The National Aerospace Laboratories (NAL) completed the first test of a solar-powered “High Altitude Pseudo Satellite Vehicle”.
| Recently, Bengaluru-based NewSpace Research and Technologies, a deep-tech start-up, flew a similar solar-powered UAV, having developed the technology through the Innovation of Defence Excellence initiative of the Defence Ministry. |
|---|
News Source: Indian Express
| Must Read | |
| NCERT Notes For UPSC | UPSC Daily Current Affairs |
| UPSC Blogs | UPSC Daily Editorials |
| Daily Current Affairs Quiz | Daily Main Answer Writing |
| UPSC Mains Previous Year Papers | UPSC Test Series 2024 |
12 nesting sites of Olive Ridley Turtles were identified in the Mangalore division of Karnataka after a gap of 29 years.
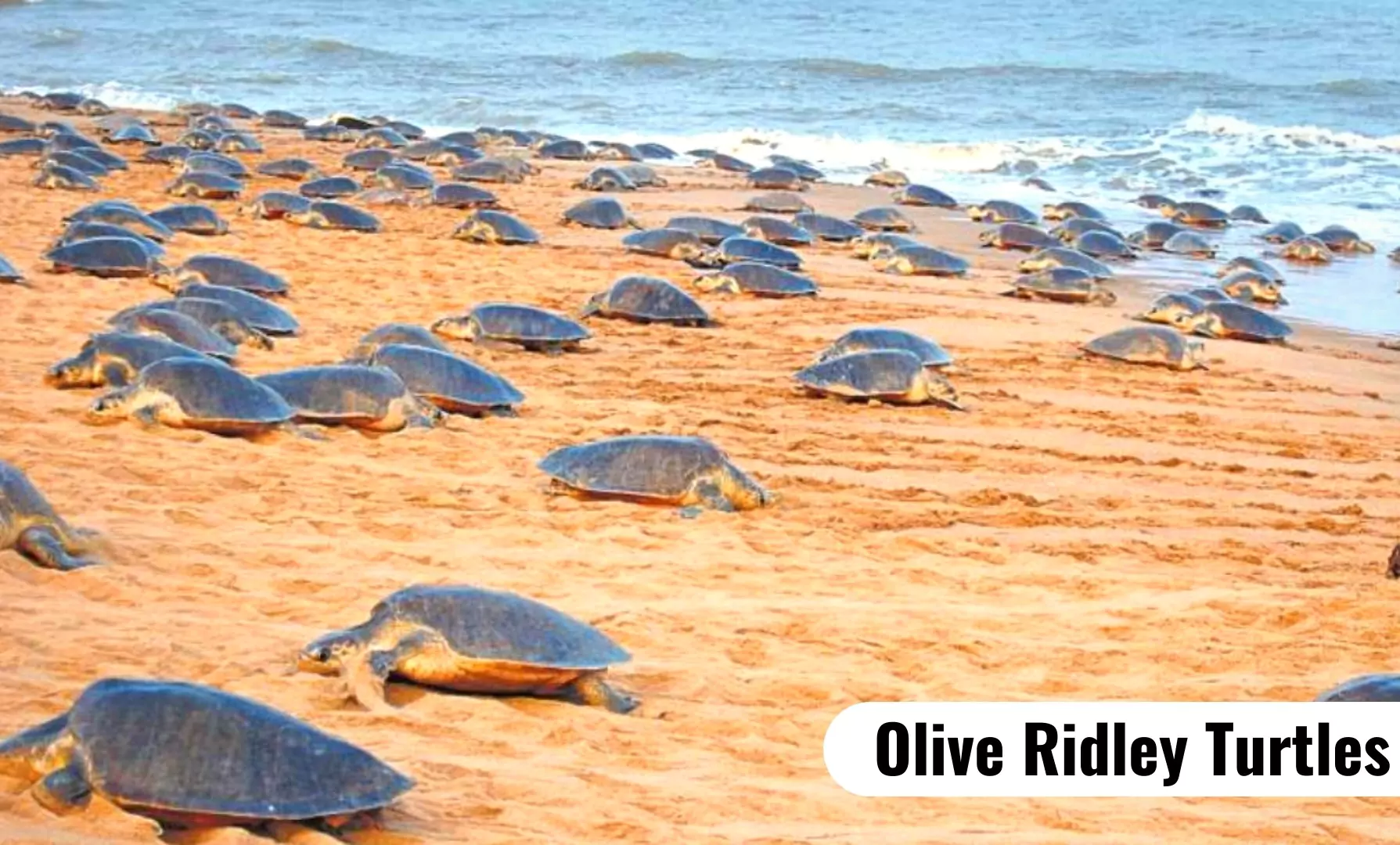

Arribada
|
|---|
News Source: DTE
| Must Read | |
| NCERT Notes For UPSC | UPSC Daily Current Affairs |
| UPSC Blogs | UPSC Daily Editorials |
| Daily Current Affairs Quiz | Daily Main Answer Writing |
| UPSC Mains Previous Year Papers | UPSC Test Series 2024 |
Recently, the Bharat Ratna, India’s highest civilian award, was conferred on former Prime Ministers PV Narasimha Rao and Chaudhary Charan Singh as well as agricultural scientist MS Swaminathan.
Important Facts About Bharat Ratna Recipient
|
|---|
 He was also the Leader of the Special Non-aligned Mission that visited countries in West Asia in 1983, in an effort to resolve the Palestinian Liberation Organisation.
