The National Centre for Disease Control (NCDC) has carried out a survey on the trend in the prescription of antibiotic use in India.
Additional Reading: Antimicrobial Resistance (AMR)
Source: DTE
|
Must Read |
|
| NCERT Notes For UPSC | UPSC Daily Current Affairs |
| UPSC Blogs | UPSC Daily Editorials |
Chinese startup Orienspace successfully launched the Gravity-1 rocket from a mobile sea platform, increasing the number of potential launch sites.
News Source: Reuters
|
Must Read |
|
| NCERT Notes For UPSC | UPSC Daily Current Affairs |
| UPSC Blogs | UPSC Daily Editorials |
During the Annual Clean City Award 2023, Surat in Gujarat and Indore in Madhya Pradesh were announced as the cleanest cities in the nation.
Theme of Survey 2023 – 2024
|
|---|
The Swachh Bharat Abhiyan:
|
|---|

Conclusion: Swachh Survekshan is a vital tool in assessing and promoting cleanliness and sanitation across cities and towns in India. However, there is a need to sort out all the problems associated with it.
News Source: The Hindu
|
Must Read |
|
| NCERT Notes For UPSC | UPSC Daily Current Affairs |
| UPSC Blogs | UPSC Daily Editorials |
Recently, the Mumbai Trans Harbour Link (MTHL), also known as Atal Setu, the longest sea bridge in India, has been inaugurated by the Prime Minister.
Advanced Features of the Atal Setu bridge
|
|---|
News Source: The Hindu
|
Must Read |
|
| NCERT Notes For UPSC | UPSC Daily Current Affairs |
| UPSC Blogs | UPSC Daily Editorials |
National Youth Day (12th January) is held every year to observe the birth anniversary of Swami Vivekananda.

