The 12th edition of MILAN 2024 is being conducted at Visakhapatnam under the aegis of Eastern Naval Command.

News Source: Indian Express
| Must Read | |
| NCERT Notes For UPSC | UPSC Daily Current Affairs |
| UPSC Blogs | UPSC Daily Editorials |
| Daily Current Affairs Quiz | Daily Main Answer Writing |
| UPSC Mains Previous Year Papers | UPSC Test Series 2024 |
A rare ape species, Skywalker Gibbon, has been found in Myanmar.
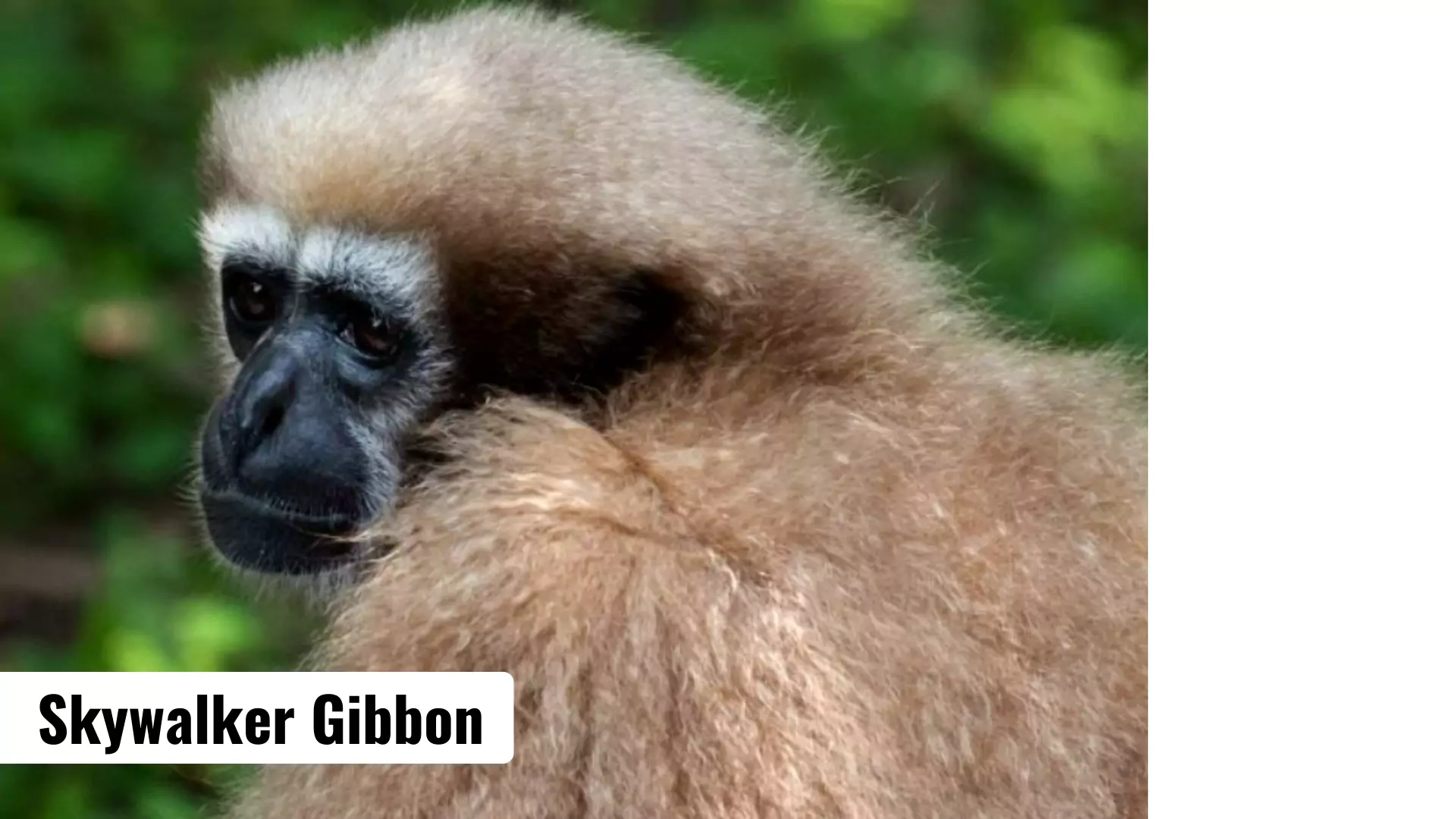

