Recently, the Defence Research & Development Organisation (DRDO) & Indian Army conducted successful trials of indigenous Man Portable Anti-tank Guided Missile Weapon System.
About Defence Research & Development Organisation
About Anti-Tank Guided Missiles (ATGMs)
About Man Portable Anti-tank Guided Missile (MPATGM)
|
| Must Read | |
| NCERT Notes For UPSC | UPSC Daily Current Affairs |
| UPSC Blogs | UPSC Daily Editorials |
| Daily Current Affairs Quiz | Daily Main Answer Writing |
| UPSC Mains Previous Year Papers | UPSC Test Series 2024 |
Operation Meghdoot completed 40 years after the commencement of presence of the Indian Army on the Siachen Glacier.
About Siachen Glacier
|
|---|
| Must Read | |
| NCERT Notes For UPSC | UPSC Daily Current Affairs |
| UPSC Blogs | UPSC Daily Editorials |
| Daily Current Affairs Quiz | Daily Main Answer Writing |
| UPSC Mains Previous Year Papers | UPSC Test Series 2024 |
Researchers at the Indian Institute of Science (IISc) have designed a sustainable hydrogel to remove microplastics from water.
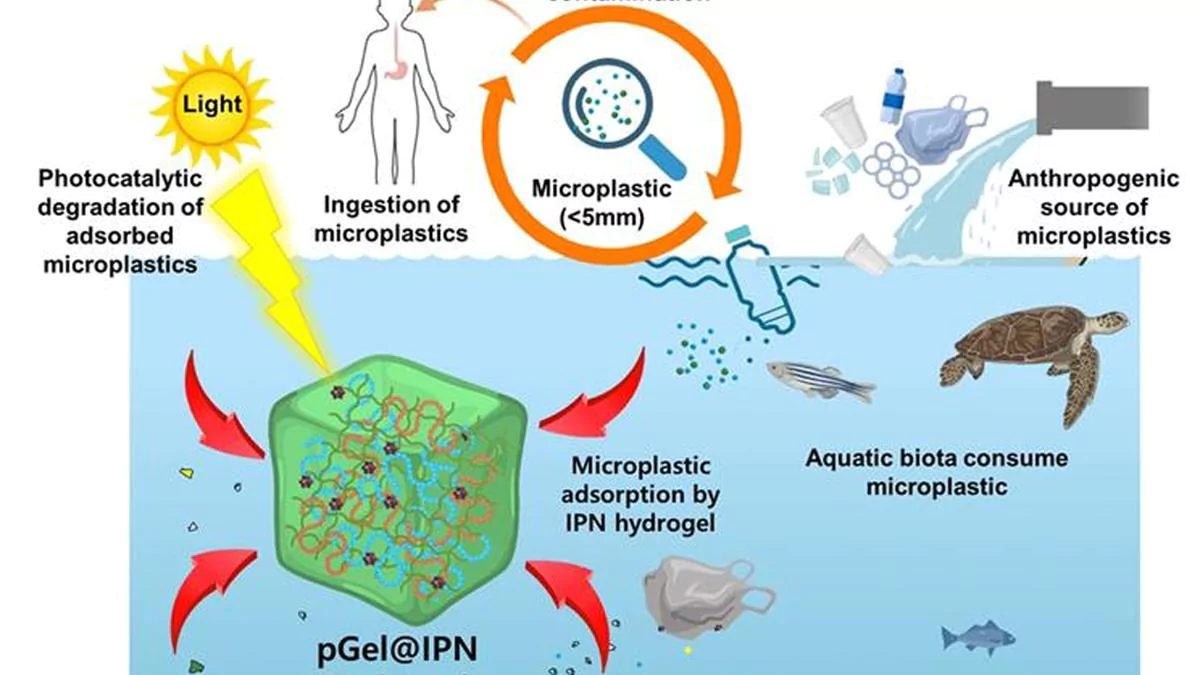
Government initiatives to tackle Plastics Pollution
|
|---|
| Must Read | |
| NCERT Notes For UPSC | UPSC Daily Current Affairs |
| UPSC Blogs | UPSC Daily Editorials |
| Daily Current Affairs Quiz | Daily Main Answer Writing |
| UPSC Mains Previous Year Papers | UPSC Test Series 2024 |
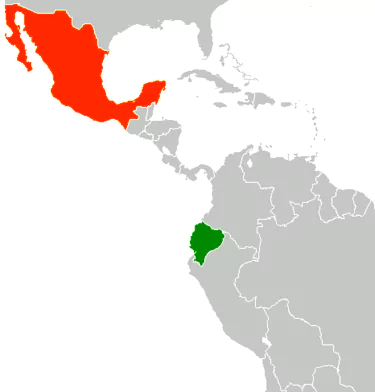
Ecuador, in a serious violation of the Vienna Convention on diplomatic relations
raided at Mexico’s embassy in Quito.
