Context: Quantum computing is one of the most attractive investment avenues, both from the public and private sectors, reaching about US$35.5 billion globally in 2022.
More on News:
- India is currently at the forefront of tapping the second quantum revolution through massive investments in the field.
- Union Budget 2020-21 proposed to spend ₹8,000 crore ($ 1.2 billion) on the newly launched National Mission on Quantum Technologies and Applications (NMQTA) and ₹ 3660 Crore for National Mission on Interdisciplinary Cyber Physical Systems (NM-ICPS).
About Quantum Computing:
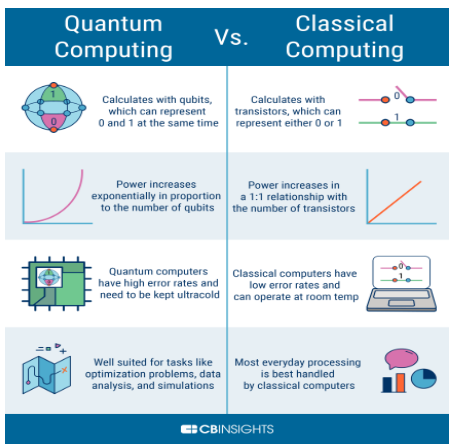
- Quantum computing is a rapidly-emerging technology that harnesses the laws of quantum mechanics to solve problems too complex for classical computers.
- Classical computers encode information in binary “bits” that can either be 0s or 1s. In a quantum computer, the basic unit of memory is a quantum bit or qubit.
Application of Quantum Computing:
- Finance: Financial institutions may be able to use quantum computing to design more effective and efficient investment portfolios for retail and institutional clients.
- They could focus on creating better trading simulators and improve fraud detection.
- Healthcare: The healthcare industry could use quantum computing to develop new drugs and genetically-targeted medical care.
- Enhancing Security: For stronger online security, quantum computing can help design better data encryption and ways to use light signals to detect intruders in the system.
- Traffic Planning: Quantum computing can be used to design more efficient, safer aircraft and traffic planning systems.
- High Privacy: A Quantum computer is highly confidential and secure. It uses the phenomenon of superposition to form the supercomputer that makes hacking impossible.
Government Initiatives:
- Quantum Computing Applications Lab (QCAL): It was launched by the Ministry of Electronics and Information Technology (MeitY) in collaboration with AWS.
Major international Quantum Computing Collaborations:
- Quantum Technologies Flagship: It was established in 2018 by the European Union (EU), with aims to bring together research, private, and public institutions, and consolidate European leadership in the field of quantum technologies over a period of 10 years.
- The AUKUS Quantum Arrangement: It was initiated in 2022 with an aim to accelerate investments in “generation-after-next” quantum capabilities.
- Quadrilateral Security Dialogue: In 2021, the Quad leaders agreed to establish a Critical and Emerging Technology Working Group to ensure that the standards and frameworks for key technologies such as 5G, Artificial Intelligence (AI) and Quantum Computing are governed by “shared interests and values”
- CERN Quantum Technology Initiative:The European Council for Nuclear Research’s (CERN) Quantum Technology Initiative is a comprehensive R&D and academic programme initiated in 2020, which aims to set up collaborations between its 23 member states as well as international initiatives in quantum technologies
|
-
- It aims to accelerate the adoption of quantum computing in India by providing access to quantum computers, tools, and resources to researchers and developers.
- The National Mission on Quantum Technologies and Applications (NM-QTA): It was launched in 2020 with the goal of creating a strong quantum technology ecosystem in India.
- National Quantum Mission: With a total cost of Rs.6003.65 crore from 2023-24 to 2030-31, it aims to nurture and scale up scientific and industrial R&D and create a vibrant & innovative ecosystem in Quantum Technology (QT).
Limitations:
- Algorithm Creation: Quantum computers can’t work like traditional computers, they need special algorithms to do tasks in their environment.
- Low Temperature Needed: Quantum computers require extreme temperatures ( -460°F.) that are hard to maintain.
- Low Precision: Quantum computers have a low level of precision. Scientists have to create their own qubits, which is difficult.
- Software: The field of creating quantum algorithms and software is still developing, and qualified professionals are in short supply.
- Cost: Building and maintaining quantum computers is currently relatively expensive, and this may prevent widespread deployment
- Interoperability: Due to the lack of standards in the realm of quantum computing, it might be challenging to compare and combine various quantum computers.
Way Forward:
- Establishing centers of excellence: The government should create specialized centers of excellence dedicated to quantum science and technology within both academic institutions and government research institutes.
- Technology development: India must harness the power of startups and Big Tech corporations involved in developing quantum technology and applications.
- Indigenization: Prioritizing the development of quantum computational capabilities is imperative for our nation, as obtaining this technology from foreign sources would pose significant challenges and cost hurdles.
- Effective Roadmap: To effectively monitor global advancements in quantum computing and evaluate and guide India’s efforts in this domain, the establishment of an Indian Quantum Computing Roadmap Group is essential.
![]() 23 Sep 2023
23 Sep 2023