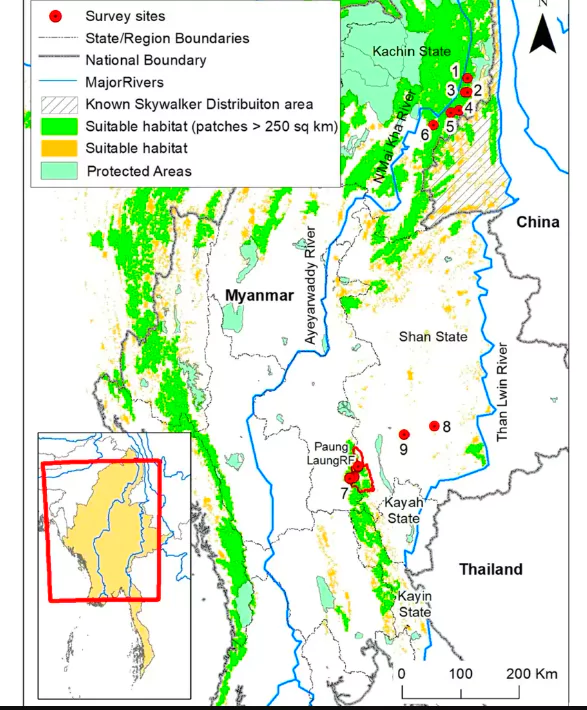 Habitat: They are found in the forests of the Gaoligong mountains, at the border between southwest China and northern Myanmar.
Habitat: They are found in the forests of the Gaoligong mountains, at the border between southwest China and northern Myanmar.News Source: Wildlife
| Must Read | |
| NCERT Notes For UPSC | UPSC Daily Current Affairs |
| UPSC Blogs | UPSC Daily Editorials |
| Daily Current Affairs Quiz | Daily Main Answer Writing |
