UPSC IFoS Chemistry Optional 2026 guide covering exam pattern, detailed syllabus of Papers I and II, previous year question papers, trends, success rate, advantages, disadvantages, and recommended books to help aspirants prepare effectively for the Indian Forest Service Mains exam.

The UPSC IFoS Chemistry Optional is a popular choice among science graduates due to its well-defined syllabus and high scoring potential. With two optional papers carrying 400 marks, Chemistry plays a decisive role in the IFS Mains 2026. This article provides a complete overview of the Chemistry optional syllabus, exam pattern, previous year papers, trends, success rates, pros and cons, and recommended books to help aspirants plan a focused and effective preparation strategy.
The UPSC IFS mains include a total of six papers with a total of 1400 marks. Out of 6 papers one paper is of English and one on General Knowledge. The remaining four papers (Paper I, Paper II, Paper III and Paper IV) cover optional subjects that candidates have chosen during the application form filling process. Although Paper I and Paper II have a maximum of 300 marks each, the remaining 800 marks of the mains examination depend on the optional subjects. It becomes very crucial to choose the right optional subject and adopt the right strategy so that candidates can score as much as possible. So in this article we will first explore the importance and weightage of optionals, and then we will analyze UPSC IFoS Chemistry Optional Paper.
In UPSC IFS mains examination candidates have to choose two optional subjects from the list specified in the official notification unlike UPSC IAS mains exam in which candidate has to choose only one optional subject. In IFS exam optional subjects have very high scoring potential because after Paper I and Paper II which consist of 600 marks optional have 800 marks so here optional plays a decisive role in determining your selection as well as to achieve a good rank.
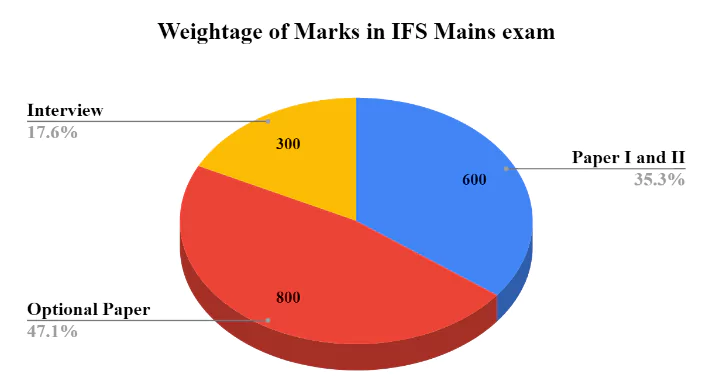
It is evident that in the entire selection process, the optional subject plays a crucial role in preparing for the UPSC IFS exam, as it accounts for almost 48% of the total marks. This substantial portion contributes significantly to the overall evaluation of the entire exam.
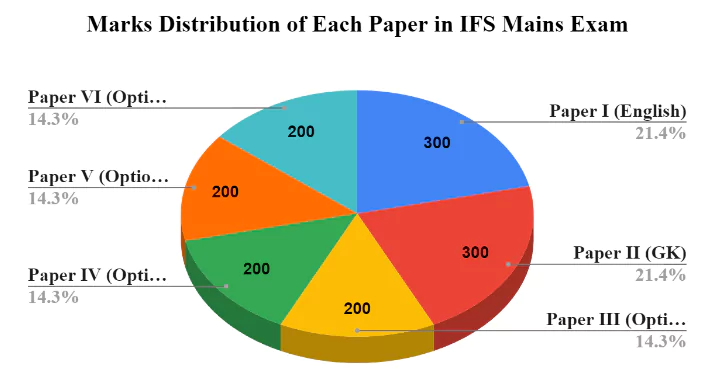
Upon further magnification, we can conclude that in the IFS mains examination, the optional section carries almost 58% of the total mains marks. Therefore, scoring well in the optional section, along with Paper I and Paper II, will result in higher overall marks in the exam.
In the UPSC IFS Mains examination, UPSC IFoS Chemistry Optional Paper include two papers, specifically Paper I and Paper II. Each of these papers have a maximum weightage of 200 marks, which makes a total of 400 marks for this optional subject. Among the various optional subjects mentioned by UPSC in IFS, Chemistry is one of the 14 optional subjects available to candidates.
| UPSC IFoS Chemistry Optional Paper | Syllabus of UPSC IFoS Chemistry Optional Paper |
| Paper I of UPSC IFoS Chemistry Optional Paper |
|
| Paper II of UPSC IFoS Chemistry Optional Paper |
|
UPSC Chemistry Optional Question Papers from 2018 to 2025 are readily available for aspirants seeking to enhance their preparation. We provided access to the UPSC IFoS Chemistry Optional Paper in PDF format, an invaluable resource for your preparation.