He was also the Leader of the Special Non-aligned Mission that visited countries in West Asia in 1983, in an effort to resolve the Palestinian Liberation Organisation.

News Source: The Hindu
| Must Read | |
| NCERT Notes For UPSC | UPSC Daily Current Affairs |
| UPSC Blogs | UPSC Daily Editorials |
| Daily Current Affairs Quiz | Daily Main Answer Writing |
| UPSC Mains Previous Year Papers | UPSC Test Series 2024 |
The Supreme Court will hear a curative petition filed by the Airports Authority of India (AAI) against the multinational conglomerate GMR Group concerning the operational management of Nagpur’s Babasaheb Ambedkar International Airport.
Legal Maxim:
|
|---|
Review Petition |
Curative Petition |
|
|
Generally, Supreme Court decisions are final and cannot be appealed within the court. The avenues like review and curative petitions exist for aggrieved parties to seek redressal to ensure impartiality in the judicial system and correct any potential misconceptions in Supreme Court judgments.
News Source : The Hindu
| Must Read | |
| NCERT Notes For UPSC | UPSC Daily Current Affairs |
| UPSC Blogs | UPSC Daily Editorials |
| Daily Current Affairs Quiz | Daily Main Answer Writing |
| UPSC Mains Previous Year Papers | UPSC Test Series 2024 |
Several Startups have recently obtained regulatory approval from RBI to operate as payment aggregators.