| UPSC Mains Previous Year Papers | UPSC Test Series 2024 |
Climate change is leading to a significant mismatch in plant cycles and pollinators behaviour, which has multiple impacts on the phenology and other traits of plants.
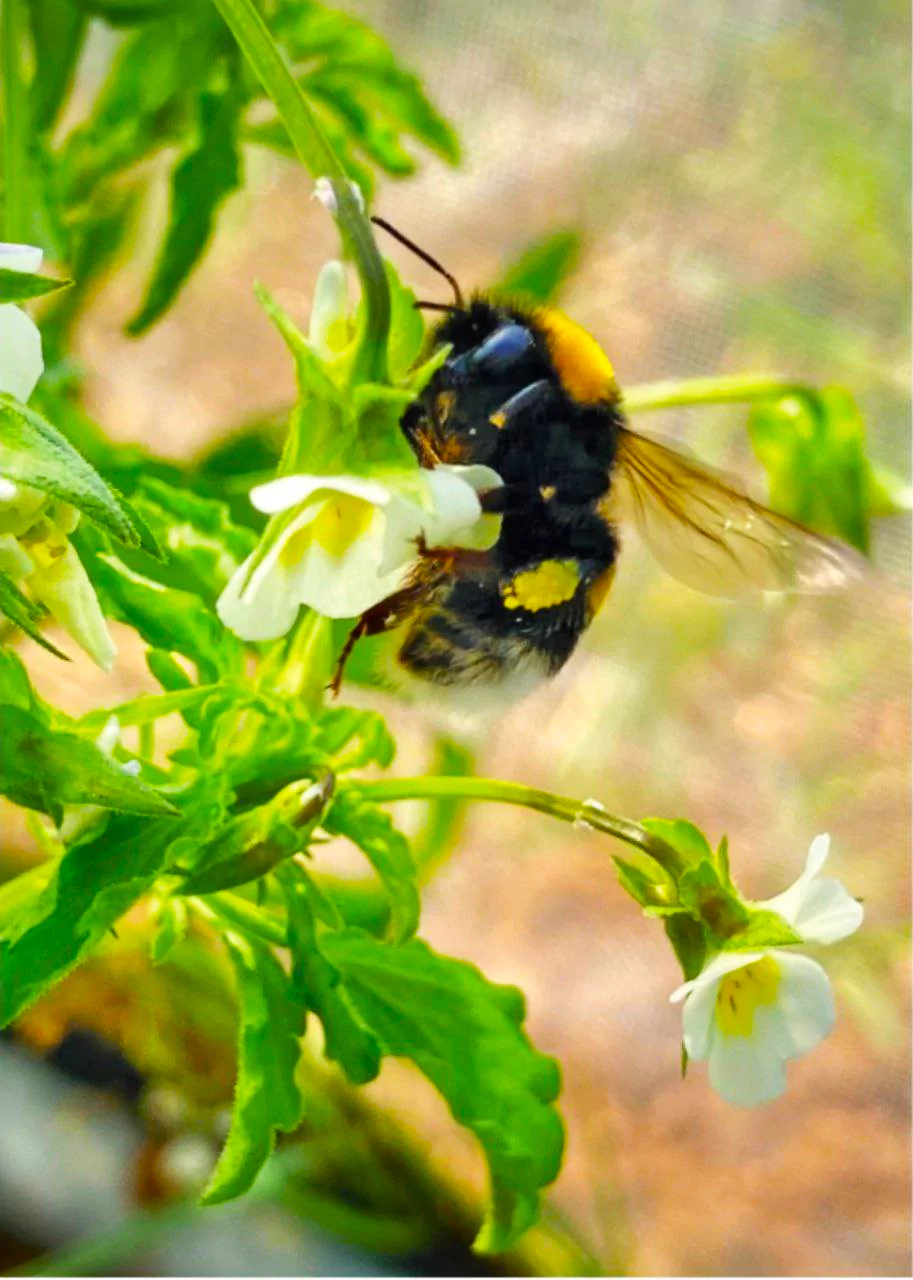

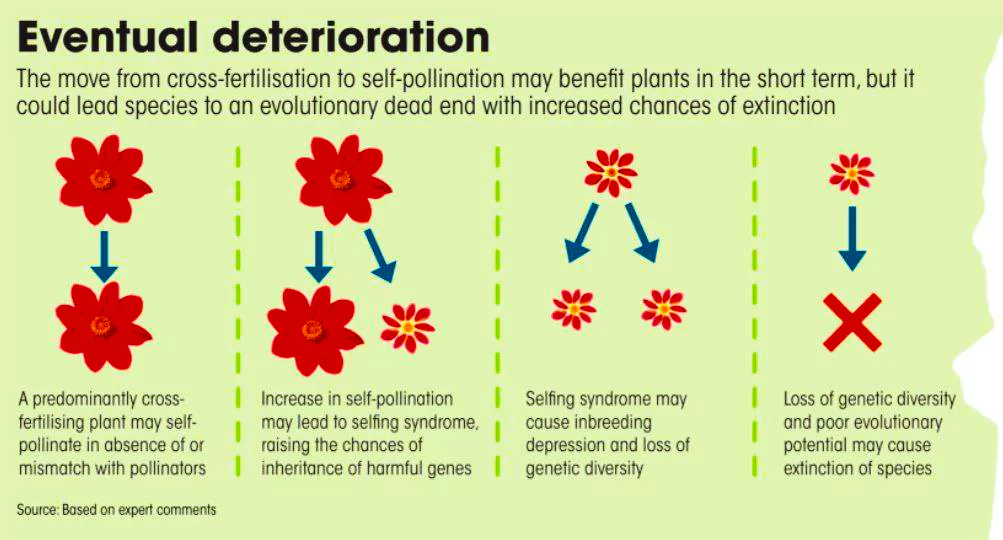
| Pollination: The process of transfer of pollen grains, from anther to the stigma of the same flower or of different flower.
