World Soil Day 2025, celebrated on December 5, focuses on the theme “Healthy soils for healthy cities.” Learn about its history, importance, significance, challenges, and the role of urban soils in building sustainable and resilient cities.

World Soil Day is observed every year on December 5 to highlight the vital importance of soil for life on Earth. With over 95% of our food relying on soil, its health is essential for humanity and the planet. World Soil Day 2025, themed ‘Healthy soils for healthy cities’, focuses on the crucial role of urban soils and the challenges posed by urbanization and soil sealing. It emphasizes how city soils support food production, filter water, store carbon, regulate temperatures, and sustain biodiversity. This year’s observance is a call to action for policymakers, scientists, city leaders, civil society, and citizens to rethink urban spaces through their soils and build healthy, green, and resilient cities where people and nature can thrive together.
World Soil Day was officially recognised by the United Nations General Assembly in 2014 to highlight the importance of soil health. It is celebrated every year to focus on the sustainable management of soil resources. This event was established under the guidance of the International Union of Soil Sciences (IUSS) and supported by the Food and Agriculture Organization (FAO).
| World Soil Day 2025 Overview | |
| Aspect | Details |
| Event Name | World Soil Day 2025 |
| Date | December 5, 2025 |
| Theme | Healthy soils for healthy cities |
| Established By | International Union of Soil Sciences (IUSS) |
| Official Recognition | Endorsed by FAO in 2013, adopted by the UN General Assembly in December 2013 |
| Purpose | To raise awareness about the importance of healthy soils and advocate for sustainable management practices |
| Significance | Highlights soil’s role in food security, climate action, and environmental resilience |
| Key Activities | Campaigns, educational events, workshops, and advocacy for sustainable soil management |
| Global Observance | Celebrated worldwide by governments, organisations, and communities |
The International Union of Soil Sciences (IUSS) presented the concept of World Soil Day in 2002, which was officially endorsed by the Food and Agriculture Organization (FAO) in 2013. The United Nations General Assembly (UNGA) adopted it in December 2013, choosing December 5 to honour the late King Bhumibol Adulyadej of Thailand, a key supporter of this initiative.
The theme for 2025, “Healthy soils for healthy cities,” emphasizes the importance of soils in cities and the problems faced by soil sealing and urbanization. Urban soils have an important role in ecosystem services, such as food production, water purification, carbon storage, temperature regulation, and biodiversity conservation.
Theme for 2025: “Healthy soils for healthy cities.”
Highlights the role of soils in urban areas.
Addresses challenges like soil sealing and rapid urbanization.
Urban soils support food production, water filtration, carbon storage, and temperature regulation.
They also help sustain biodiversity in cities.
World Soil Day 2025 urges collective action to protect and restore urban soils.
This year’s theme encourages policymakers, scientists, city leaders, and citizens to build healthy, green, sustainable cities.
Soil is a crucial natural resource that supports agriculture, biodiversity, and water purification. However, increasing threats like erosion, deforestation, and industrial activities have led to significant soil degradation. Here’s why World Soil Day 2025 is celebrated:
Soil is the uppermost layer of the Earth’s crust, composed of minerals, organic matter, water, and air. It serves as the foundation for plant growth and is essential for supporting life on the planet.
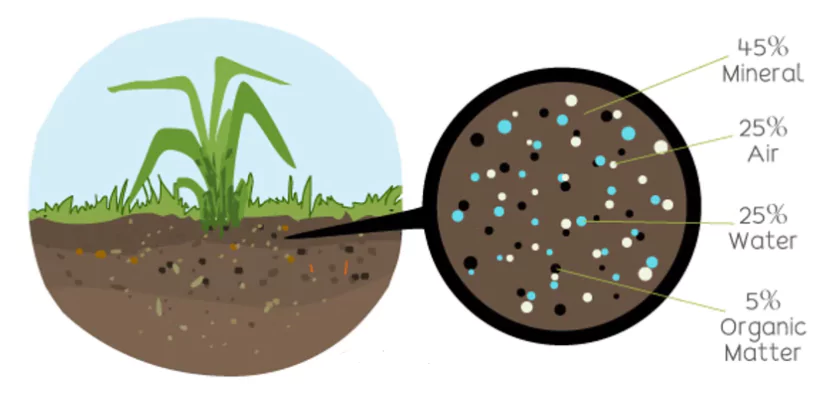
Soil forms over thousands of years through the weathering of rocks and the decomposition of organic materials. It is classified into various types based on texture, colour, and composition.
