In Alabama, USA a convict has been executed using nitrogen hypoxia for the first time as a method of capital punishment.
| ICCPR: Article 6 allows limited use but emphasises the possibility of abolition by any State Party without delay. |
|---|
News Source: The Hindu
| Must Read | |
| NCERT Notes For UPSC | UPSC Daily Current Affairs |
| UPSC Blogs | UPSC Daily Editorials |
| Daily Current Affairs Quiz | Daily Main Answer Writing |
| UPSC Mains Previous Year Papers | UPSC Test Series 2024 |
New Aadhaar cards now come with an explicit disclaimer of it being a proof of identity and not of citizenship or date of birth.

The Unique Identification Authority of India (UIDAI)
|
|---|
Also Read:
News Source: The Hindu
| Must Read | |
| NCERT Notes For UPSC | UPSC Daily Current Affairs |
| UPSC Blogs | UPSC Daily Editorials |
| Daily Current Affairs Quiz | Daily Main Answer Writing |
| UPSC Mains Previous Year Papers | UPSC Test Series 2024 |
Scientists from South African universities survey Marion Island to locate and record each wandering albatross nest.

Environmental Variables Affecting the Birds’ Choice of Nest Site
|
|---|
News Source: Down To Earth
| Must Read | |
| NCERT Notes For UPSC | UPSC Daily Current Affairs |
| UPSC Blogs | UPSC Daily Editorials |
| Daily Current Affairs Quiz | Daily Main Answer Writing |
| UPSC Mains Previous Year Papers | UPSC Test Series 2024 |
On the Occasion of 75th Republic Day, the PM, all three military chiefs placed a wreath on the Amar jawan Jyoti situated at the Amar Chakra of the National War Memorial in New Delhi.
History of Amar Jawan Jyoti
|
|---|
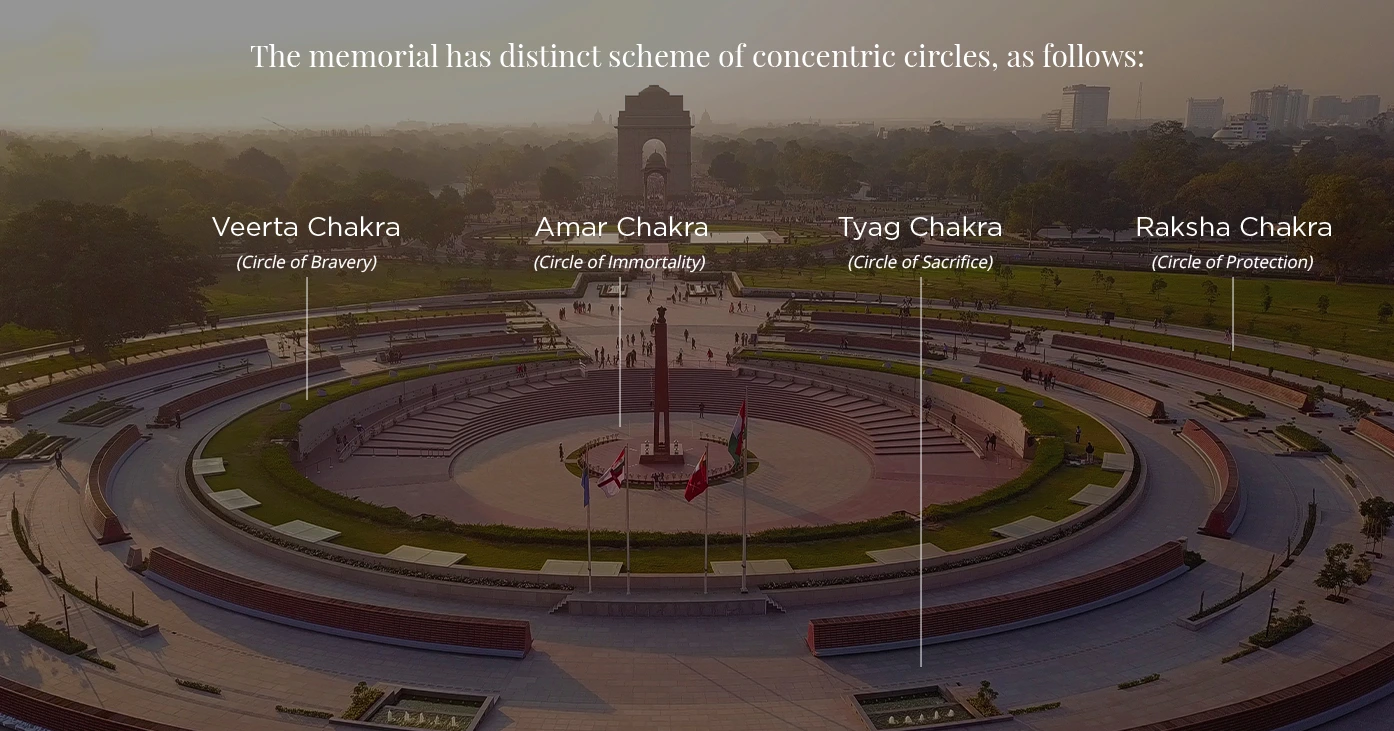 Veerta Chakra (Circle of Bravery): It signifies the bravery of Indian soldiers in the form of a covered gallery with six bronze paintings representing courageous fighting acts of the Indian Armed Forces.