Self pollination :
Cross Pollination :
Also Read: Sexual Reproduction In Plants |
|---|
News Source : DTE
| Must Read | |
| NCERT Notes For UPSC | UPSC Daily Current Affairs |
| UPSC Blogs | UPSC Daily Editorials |
| Daily Current Affairs Quiz | Daily Main Answer Writing |
| UPSC Mains Previous Year Papers | UPSC Test Series 2024 |
The United States rejected a proposed resolution (Algerian-draft resolution) in the UN Security Council regarding the Israel-Hamas war, preventing a call for an immediate humanitarian ceasefire.
News Source: Indianexpress
| Must Read | |
| NCERT Notes For UPSC | UPSC Daily Current Affairs |
| UPSC Blogs | UPSC Daily Editorials |
| Daily Current Affairs Quiz | Daily Main Answer Writing |
| UPSC Mains Previous Year Papers | UPSC Test Series 2024 |
Recently, the Government said that Four of the 20 relics of Buddha presently kept in the National Museum in New Delhi will be taken to Thailand.

About Buddha’s Life
Also Read: Contemporary Relevance Of Buddha’s Teachings |
|---|
News Source: PIB
| Must Read | |
| NCERT Notes For UPSC | UPSC Daily Current Affairs |
| UPSC Blogs | UPSC Daily Editorials |
| Daily Current Affairs Quiz | Daily Main Answer Writing |
| UPSC Mains Previous Year Papers | UPSC Test Series 2024 |
The Central Consumer Protection Authority has recently sought public comments on Draft Guidelines for the Prevention and Regulation of Greenwashing.
Central Consumer Protection Authority (CCPA)
|
|---|
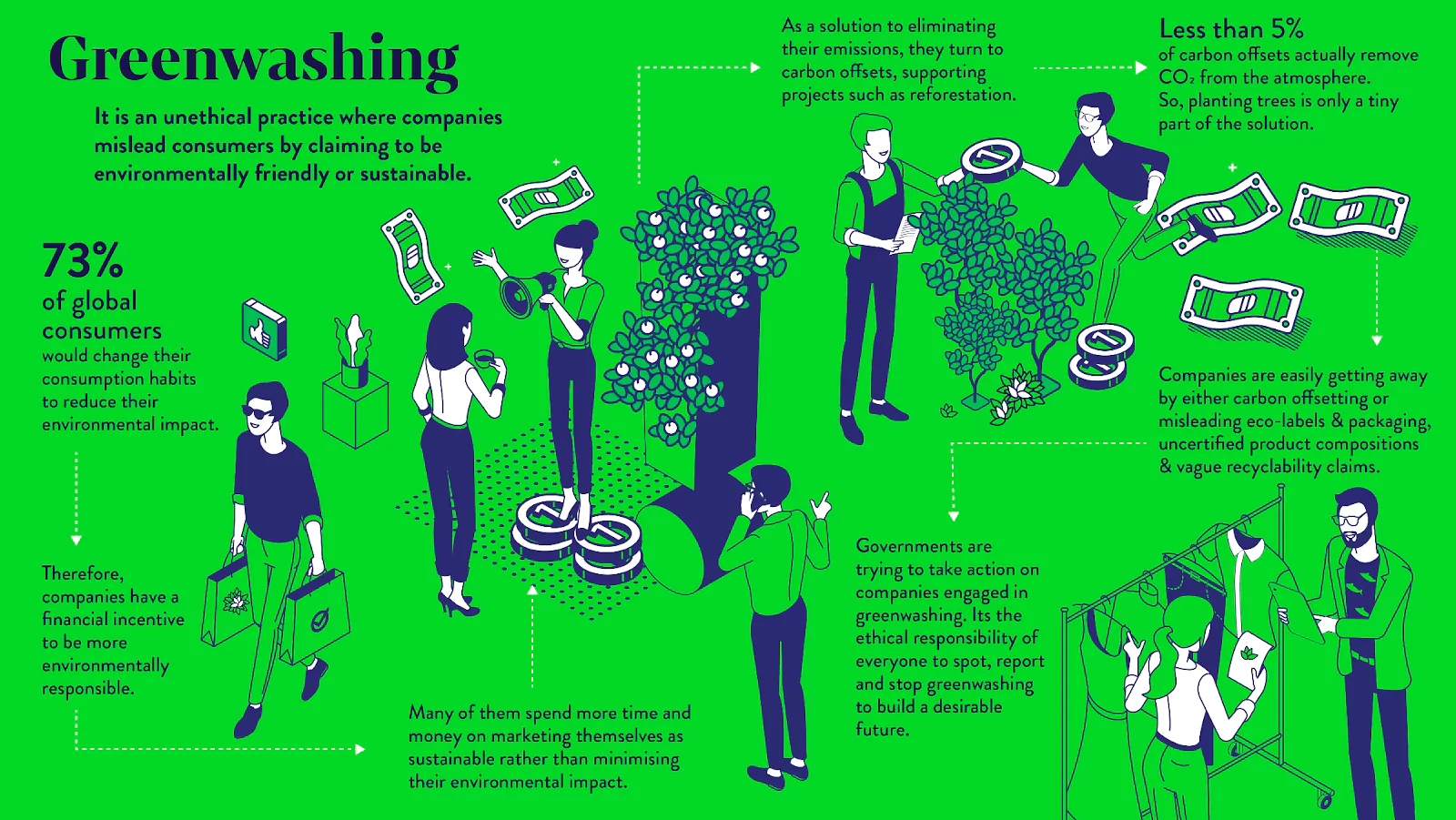
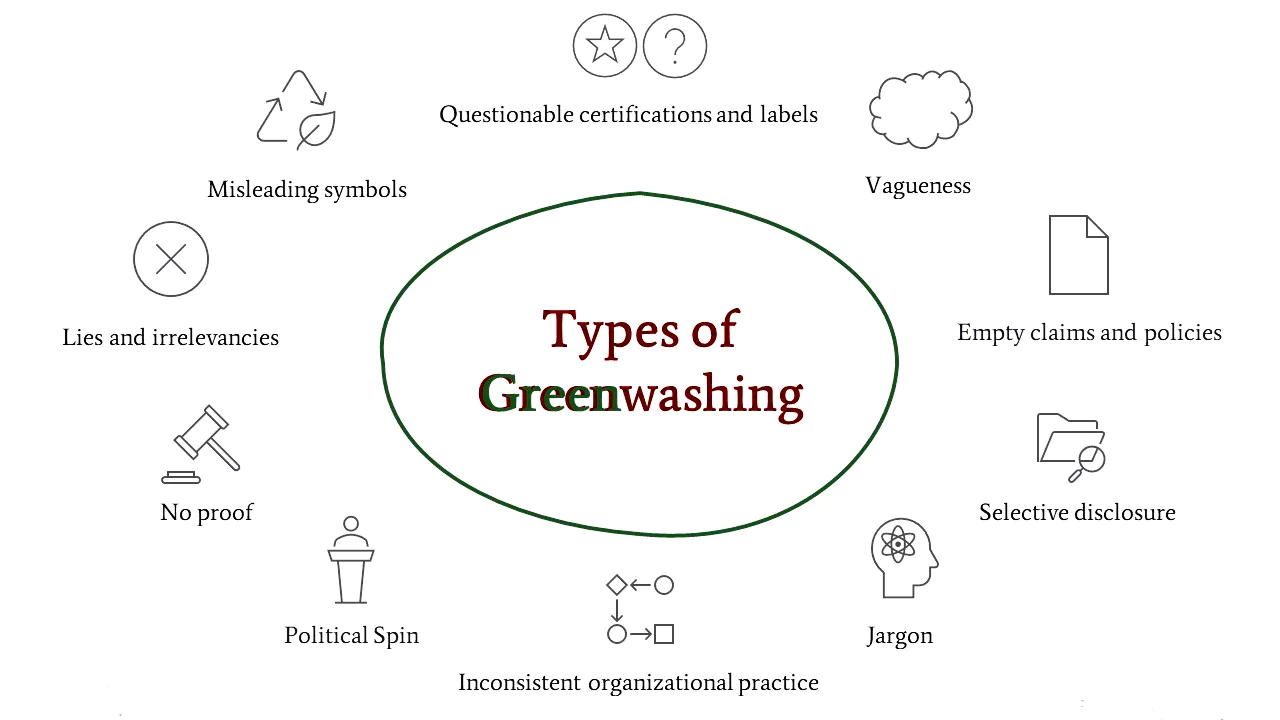
News Source: AIR
| Must Read | |
| NCERT Notes For UPSC | UPSC Daily Current Affairs |
| UPSC Blogs | UPSC Daily Editorials |
| Daily Current Affairs Quiz | Daily Main Answer Writing |
| UPSC Mains Previous Year Papers | UPSC Test Series 2024 |
Dr Shashi Tharoor, a renowned writer and a former diplomat was awarded the highest civilian honor of France, known as the “Chevalier de la Legion d’honneur.”