More on News:
| Must Read | |
| NCERT Notes For UPSC | UPSC Daily Current Affairs |
| UPSC Blogs | UPSC Daily Editorials |
| Daily Current Affairs Quiz | Daily Main Answer Writing |
| UPSC Mains Previous Year Papers | UPSC Test Series 2024 |
A panel was formed by the southern bench of the National Green Tribunal (NGT) to probe the cause of the sea turning red in Puducherry in October and November 2023.
| Plankton: These are organisms that cannot swim against currents, relying on water movements for their mobility.
Examples include algae, protozoans, bacteria, mollusks, and coelenterates. Larger organisms like jellyfish are also considered plankton due to their inability to swim against currents. Algal bloom: It is excessive multiplying of algae or phytoplankton due to favorable environmental conditions. Causes of Algal Bloom:
|
|---|
| Must Read | |
| NCERT Notes For UPSC | UPSC Daily Current Affairs |
| UPSC Blogs | UPSC Daily Editorials |
| Daily Current Affairs Quiz | Daily Main Answer Writing |
| UPSC Mains Previous Year Papers | UPSC Test Series 2024 |
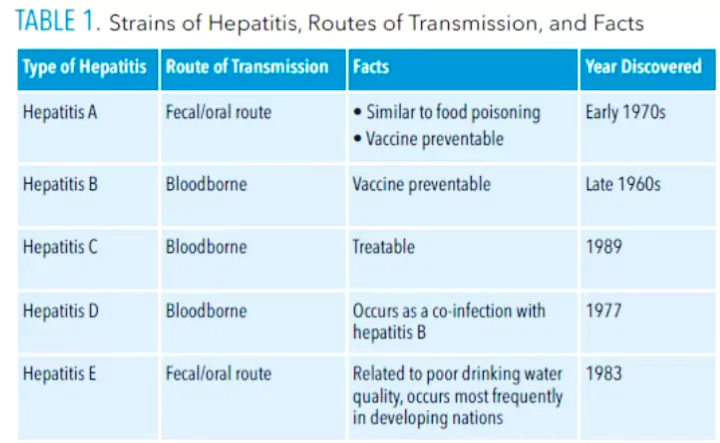
According to the 2024 Global Hepatitis Report by the World Health Organization (WHO), India accounted for a significant 11.6 per cent of the world’s hepatitis cases in 2022.
| Must Read | |
| NCERT Notes For UPSC | UPSC Daily Current Affairs |
| UPSC Blogs | UPSC Daily Editorials |
| Daily Current Affairs Quiz | Daily Main Answer Writing |
| UPSC Mains Previous Year Papers | UPSC Test Series 2024 |
The Dr Ambedkar Foundation (DAF) celebrated the 134th Dr Ambedkar Jayanti on April 14, 2024 (DAF) on behalf of the Ministry of Social Justice & Empowerment, Govt. of India.
| In his honour, Mhow is officially known as Dr Ambedkar Nagar. |
|---|

The birth anniversary of Dr Ambedkar was celebrated near the statue of Babasaheb Dr. B.R. Ambedkar at the Parliament House Lawn.
Famous Quotes of Dr Ambedkar
|
|---|
| Separate Electorates are elections where minorities choose their representatives individually, while Joint Electorates involve selecting representatives collectively. |
|---|
The legacy of Dr. Ambedkar is very significant today too.