Veerta Chakra (Circle of Bravery): It signifies the bravery of Indian soldiers in the form of a covered gallery with six bronze paintings representing courageous fighting acts of the Indian Armed Forces. Also Read:
News Source: PIB
| Must Read | |
| NCERT Notes For UPSC | UPSC Daily Current Affairs |
| UPSC Blogs | UPSC Daily Editorials |
| Daily Current Affairs Quiz | Daily Main Answer Writing |
| UPSC Mains Previous Year Papers | UPSC Test Series 2024 |
For the year 2024, the President approved conferment of 132 Padma awards, up from 106 such awards last year.
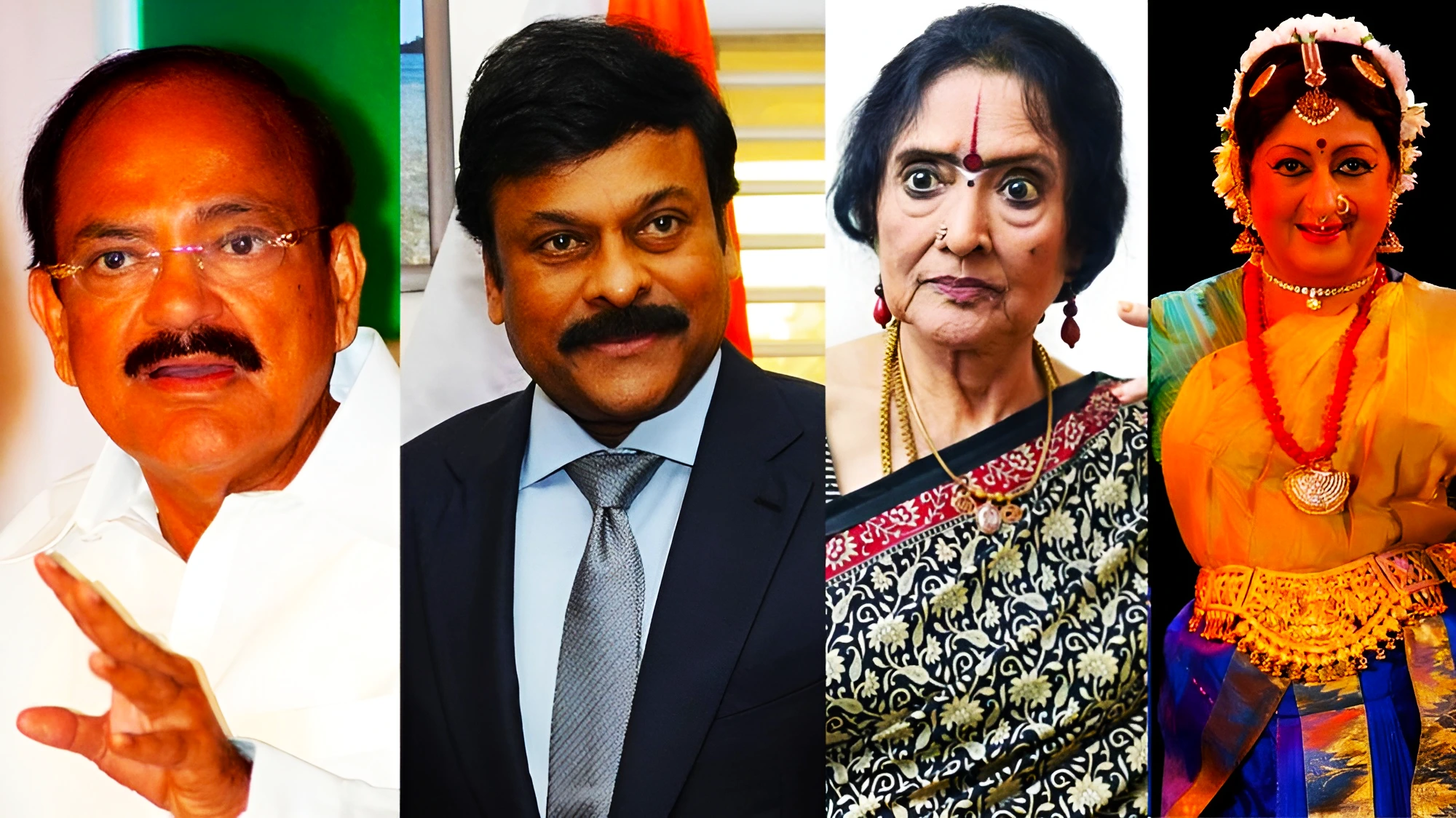

| Name | Field | State/Region |
| Ms. Vyjayantimala Bali | Art | Tamil Nadu |
| Shri Konidela Chiranjeevi | Art | Andhra Pradesh |
| Shri M Venkaiah Naidu | Public Affairs | Andhra Pradesh |
| Shri Bindeshwar Pathak
(Posthumous) |
Social Work | Bihar |
| Ms. Padma Subrahmanyam | Art | Tamil Nadu |