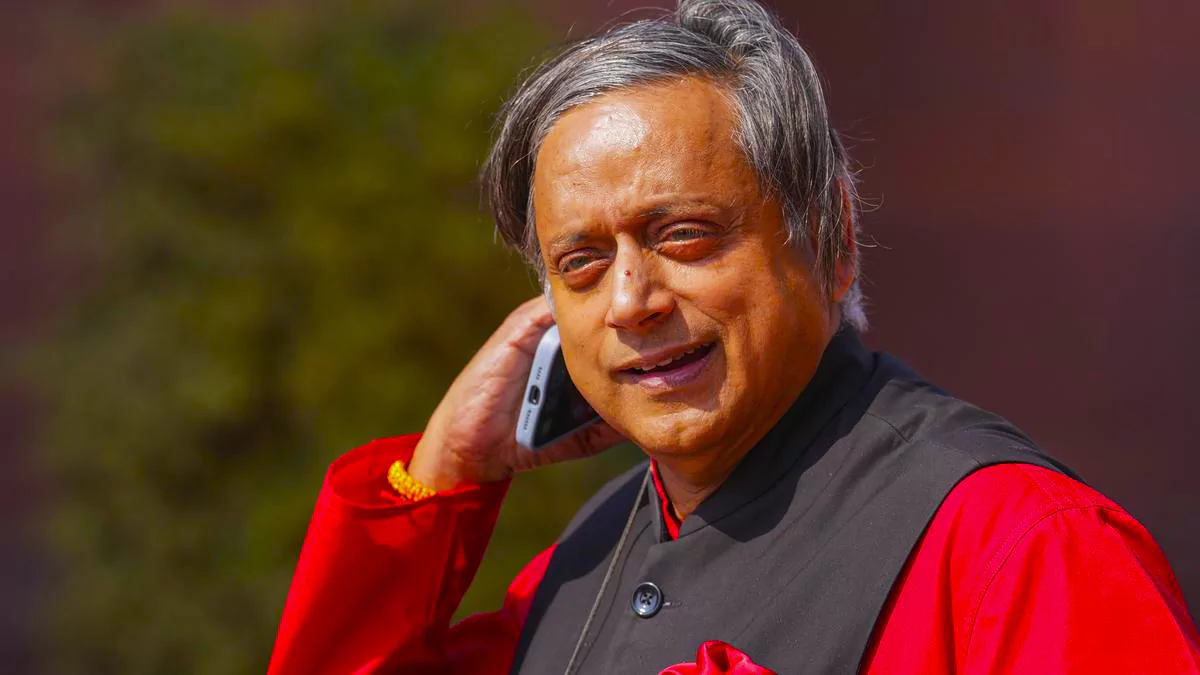

 Purpose: To Acknowledge remarkable achievements and expertise across various fields.
Purpose: To Acknowledge remarkable achievements and expertise across various fields.| Grand Cross of the Legion of Honour:
Last year, Prime Minister Narendra Modi was awarded the ‘Grand Cross of the Legion of Honour award during his visit to France by French President Emmanuel Macron. |
|---|
News Source: Thehindu
| Must Read | |
| NCERT Notes For UPSC | UPSC Daily Current Affairs |
| UPSC Blogs | UPSC Daily Editorials |
| Daily Current Affairs Quiz | Daily Main Answer Writing |
| UPSC Mains Previous Year Papers | UPSC Test Series 2024 |
Recently, the World Health Organization (WHO) launched the Global Initiative on Digital Health (GIDH) virtually, a platform for sharing knowledge and digital products among countries.
