![]() May 4, 2024
May 4, 2024
![]() 24859
24859
![]() 0
0
The Himalayas, a majestic mountain range stretching from the Indus River to the Brahmaputra River, dominate the northern landscape of India. Comprising three parallel ranges, the Great Himalayas stand as the highest peaks, boasting an average height of 6,000 meters. These geologically young mountains, with their rugged terrain and expansive valleys, serve as a formidable natural barrier. From the wide expanse of the North Himalayas to the Shiwalik Hills, these iconic ranges shape the geography and culture of the regions it spans.
Division of Himalaya: The Himalayas consist of three main parallel ranges: the Great Himalayas (Himadri), Lesser Himalayas (Himachal), and Shiwaliks (Refer Figure)
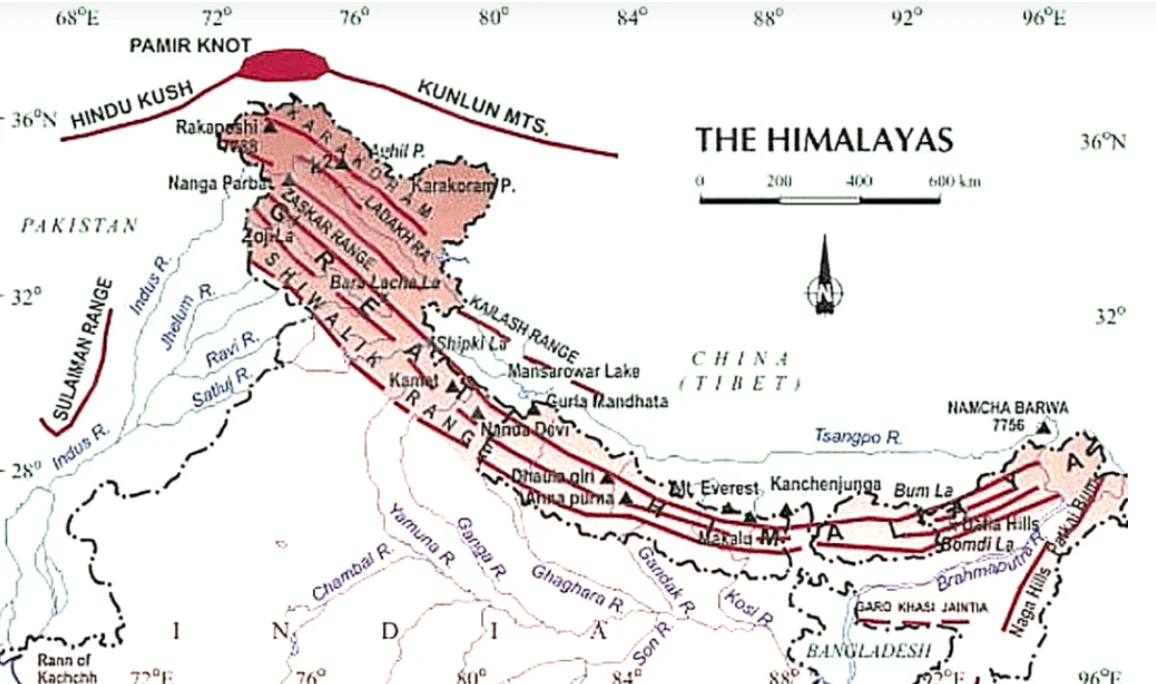
| Namcha Barwa: situated in south east Tibet; Nanda Devi (part of Kumaon Himalayas) is the third highest peak in India. [UPSC 2023] |
| Must Read | |
| Current Affairs | Editorial Analysis |
| Upsc Notes | Upsc Blogs |
| NCERT Notes | Free Main Answer Writing |
Conclusion
In India’s geography, the North-South division of the Himalayas is split into three parts: the Greater, Middle, and Siwaliks HImalayas. These mountains are strong and remarkable. They have existed for a long time and have witnessed many events. They have a significant impact on their surroundings, influencing the weather and the way people live. And they will continue to be important for a long time to come.
<div class="new-fform">
</div>
Latest Comments