Eligibility: Individuals from all backgrounds, irrespective of race, occupation, position, or gender, can qualify for these awards. Nevertheless, government employees, excluding doctors and scientists, are not eligible, including those employed in public sector undertakings (PSUs).
Purpose: The award is given to recognize outstanding achievements in various fields.
Fields Recognized:
Some Important Facts About Padma Awards:
|
|---|
News source: The Hindu
| Must Read | |
| NCERT Notes For UPSC | UPSC Daily Current Affairs |
| UPSC Blogs | UPSC Daily Editorials |
| Daily Current Affairs Quiz | Daily Main Answer Writing |
| UPSC Mains Previous Year Papers | UPSC Test Series 2024 |
On the eve of the 75th Republic Day, the President of India approved Gallantry awards to 80 Armed Forces personnel, including 12 posthumously.
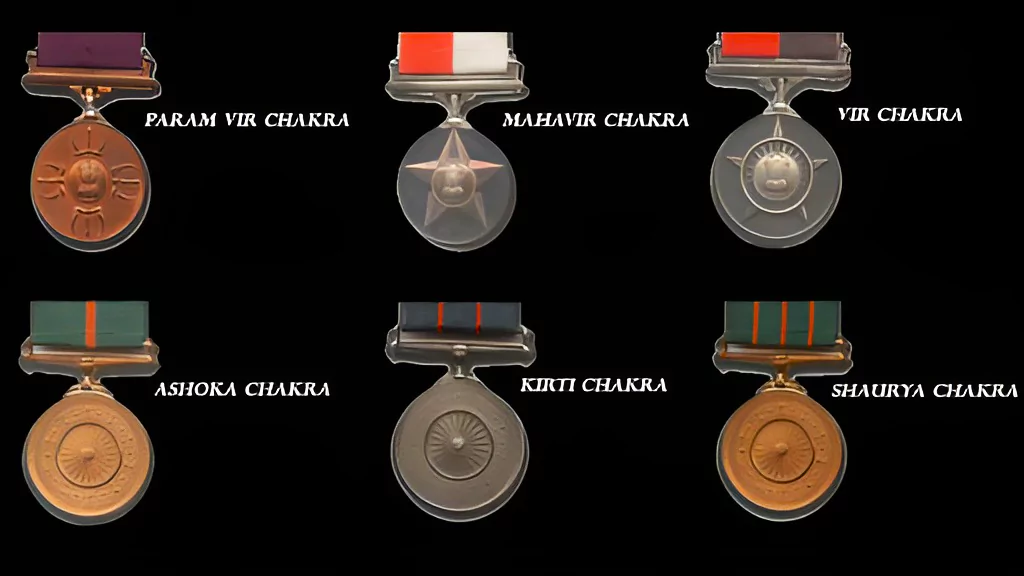

Order of Precedence: The Param Vir Chakra, the Ashoka Chakra, the Mahavir Chakra, the Kirti Chakra, the Vir Chakra and the Shaurya Chakra.