About Digital Health:
The WHO Global Strategy on Digital Health:
|
|---|
News Source: The Indian Express
| Must Read | |
| NCERT Notes For UPSC | UPSC Daily Current Affairs |
| UPSC Blogs | UPSC Daily Editorials |
| Daily Current Affairs Quiz | Daily Main Answer Writing |
| UPSC Mains Previous Year Papers | UPSC Test Series 2024 |
The Ministry of Corporate Affairs has notified the introduction of the “Leniency Plus” regime to revolutionise AntiTrust enforcement in the country
Cartels
|
|---|
News Source: The Hindu
| Must Read | |
| NCERT Notes For UPSC | UPSC Daily Current Affairs |
| UPSC Blogs | UPSC Daily Editorials |
| Daily Current Affairs Quiz | Daily Main Answer Writing |
| UPSC Mains Previous Year Papers | UPSC Test Series 2024 |
This article is based on the news “India contributes 1 million US Dollars to Poverty and Hunger Alleviation Fund” which was published in the All India Radio. India participates in the 3rd IBSA Sherpas and Sous-Sherpas Meeting.
| Relevancy for Prelims: INDIA-BRAZIL-SOUTH AFRICA (IBSA), BRICS, Virtual BRICS-Plus Summit, and United Nations.
Relevancy for Mains: IBSA (India-Brazil-South Africa) and IBSA Fund: Significance, Challenges, and Way Forward. |
|---|

| Sherpa: |
|---|
IBSA Vs BRICS (Brazil, Russia, India, China,South Africa)
|
|---|
| Mains Question: Establish the relationship between land reform, agriculture productivity and elimination of Poverty. (10 marks, 150 words) |
|---|
| Must Read | |
| NCERT Notes For UPSC | UPSC Daily Current Affairs |
| UPSC Blogs | UPSC Daily Editorials |
| Daily Current Affairs Quiz | Daily Main Answer Writing |
| UPSC Mains Previous Year Papers | UPSC Test Series 2024 |
This article is based on the news “What is Article 142, invoked by Supreme Court to overturn Chandigarh mayoral poll results?” which was published in the Indian Express. The Supreme Court invoked the powers of Article 142 of the constitution in overturning the results of controversial Chandigarh’s mayoral election.
| Relevancy for Prelims: Indian Judiciary, Supreme Court, Indian Constitution, Judicial Activism, and Municipalities In Indian Polity.
Relevancy for Mains: Article 142 Of Indian Constitution: Provisions, Significance, Challenges, Criticism, and Way Forward. |
|---|
About Mayor:
|
|---|
The Bharatiya Janata Party (BJP) emerged victorious in the Chandigarh mayoral polls on January 30, securing a win over the Aam Aadmi Party-Congress alliance candidate.

| Prelims PYQ (2019):
With reference to the Constitution of India, prohibition or limitations or provisions contained in ordinary laws cannot act as prohibitions or limitations on the constitutional powers under Article 142. It could mean which one of the following? (a) The decisions taken by the Election Commission of India while discharging its duties cannot be challenged in any court of law. (b) The Supreme Court of India is not constrained in the exercise of its powers by laws made by the Parliament. (c) In the event of grave financial crisis in the country, the President of India can declare Financial Emergency without the counsel from the Cabinet. (d) State Legislatures cannot make laws on certain matters without the concurrence of Union Legislature. Ans: (b) |
|---|
| Mains Question: The separation of powers doctrine is essential in a democratic system. Discuss its significance in India, emphasizing the concept of ‘checks and balances’. (15 Marks, 250 Words) |
|---|
| Must Read | |
| NCERT Notes For UPSC | UPSC Daily Current Affairs |
| UPSC Blogs | UPSC Daily Editorials |
| Daily Current Affairs Quiz | Daily Main Answer Writing |
| UPSC Mains Previous Year Papers | UPSC Test Series 2024 |
<div class="new-fform">
</div>