Soil contains 15 of the 18 naturally occurring elements essential for plants, which makes it a cornerstone of agriculture and food security. These include primary nutrients like nitrogen, phosphorus, and potassium, and secondary nutrients like calcium, magnesium, and sulfur.
India’s diverse geography and climatic conditions produce various types of soil, each of them having unique properties and suitability for specific crops. Understanding these soil types is necessary for optimising agricultural practices and ensuring food security in India. Here’s an overview:
| Types of Soil Found in India | |||
| Type of Soil | Characteristics | Regions Found | Crops Grown |
| Alluvial Soil | Fertile, rich in nutrients, loamy | Indo-Gangetic Plains | Wheat, rice, sugarcane |
| Black Soil | Retains moisture, rich in lime | Deccan Plateau | Cotton, sorghum, millet |
| Red Soil | Sandy, rich in iron | Eastern and Southern India | Groundnuts, pulses, millet |
| Laterite Soil | Acidic, poor in fertility | Western Ghats, Eastern Ghats | Cashew, tea, coffee |
| Desert Soil | Sandy, low in organic matter | Rajasthan, Gujarat | Millets, barley |
| Mountain Soil | Rich in organic matter | Himalayan Region | Tea, apples, cardamom |
Source: mapsofindia.com
Primary nutrients are often added to soil in the form of fertilizers to ensure optimum agricultural yield. The three primary nutrients essential for plant growth are:
Secondary nutrients are present in smaller amounts but are vital for balanced soil nutrition. Apart from the primary nutrients, secondary nutrients are equally crucial for soil health:
Soils face significant threats from degradation, pollution, and unsustainable practices. These challenges reduce soil fertility, disrupt ecosystems, and threaten global food security, which all make immediate intervention a necessity.
| According to the New Delhi-based National Academy of Agricultural Sciences (NAAS), the annual soil loss rate in our country is about 15.35 tonnes per ha, resulting in a loss of 5.37 to 8.4 million tonnes of nutrients. |
|---|
India faces many challenges in soil conservation due to deforestation, urbanization, and unsustainable farming. To combat these issues, the government and various organizations have implemented several strategies:
As individuals, we can take small yet impactful steps toward soil conservation, on World Soil Day 2025:
World Soil Day serves as a reminder of the indispensable role soil plays in sustaining life. As the global population grows, protecting and restoring soil health has never been more critical. By understanding what is soil, the types of soil in India, and the importance of nutrients, we can take steps to ensure a sustainable future.
This World Soil Day 2025, let us pledge to work towards healthier soils for a healthier planet. Together, we can build awareness and take action to preserve this vital resource for generations to come.
Ready to boost your UPSC 2026 preparation? Join PW’s UPSC online courses today!
Check Out UPSC CSE Books
Visit PW Store
World Soil Day is observed on December 5 each year to promote awareness about soil health and advocate for sustainable soil management.
World Soil Day 2025 highlights the role of healthy soils in food security, biodiversity, and climate action under the theme Caring for Soils: Measure, Monitor, Manage.
Soil is a mix of minerals, organic matter, water, and air, vital for plant growth, water filtration, and supporting biodiversity.
India has diverse soils like alluvial, black, red, laterite, desert, and mountain soils, each supporting specific crops.
The three primary nutrients are nitrogen, phosphorus, and potassium, essential for plant growth and health.
Soil conservation in India includes practices like crop rotation, organic farming, cover cropping, and the Soil Health Card scheme to maintain fertility and prevent erosion.
<div class="new-fform">
</div>