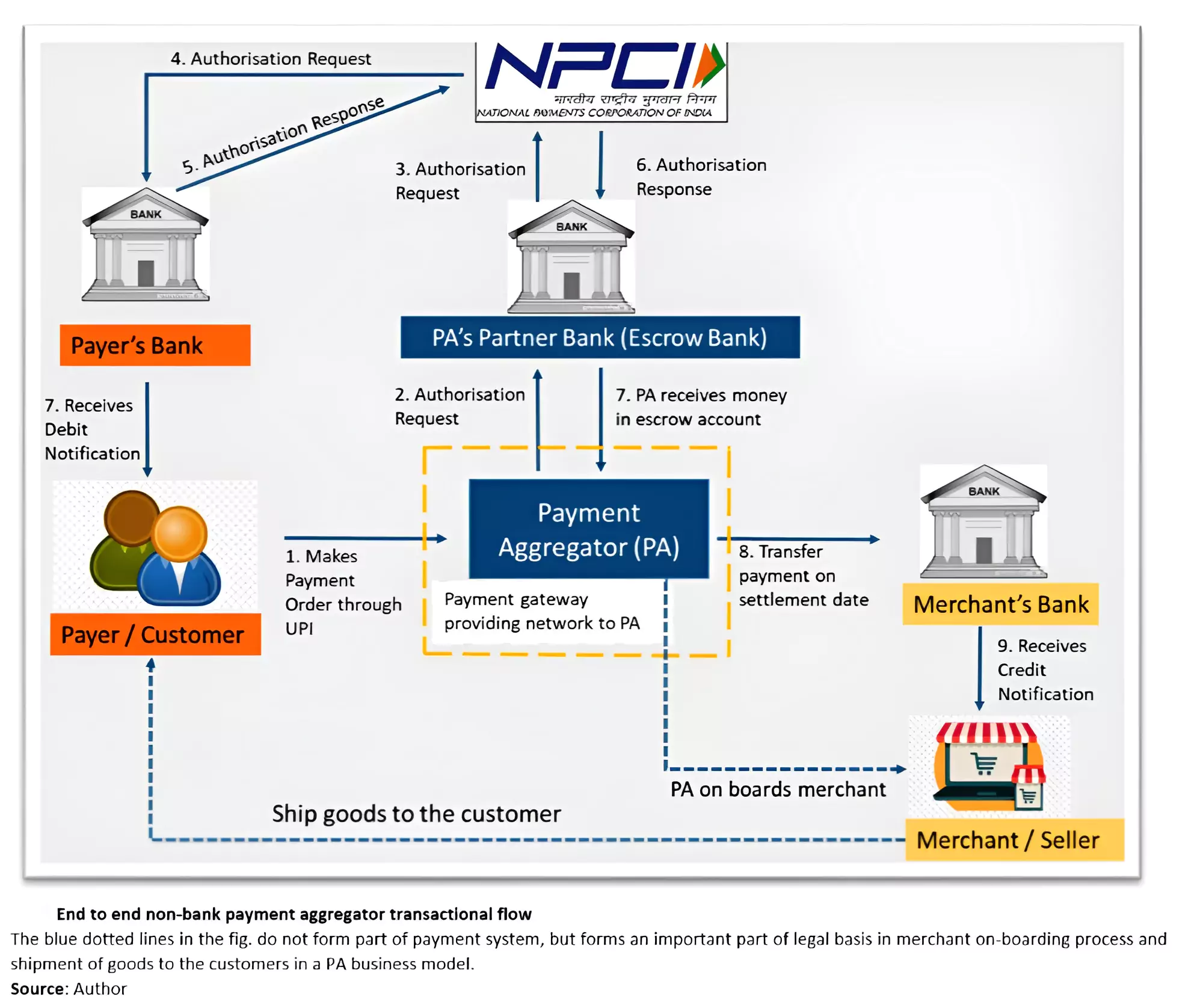
News Source : Business Standard
| Must Read | |
| NCERT Notes For UPSC | UPSC Daily Current Affairs |
| UPSC Blogs | UPSC Daily Editorials |
| Daily Current Affairs Quiz | Daily Main Answer Writing |
| UPSC Mains Previous Year Papers | UPSC Test Series 2024 |
Research at IIT Jodhpur has revealed that Indians under report mental health concerns, despite their prevalence.