News Source: PIB
| Must Read | |
| NCERT Notes For UPSC | UPSC Daily Current Affairs |
| UPSC Blogs | UPSC Daily Editorials |
| Daily Current Affairs Quiz | Daily Main Answer Writing |
| UPSC Mains Previous Year Papers | UPSC Test Series 2024 |
India celebrates its 75th Republic Day on 26 January 2024.
| States / Ministries | Themes |
| Ministry of Culture | Evolution of Democracy from Ancient time to Present |
| Andhra Pradesh | Transforming school education and making students globally competitive and Kuchipudi classical dance. |
| Odisha | Women in Handicrafts and Handlooms |
| Rajasthan | Showcasing Ghoomar dance, Meera Bai’s statue, and traditional handicrafts of bandhej, bagru print, and applique work. |
| Haryana | Women Empowerment through the ‘Mera Parivar – Meri Pehchan’ program. |
| Madhya Pradesh | It features Avani Chaturvedi, MPs first woman fighter pilot |
| Chhattisgarh | Muria Darbar Tradition in Bastar |
| Ladakh | The Indian women’s ice hockey team |
| Manipur | It features women working with lotus stems, ‘Ima Keithel’ all women market, and lotus silk making. |
| Gujrat
|
Dhordo: Global Identity of Gujarat’s Border Tourism |
| Tamil Nadu
|
Kudavolai System: Polling process in 10th century Chola era, by displaying leaf ballots in pots. |
| ISRO | The Chandrayaan-3 mission with major contributions of women scientist |
| Ministry of Electronics and Information Technology | Role of artificial intelligence in diverse industries. |
| IAF | showcases major assets of the IAF with the theme ‘power without boundaries’ |
| CRPF | Central Armed Police Forces’ tableaux focusing on empowering women. |
| Ministry of Ports, Shipping and Waterways | Development of India’s maritime sector and rise in the number of women seafarers |
| Uttar Pradesh
|
It will feature “Namo Bharat Train” and the Regional Rapid Transit System (RRTS) Sahibabad Station. |
News Source: The Hindu
| Must Read | |
| NCERT Notes For UPSC | UPSC Daily Current Affairs |
| UPSC Blogs | UPSC Daily Editorials |
| Daily Current Affairs Quiz | Daily Main Answer Writing |
| UPSC Mains Previous Year Papers | UPSC Test Series 2024 |
Recently, The General Insurance Council launched the “Cashless Everywhere initiative in consultation with all the General and Health Insurance Companies.
Insurance Sector in India: Legal Framework
IRDAI: Regulatory Oversight in the Indian Insurance Sector
|
|---|
News Source: The Indian Express
| Must Read | |
| NCERT Notes For UPSC | UPSC Daily Current Affairs |
| UPSC Blogs | UPSC Daily Editorials |
| Daily Current Affairs Quiz | Daily Main Answer Writing |
| UPSC Mains Previous Year Papers | UPSC Test Series 2024 |
Recently, the Delhi High Court rejected a challenge to the constitutionality of Section 5(v) of the Hindu Marriage Act, 1955 (HMA), which prohibits marriage between Hindus if they are “sapindas” of each other.
Why Delhi HC Has Banned Sapinda Marriages?
Delhi High Court Ruling:
|
|---|
Similar to Sapinda Marriages in Other Countries
Note:
|
|---|
News Source: The Indian Express
| Must Read | |
| NCERT Notes For UPSC | UPSC Daily Current Affairs |
| UPSC Blogs | UPSC Daily Editorials |
| Daily Current Affairs Quiz | Daily Main Answer Writing |
| UPSC Mains Previous Year Papers | UPSC Test Series 2024 |
The pro-Taiwan leader of the Pacific islands nation of Tuvalu has lost his seat in recent elections.