| Year | Paper of UPSC IFoS Chemistry Optional Paper |
| UPSC IFS Chemistry Optional Question Paper 2018 | Download Paper I |
| UPSC IFS Chemistry Optional Question Paper 2019 | Download Paper I |
| UPSC IFS Chemistry Optional Question Paper 2020 | Download Paper I |
| UPSC IFS Chemistry Optional Question Paper 2021 | Download Paper I |
| UPSC IFS Chemistry Optional Question Paper 2022 | Download Paper I |
| UPSC IFS Chemistry Optional Question Paper 2023 | Download Paper I |
| UPSC IFS Chemistry Optional Question Paper 2024 | Download Paper I |
| UPSC IFS Chemistry Optional Question Paper 2025 | Download Paper I |
The IFoS Chemistry Optional Syllabus PDF provides a comprehensive and structured outline of Paper I and Paper II topics prescribed by UPSC. It helps candidates understand syllabus coverage, identify high-weightage areas, plan systematic study schedules, and align preparation with the latest IFS Mains examination pattern and trends.
Candidates appearing for the UPSC (Union Public Service Commission) IFS examination must make a thoughtful decision while selecting their optional subject, as it holds substantial weightage in the evaluation process. With a total of 800 marks allotted, the optional subject carry approximately 48% of the combined marks for both the written exam and the personality test (interview).
The table below offers a comprehensive overview of the success rate achieved by candidates who opted for UPSC IFoS Chemistry Optional Paper as their optional.
| Year | Number of Candidates for UPSC IFoS Chemistry Optional Paper | ||
| Appeared in Interview | Recommended | Passing (%) | |
| 2015 | 14 | 7 | 50 |
| 2016 | 18 | 8 | 44.4 |
| 2017 | 18 | 9 | 50 |
| 2018 | 22 | 8 | 36.4 |
| 2019 | 8 | 1 | 12.5 |
| 2020 | 12 | 6 | 50 |
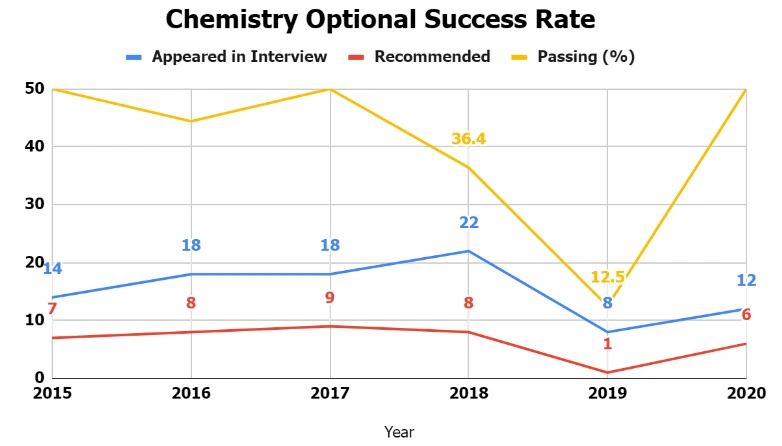
By examining the past papers of the Chemistry Optional, we can identify a trend in the types of questions asked. There is also a noticeable shift in the themes of the questions. Understanding the UPSC IFoS Chemistry Optional Paper Trend Analysis is advantageous, as it allows candidates to streamline their preparation effectively and enhance their performance in this optional subject.
Pros of opting Chemistry as an optional Subject: A Strategic Choice for Exam Success
Please note that before selecting Chemistry Paper as your optional subject, carefully weigh these disadvantages against the advantages and consider your own background, interests, and the time you can dedicate to preparation.
| Must Read | |
| NCERT Notes For UPSC | UPSC Daily Current Affairs |
| UPSC Blogs | UPSC Daily Editorials |
| Daily Current Affairs Quiz | Daily Main Answer Writing |
| UPSC Mains Previous Year Papers | UPSC Test Series |
Check Out UPSC CSE Books
Visit PW Store
There are a total 14 subjects mentioned in the official notification for IFoS main optional Papers.
Yes, Chemistry is a good optional for candidates with a strong academic background in chemistry. It has a well-defined syllabus, conceptual clarity, and good scoring potential, but requires consistent practice and answer-writing skills.
The IFoS Chemistry Optional consists of two descriptive papers—Paper I and Paper II, each carrying 200 marks, making a total of 400 marks in the Indian Forest Service Mains examination.
Syllabus of chemical engineering optional paper is same to some extent but more than half of the syllabus is different.
Both Paper I and Paper II are descriptive in nature, each of 3 hours duration and 200 marks, with questions based strictly on the UPSC-prescribed syllabus.
<div class="new-fform">
</div>