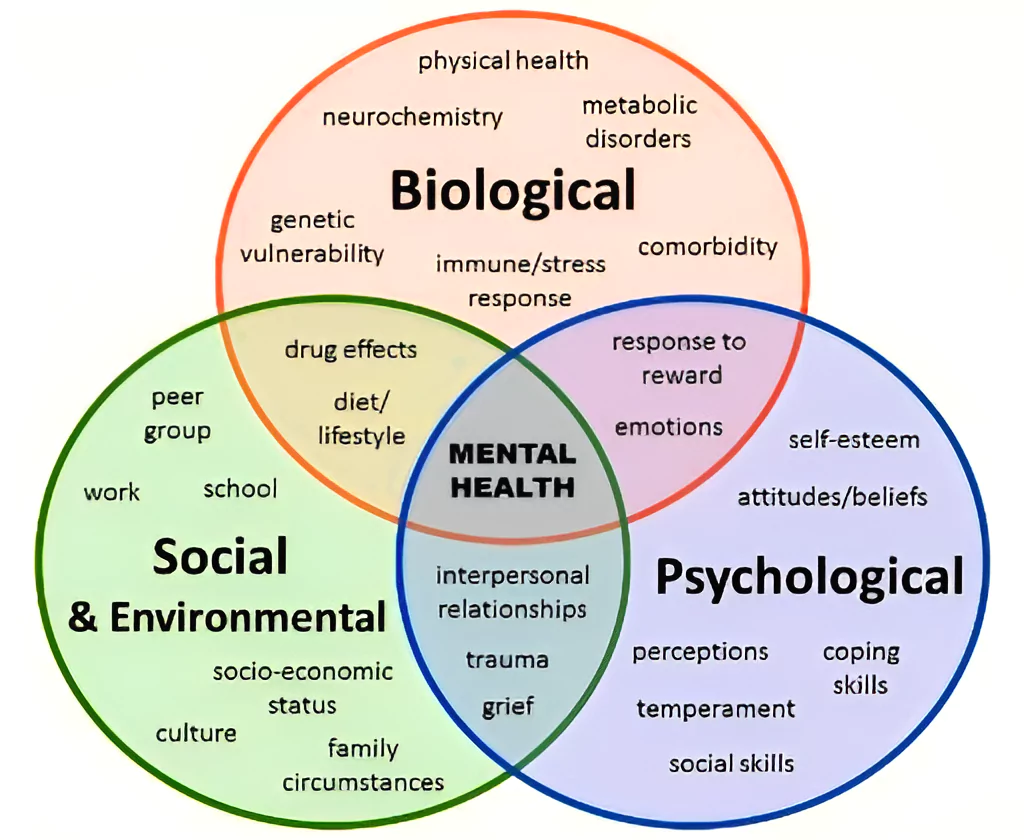
News Source: TheHindu
| Must Read | |
| NCERT Notes For UPSC | UPSC Daily Current Affairs |
| UPSC Blogs | UPSC Daily Editorials |
| Daily Current Affairs Quiz | Daily Main Answer Writing |
| UPSC Mains Previous Year Papers | UPSC Test Series 2024 |
The 7th session of the Indian Ocean Conference will be held at Perth, Australia.
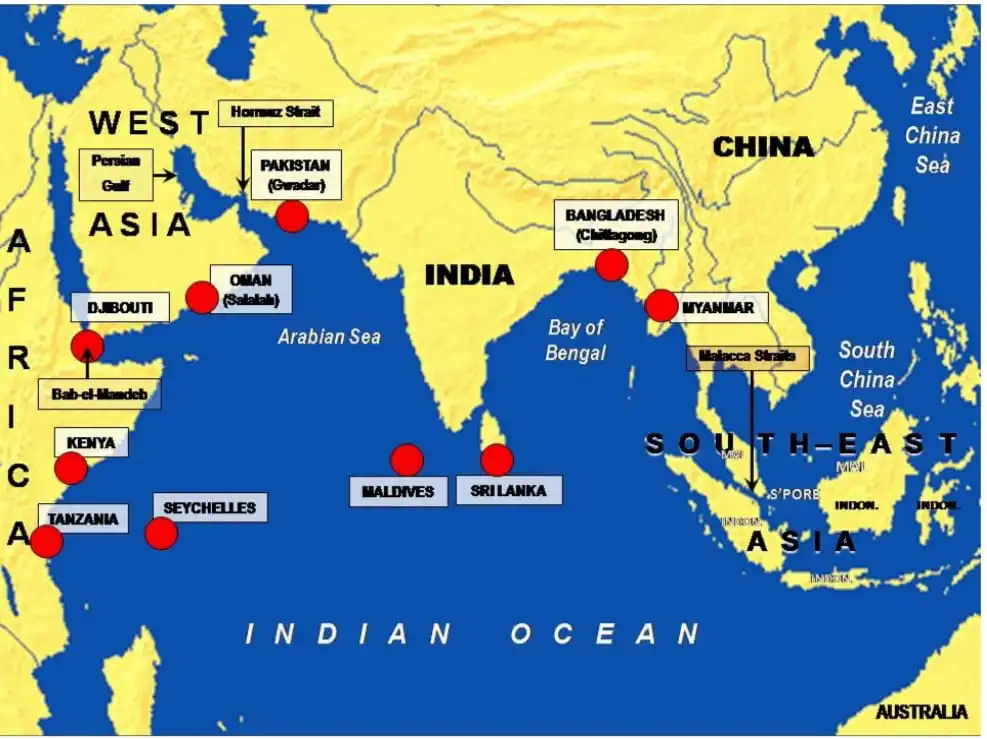