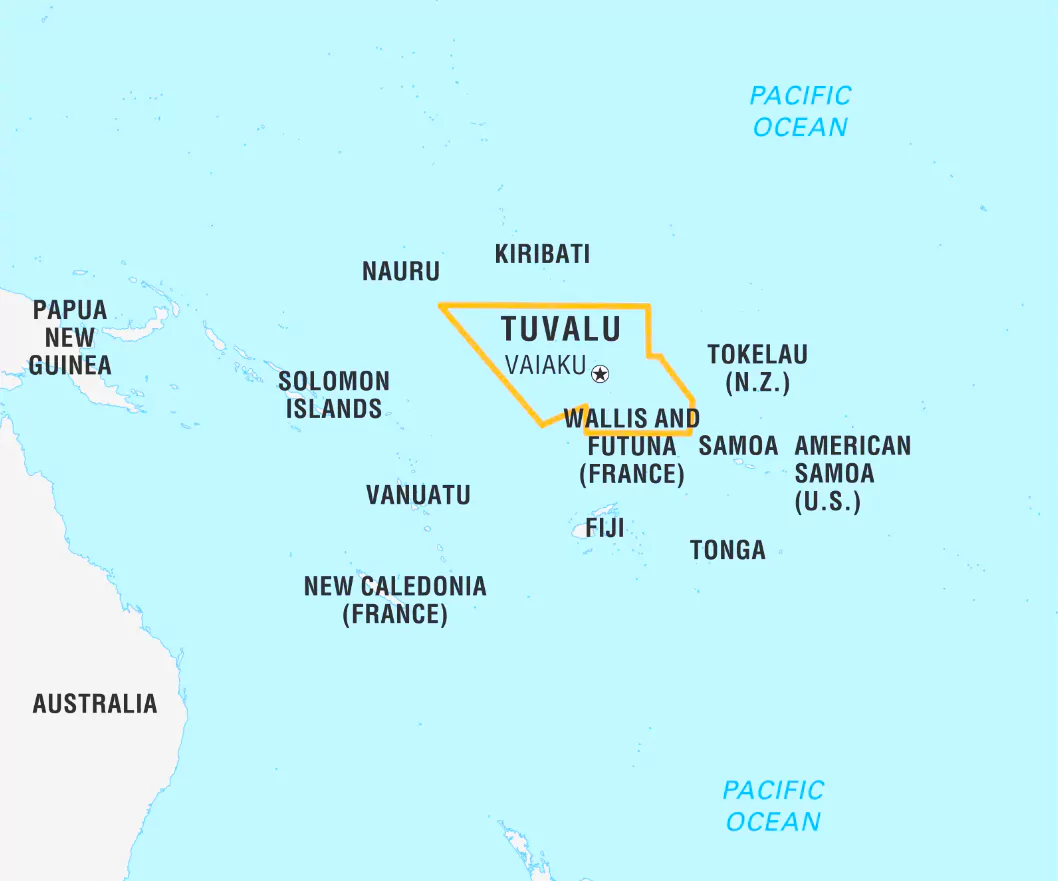
Tuvalu Map
News Source: Reuters
| Must Read | |
| NCERT Notes For UPSC | UPSC Daily Current Affairs |
| UPSC Blogs | UPSC Daily Editorials |
| Daily Current Affairs Quiz | Daily Main Answer Writing |
| UPSC Mains Previous Year Papers | UPSC Test Series 2024 |
This article is based on the news “Path of brotherhood will ensure India’s progress, says Mohan Bhagwat” which was published in the Hindu. The Rashtriya Swayamsevak Sangh (RSS) chief recently emphasised the importance of fostering ‘bhaichara’ (brotherhood) among people.
| Relevancy for Prelims: Fraternity In India, Rashtriya Swayamsevak Sangh (RSS) ,Constitution Of India, Preamble Of The Indian Constitution, and Republic Day 2024.
Relevancy for Mains: Fraternity in Indian Constitution: Origin, Challenges, and Way Forward. |
|---|
Theory of Justice (1971) by John Rawls
|
|---|

Judiciary’s Role in Promoting Fraternity
Constitutional Morality
|
|---|
Fraternity in Western World
|
|---|
| Must Read | |
| NCERT Notes For UPSC | UPSC Daily Current Affairs |
| UPSC Blogs | UPSC Daily Editorials |
| Daily Current Affairs Quiz | Daily Main Answer Writing |
| UPSC Mains Previous Year Papers | UPSC Test Series 2024 |
This article is based on the news “India-France defence ties take a bigger leap” which was published in the Hindu. The French President Emmanuel Macron attended the 2024 Republic Day as the chief guest.
| Relevancy for Prelims: India-France, Republic Day 2024, Indian Ocean Rim Association (IORA), China’s Belt And Road Initiative, Indo Pacific Region, Rafale Marine Fighter Jets, and International Solar Alliance (ISA).
Relevancy for Mains: India France Relations: Background, Significance, Recent Development, Way Forward. |
|---|

 Pillars of Cooperation: Cooperation in the areas of defence & security, space and civil nuclear matters constitute the principal pillars of the Strategic Partnership.
Pillars of Cooperation: Cooperation in the areas of defence & security, space and civil nuclear matters constitute the principal pillars of the Strategic Partnership.
India France Relations: India France Trade in Goods |
|
Top 5 Exports from India to France (FY 2022-23):
|
Top 5 Imports by India from France (FY 2022-23):
|
| Must Read | |
| NCERT Notes For UPSC | UPSC Daily Current Affairs |
| UPSC Blogs | UPSC Daily Editorials |
| Daily Current Affairs Quiz | Daily Main Answer Writing |
| UPSC Mains Previous Year Papers | UPSC Test Series 2024 |
<div class="new-fform">
</div>