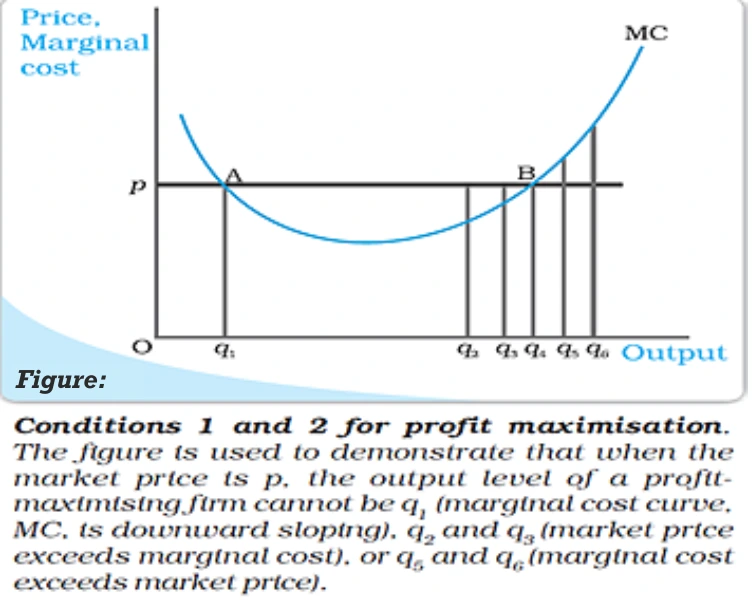
Condition 3 is crucial for determining the Profit maximization output level when it’s positive, with distinct implications in the short run and long run.
Short Run Scenario (Case 1): Avoiding Losses in Short-Run Production
Price ≥ Average Variable Cost (AVC) Refer to figure The assertion is that a Profit maximization firm will avoid production at an output level where the market price falls below the AVC in the short run.
Analysis at Output Level q1: Price vs. Costs in Short-Run Production
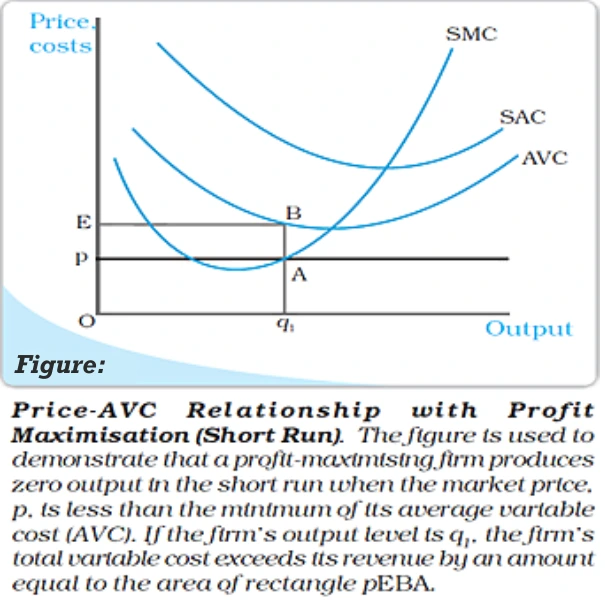
Profit Comparison at Zero Output: Short-Run Comparison at q1
Long Run Scenario (Case 2): Price ≥ Average Cost (AC) Refer to Figure
Analysis at Output Level q1: Price, Revenue, and Total Cost Dynamics
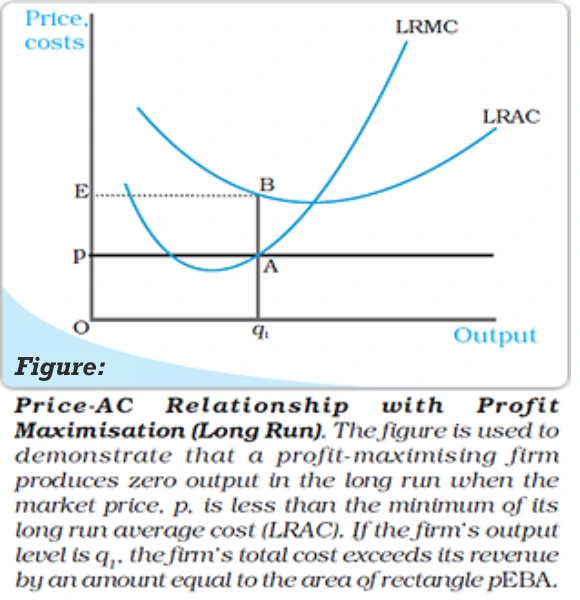
Profit and Loss Analysis: Profitability Evaluation
The Profit Maximisation Problem: Graphical Representation
<div class="new-fform">
</div>