News Source: AIR
| Must Read | |
| NCERT Notes For UPSC | UPSC Daily Current Affairs |
| UPSC Blogs | UPSC Daily Editorials |
| Daily Current Affairs Quiz | Daily Main Answer Writing |
| UPSC Mains Previous Year Papers | UPSC Test Series 2024 |
Sovereign Gold Bonds 2023-24 (Series IV) will be opened for subscription from 12th-16th February, 2024.

News Source: PIB
| Must Read | |
| NCERT Notes For UPSC | UPSC Daily Current Affairs |
| UPSC Blogs | UPSC Daily Editorials |
| Daily Current Affairs Quiz | Daily Main Answer Writing |
| UPSC Mains Previous Year Papers | UPSC Test Series 2024 |
Chhattisgarh’s Ocher Studio is helping to preserve India’s 4,000-year-old craft – Dhokra Shilpkala.
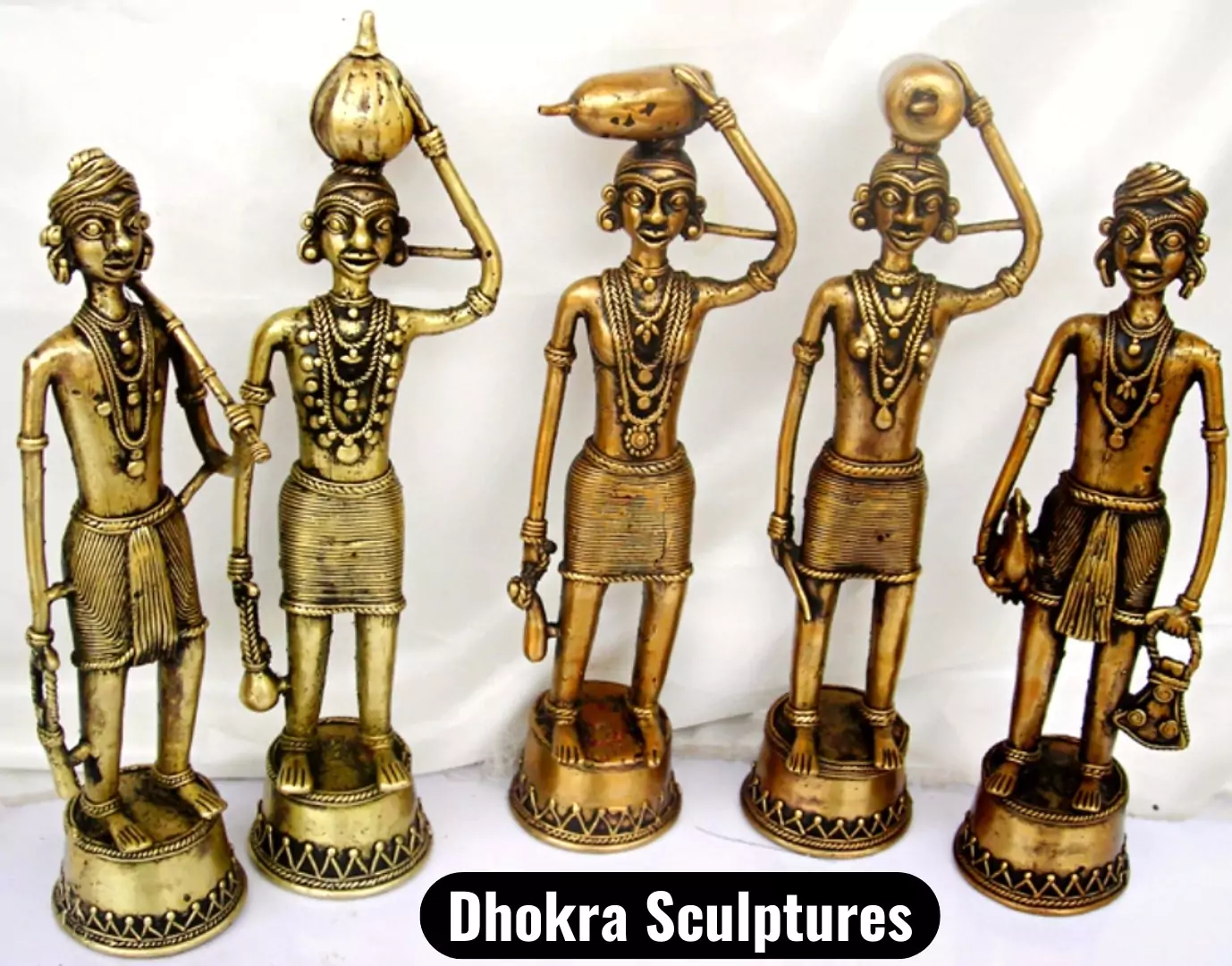

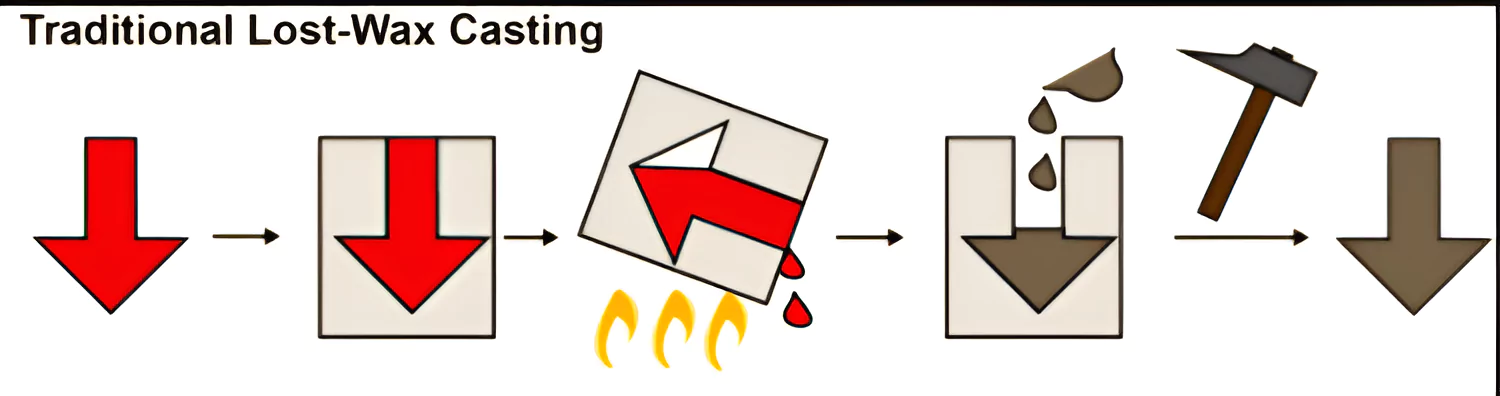
News Source: ET
| Must Read | |