National Youth Day
|
|---|
News Source: PIB
|
Must Read |
|
| NCERT Notes For UPSC | UPSC Daily Current Affairs |
| UPSC Blogs | UPSC Daily Editorials |
Serbian farmers and officials rescued dozens of starving horses and cattle stranded on the island of Krcedinska Ada in the Danube River.
News Source: Reuters
|
Must Read |
|
| NCERT Notes For UPSC | UPSC Daily Current Affairs |
| UPSC Blogs | UPSC Daily Editorials |
Russia has begun to evacuate residents from the border region of Belgorod following a surge in Ukrainian strikes.
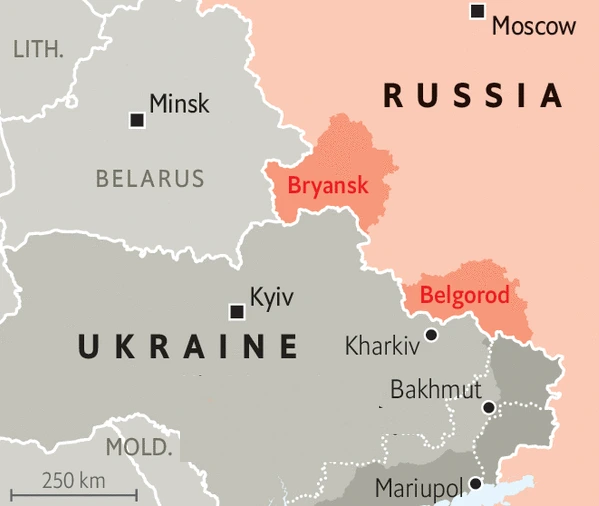
News Source: The Hindu
|
Must Read |
|
| NCERT Notes For UPSC | UPSC Daily Current Affairs |
| UPSC Blogs | UPSC Daily Editorials |
Recently, Scientists have detected a rare and extremely high-Energetic Particles cosmic ray known as Amaterasu particles falling to Earth.
News Source: The Hindu
|
Must Read |
|
| NCERT Notes For UPSC | UPSC Daily Current Affairs |
| UPSC Blogs | UPSC Daily Editorials |
The Uttar Pradesh Government has recently built India’s First Cow Sanctuary, a Centrally funded at Muzaffarnagar district under the Rashtriya Gokul Mission (RGM).
Rashtriya Gokul Mission
|
|---|
Read More: Rashtriya Gokul Mission
Additional Reading: Indigenous Cattle Breeds of India: Why They Are Preferred to Exotic Breeds?
News source: Indian Express
|
Must Read |
|
| NCERT Notes For UPSC | UPSC Daily Current Affairs |
| UPSC Blogs | UPSC Daily Editorials |
Recently, Karnataka, Punjab, and West Bengal tableaux proposals were rejected by the Ministry of Defence for the Republic Day Parade.
News source: Indian Express
|
Must Read |
|
| NCERT Notes For UPSC | UPSC Daily Current Affairs |
| UPSC Blogs | UPSC Daily Editorials |
The National Mission for Clean Ganga (NMCG) has been entrusted with powers to permit the discharge of treated sewage and effluents into the river, canals or water bodies.
The Environment (Protection) Act 1986
|
|---|
News Source: The Indian Express
|
Must Read |
|
| NCERT Notes For UPSC | UPSC Daily Current Affairs |
| UPSC Blogs | UPSC Daily Editorials |
The Indian Space Research Organisation (ISRO) has placed the Aditya-L1 spacecraft in a halo orbit around the Lagrange Point (L1).
Additional Information: Aditya-L1 Mission
News Source: The Hindu
|
Must Read |
|
| NCERT Notes For UPSC | UPSC Daily Current Affairs |
| UPSC Blogs | UPSC Daily Editorials |
Recently, the West Bengal Chief Minister asked the central government to officially list Bengali as a “classical language”.
Benefits of a Classical Language:
|
|---|
News Source: The Hindu
|
Must Read |
|
| NCERT Notes For UPSC | UPSC Daily Current Affairs |
| UPSC Blogs | UPSC Daily Editorials |
Recently, the World Health Organisation (WHO) officially unveiled the International Classification of Diseases (ICD 11), Traditional Medicine Module 2.
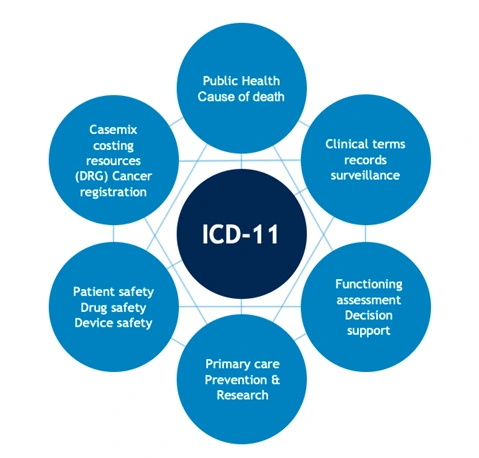
Traditional Medicines in ICD 11: Blending Cultural Wisdom with Modern Healthcare Standards
|
|---|
News Source: PIB
|
Must Read |
|
| NCERT Notes For UPSC | UPSC Daily Current Affairs |
| UPSC Blogs | UPSC Daily Editorials |
Context: A seven-judge Bench of the Supreme Court started hearing the matter of Aligarh Muslim University’s minority character.

Constitutional Protections for minority Character Status:
National Commission for Minorities (NCM)
National Commission for Minority Educational Institutions (NCMEI): It is a quasi-judicial body enacted to safeguard the educational rights of the minorities enshrined in Article 30(1) of the Constitution under the NCMEI Act 2004. |
|---|
Conclusion: Lack of education among the minorities section, especially muslims is a reason for their backwardness. Thus, there is a need to balance the rights of minorities and the educational rights of other backward Sections.
|
Must Read |
|
| NCERT Notes For UPSC | UPSC Daily Current Affairs |
| UPSC Blogs | UPSC Daily Editorials |
SC Verdict on Newsclick Shows Adherence to Due Pro...
Stay Invested: On Chabahar and India-Iran Relation...
Credit Rating Agencies, Impact on India’s De...
Catapulting Indian Biopharma Industry
Globalisation Under Threat, US Import Tariffs Have...
Global Report on Hypertension, Global Insights and...
<div class="new-fform">
</div>