Ambedkar Circuit
|
|---|
‘Year of Social Justice’
|
|---|
| Must Read | |
| NCERT Notes For UPSC | UPSC Daily Current Affairs |
| UPSC Blogs | UPSC Daily Editorials |
| Daily Current Affairs Quiz | Daily Main Answer Writing |
| UPSC Mains Previous Year Papers | UPSC Test Series 2024 |
The International Monetary Fund (IMF) report titled “Cyber Risk: A Growing Concern for Macrofinancial Stability” presents a concerning picture of the increasing threats posed by cyber incidents to the financial sector.
Financial Stability Board (FSB): An international body that monitors and makes recommendations about the global financial system.
Asia Pacific Economic Cooperation (APEC):
|
|---|
| Must Read | |
| NCERT Notes For UPSC | UPSC Daily Current Affairs |
| UPSC Blogs | UPSC Daily Editorials |
| Daily Current Affairs Quiz | Daily Main Answer Writing |
| UPSC Mains Previous Year Papers | UPSC Test Series 2024 |

Recently, the Election Commission of India (ECI), has provided the facility of home voting for the elderly and Persons with Disabilities in the 2024 Lok Sabha elections.

The category of essential services (Those who work in metros, railways and health care )is notified by the ECI under Section 60(C) of the R.P. Act, 1951 in consultation with the Government.
Electronically Transmitted Postal Ballot System (ETPBS):
|
|---|
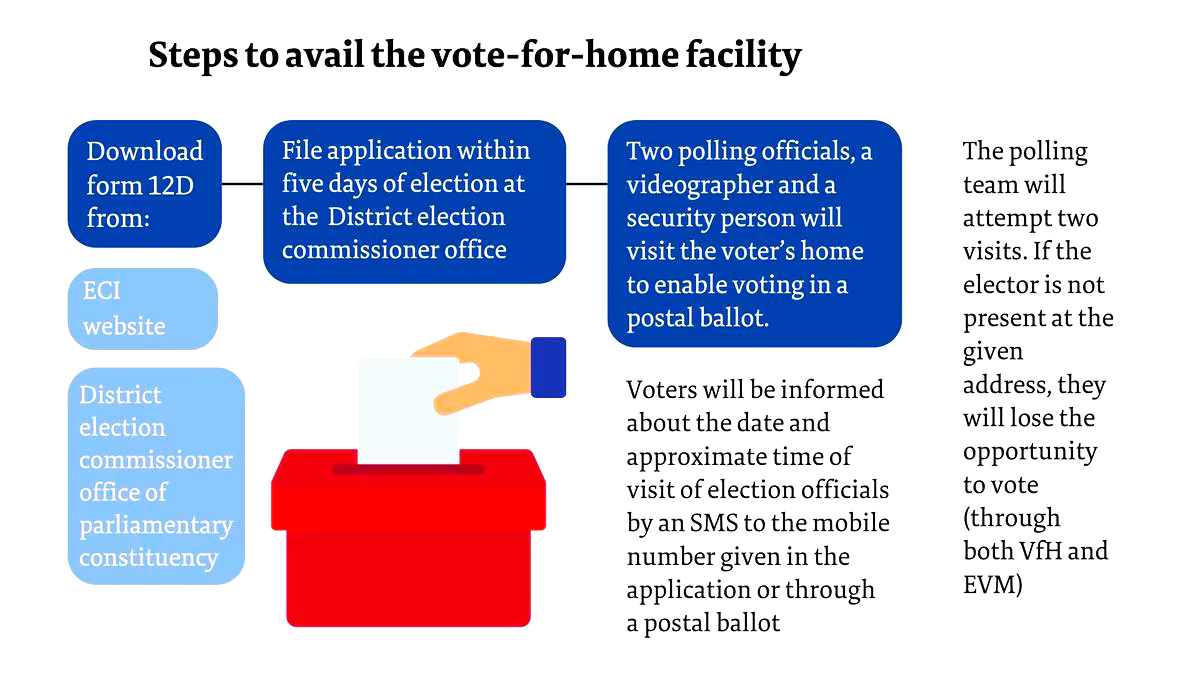
This initiative marks a significant stride towards ensuring inclusivity and accessibility of the electoral process and bolstering democratic participation.