| NCERT Notes For UPSC | UPSC Daily Current Affairs |
| UPSC Blogs | UPSC Daily Editorials |
| Daily Current Affairs Quiz | Daily Main Answer Writing |
| UPSC Mains Previous Year Papers | UPSC Test Series 2024 |
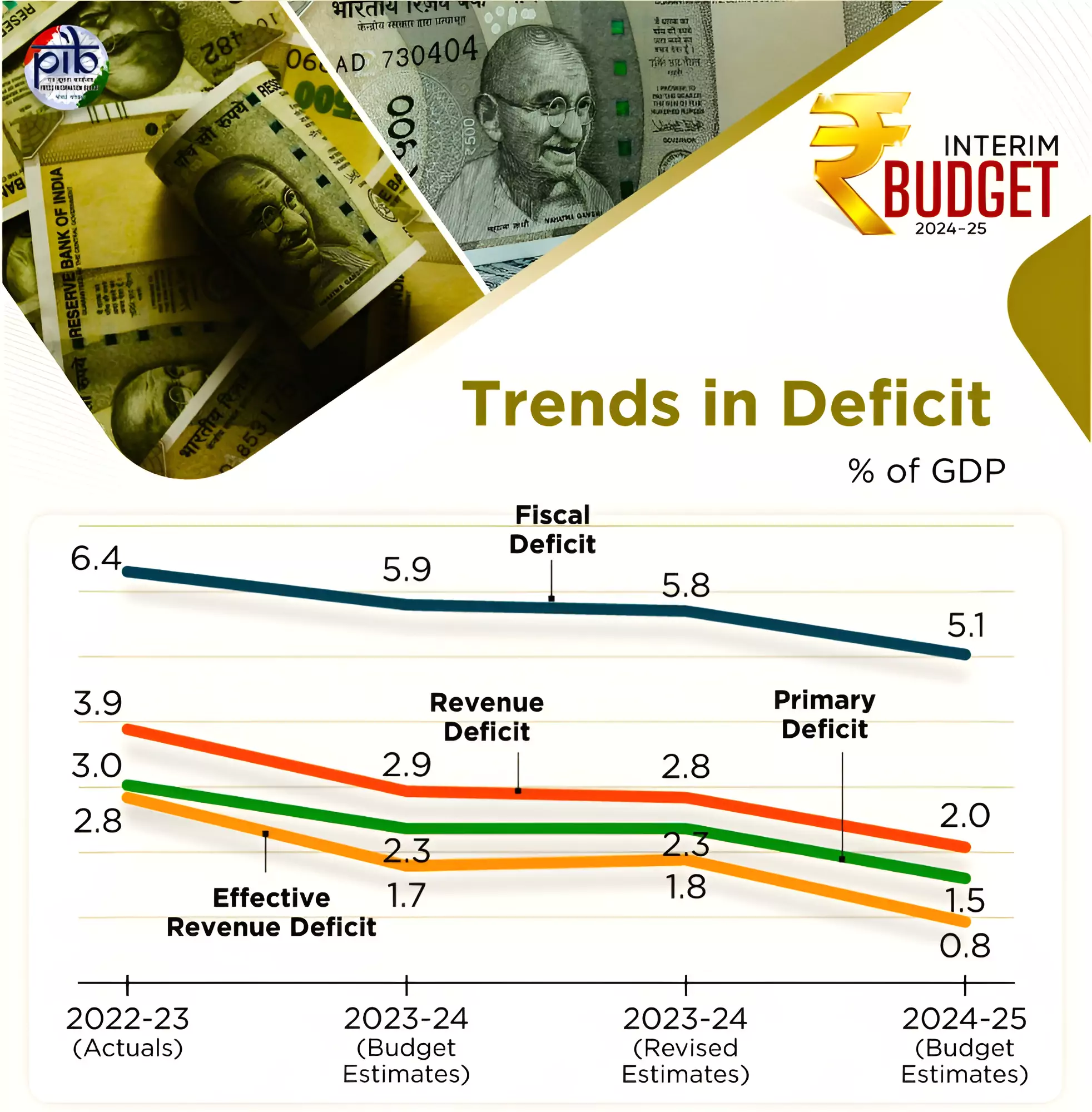
In her interim budget 2024-25 speech Finance Minister Nirmala Sitharaman announced that the centre would reduce its fiscal deficit to 5.1% of GDP in 2024-25.
