Introduction:
The Dravidian style of architecture, prevalent in Southern India, is characterized by towering gopurams, intricately carved pillared halls, and vimanas atop temples. It embodies a unique and ornate design.
Architectural Distinctions of Dravida Temples:
- New Features:Dravida temples, in contrast to nagara temples, are enclosed within a compound wall.
- Gopuram: The entrance wall boasts a central gateway known as a gopuram.
- Structural Changes: The vimana, the main temple tower in Tamil Nadu, takes the form of a geometrically rising stepped pyramid, differing from the curving shikhara of North India.
Enroll now for UPSC Online Course
Shikhara: Exploring South Indian Temple Architecture
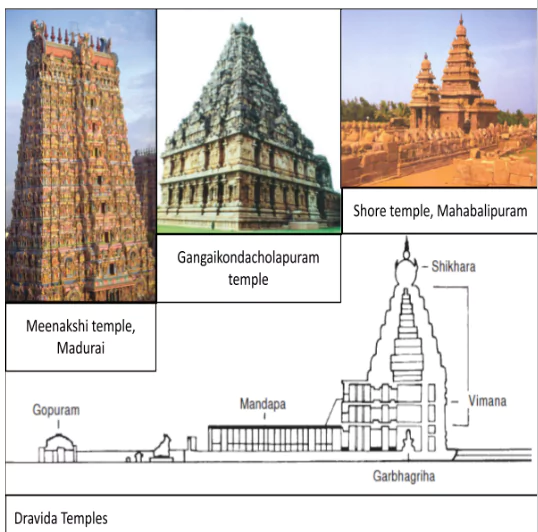
- Shikhara: In South Indian temples, the term ‘shikhara’ refers only to the crowning element, usually shaped like a small stupika or an octagonal cupola (equivalent to the amlak and kalasha of North Indian temples).
- Guards: Entrance sculptures typically depict fierce dvarapalas (door-keepers) guarding the temple.
- Water Reservoir: Temple complexes often include large water reservoirs or temple tanks.
Evolution of Temple Size
- Differentiating Elements: Unlike North Indian temples with clusters of shikharas, South Indian temples often have the main temple with one of the smallest towers, indicating its historical significance.
- Huge Gopuram: Over time, as towns expanded, new boundary walls with loftier gopurams were constructed around the temple.
- Example: Srirangam temple in Tiruchirapalli showcases multiple concentric rectangular enclosure walls, each with gopurams of varying heights.
Urbanization and Administrative Centers
- Main Areas: Temples in TamilNadu, such as those in Kanchipuram, Thanjavur, Madurai, and Kumbakonam, became focal points of urban architecture.
- Transformation: Temples transformed into rich administrative centers, exerting control over extensive land areas during the eighth to twelfth centuries.
Classification of Dravida Temples
- Dravida temples are categorized into five shapes:
- Square (kuta or caturasra),
- Rectangular (shala or ayatasra),
- Elliptical (gaja-prishta or vrittayata),
- Circular (vritta), and
- Octagonal (ashtasra).
- The choice of temple plan and vimana shape is influenced by the iconographic nature of the consecrated deity.
Enroll now for UPSC Online Classes
Conclusion
- With its distinctive features and spiritual significance, the Dravida style continues to inspire awe and reverence, serving as a testament to the enduring legacy of South Indian craftsmanship and devotion.