| Must Read | |
| NCERT Notes For UPSC | UPSC Daily Current Affairs |
| UPSC Blogs | UPSC Daily Editorials |
| Daily Current Affairs Quiz | Daily Main Answer Writing |
| UPSC Mains Previous Year Papers | UPSC Test Series 2024 |
The Prime Minister tribute recently honored the victims of the 1919

Views of historians or prominent figures Over Jallianwala Bagh Massacre:
|
|---|
| Must Read | |
| NCERT Notes For UPSC | UPSC Daily Current Affairs |
| UPSC Blogs | UPSC Daily Editorials |
| Daily Current Affairs Quiz | Daily Main Answer Writing |
| UPSC Mains Previous Year Papers | UPSC Test Series 2024 |
Recently, Iran carried out a series of air strikes on Israel using 200-300 drones and ballistic missiles.
| Relevance For Prelims: 2024 Iran Israel Conflict, United Nations, Israel-Hamas Conflict, How Effective is the United Nations (UN) in Conflict Mitigation, UNSC Reform, and Is The United Nations Toothless In Ending Wars?.
Relevance For Mains: Iran Israel Conflict – Its Impact on India and the World. |
|---|
About Zionism:
|
|---|
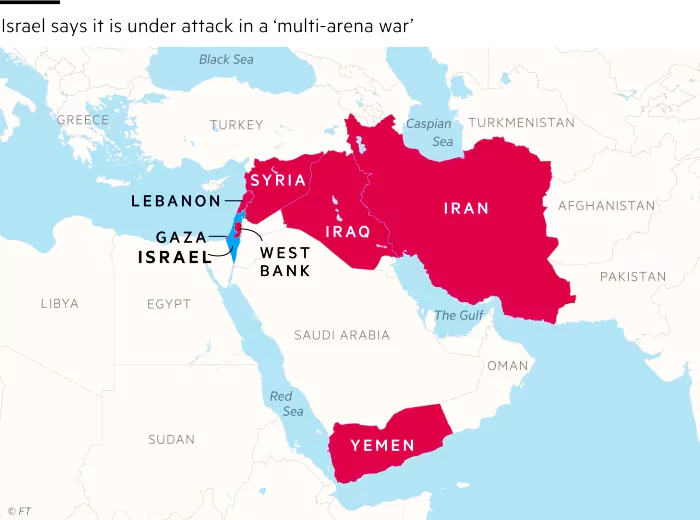
 India’s Position: It wants there should be “immediate de-escalation” and “step back from violence” and “return to the path of diplomacy” is, therefore, crucial to its national interest.
India’s Position: It wants there should be “immediate de-escalation” and “step back from violence” and “return to the path of diplomacy” is, therefore, crucial to its national interest.
Significance of Iran for India:
|
|---|
Significance of Israel for India:
|
|---|
| Prelims PYQ (2023):
Consider the following statements: Statement-I: Israel has established diplomatic relations with some Arab States. Statement-II: The ‘Arab Peace Initiative’ Mediated by Saudi Arabia was signed by Israel and Arab League. Which one of the following is correct in respect of the above statements? (a) Both Statement-I and Statement-II are correct and StatementII is the correct explanation for Statement-I (b) Both Statement-I and Statement-II are correct and StatementII is not the correct explanation for Statement-I (c) Statement-I is correct but StatementII is incorrect (d) Statement-I is incorrect but Statement-II is correct Ans: (c) |
|---|
| Mains Question: “India’s relations with Israel have, of late, acquired a depth and diversity, which cannot be rolled back” Discuss [150 Words, 10 Marks]. |
|---|
| Must Read | |
| NCERT Notes For UPSC | UPSC Daily Current Affairs |
| UPSC Blogs | UPSC Daily Editorials |
| Daily Current Affairs Quiz | Daily Main Answer Writing |
| UPSC Mains Previous Year Papers | UPSC Test Series 2024 |
<div class="new-fform">
</div>