Positive Aspect of Fiscal Deficit |
Negative Aspect of Fiscal Deficit |
|
|
Legislation Related to Fiscal Management in India
|
|---|
Fiscal consolidation measures can involve tough policy choices and may have short-term economic costs including reduced public spending but it underscores the importance of structural reforms to enhance productivity and competitiveness.
Also Read:
News Source: The Hindu
| Must Read | |
| NCERT Notes For UPSC | UPSC Daily Current Affairs |
| UPSC Blogs | UPSC Daily Editorials |
| Daily Current Affairs Quiz | Daily Main Answer Writing |
| UPSC Mains Previous Year Papers | UPSC Test Series 2024 |
This article is based on the news “PROMOTION OF STARTUPS IN AGRICULTURE SECTOR” which was published in the Pib. Dept of Agriculture and Farmers Welfare is implementing the “Innovation and Agri-Entrepreneurship Development” program.
| Relevancy for Prelims: Agricultural Development, Agriculture In India, Voluntary Carbon Market In Agriculture Sector, and Union Budget 2024 For Agriculture Sector.
Relevancy for Mains: Agriculture Startups in India: Need, Significance, Challenges, Government Initiatives, and Way Forward. |
|---|
Agriculture Startups in Spotlight
|
|---|

Rashtriya Krishi Vikas Yojana (RKVY)
|
|---|
Agriculture startups are developing innovative solutions for various aspects of agriculture, including precision farming, supply chain management, and market linkages. As the sector continues to grow, it has the potential to not only transform India’s agriculture sector but also create new employment opportunities and contribute towards the growth of the country’s economy.
| Mains Question: Explain how land pooling is answer to issues of growing land fragmentation and lack of mechanization in the Indian agriculture field. (10 marks, 150 words) |
|---|
| Must Read | |
| NCERT Notes For UPSC | UPSC Daily Current Affairs |
| UPSC Blogs | UPSC Daily Editorials |
| Daily Current Affairs Quiz | Daily Main Answer Writing |
| UPSC Mains Previous Year Papers | UPSC Test Series 2024 |
This article is based on the news “Could Preamble have been amended without altering Constitution’s adoption date, SC asks” which was published in the Hindustan Times. The Supreme Court was hearing a pair of petitions that sought deletion of words secular and socialist from the Preamble of Indian Constitution.
| Relevancy for Prelims: Supreme Court , Constitution Of India, Preamble Of The Indian Constitution, Words Socialist and Secular In Preamble,
Relevancy for Mains: Removal of Socialist and Secular Words From Preamble Of Indian Constitution: Origin, Amendments, Challenges, and Arguments. |
|---|

Who Said What?
|
|---|
Indian Secularism (Positive Secularism)
|
|---|
Removing Socialist and Secular from Indian preamble upholds original constitutional intent. Whereas, retaining “Socialist” and “Secular” in the Preamble reflects contemporary values, enhances clarity, and promotes social justice. Thus, it is upto the Supreme Court, whether to retain or remove these word in the Preamble of the Constitution of India.
| Must Read | |
| NCERT Notes For UPSC | UPSC Daily Current Affairs |
| UPSC Blogs | UPSC Daily Editorials |
| Daily Current Affairs Quiz | Daily Main Answer Writing |
| UPSC Mains Previous Year Papers | UPSC Test Series 2024 |
SC Verdict on Newsclick Shows Adherence to Due Pro...
Stay Invested: On Chabahar and India-Iran Relation...
Credit Rating Agencies, Impact on India’s De...
Catapulting Indian Biopharma Industry
Globalisation Under Threat, US Import Tariffs Have...
Global Report on Hypertension, Global Insights and...
<div class="new-fform">
</div>
