Northern Ireland (NI) has finally developed a new government this month after a two-year political stalemate between the two main parties since the 2022 elections to the Stormont Assembly.
The Good Friday Agreement/ the Belfast Agreement, signed on 10 April 1998, was a political deal designed to bring an end to 30 years of violent conflict in Northern Ireland, known as the Troubles.
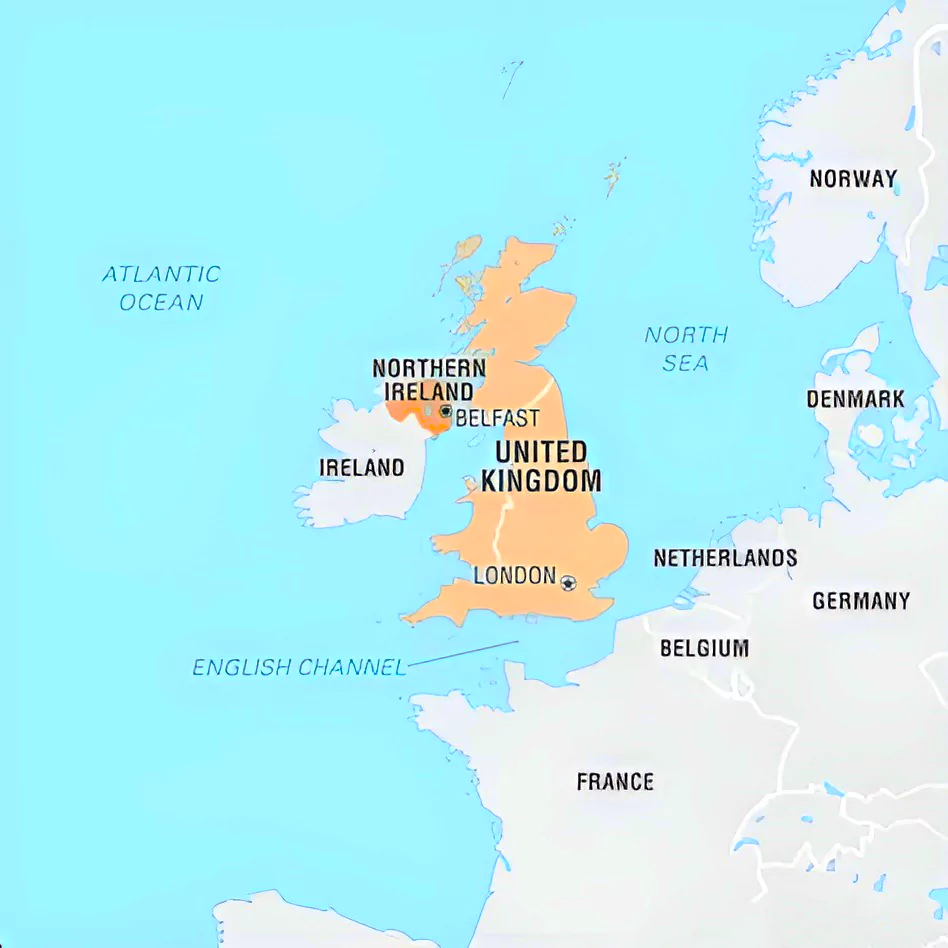
News Source: The Hindu
| Must Read | |
| NCERT Notes For UPSC | UPSC Daily Current Affairs |
| UPSC Blogs | UPSC Daily Editorials |
| Daily Current Affairs Quiz | Daily Main Answer Writing |
| UPSC Mains Previous Year Papers | UPSC Test Series 2024 |
The European Union launched a naval mission to protect the Red Sea shipping lane from Yemen’s Houthi rebels.
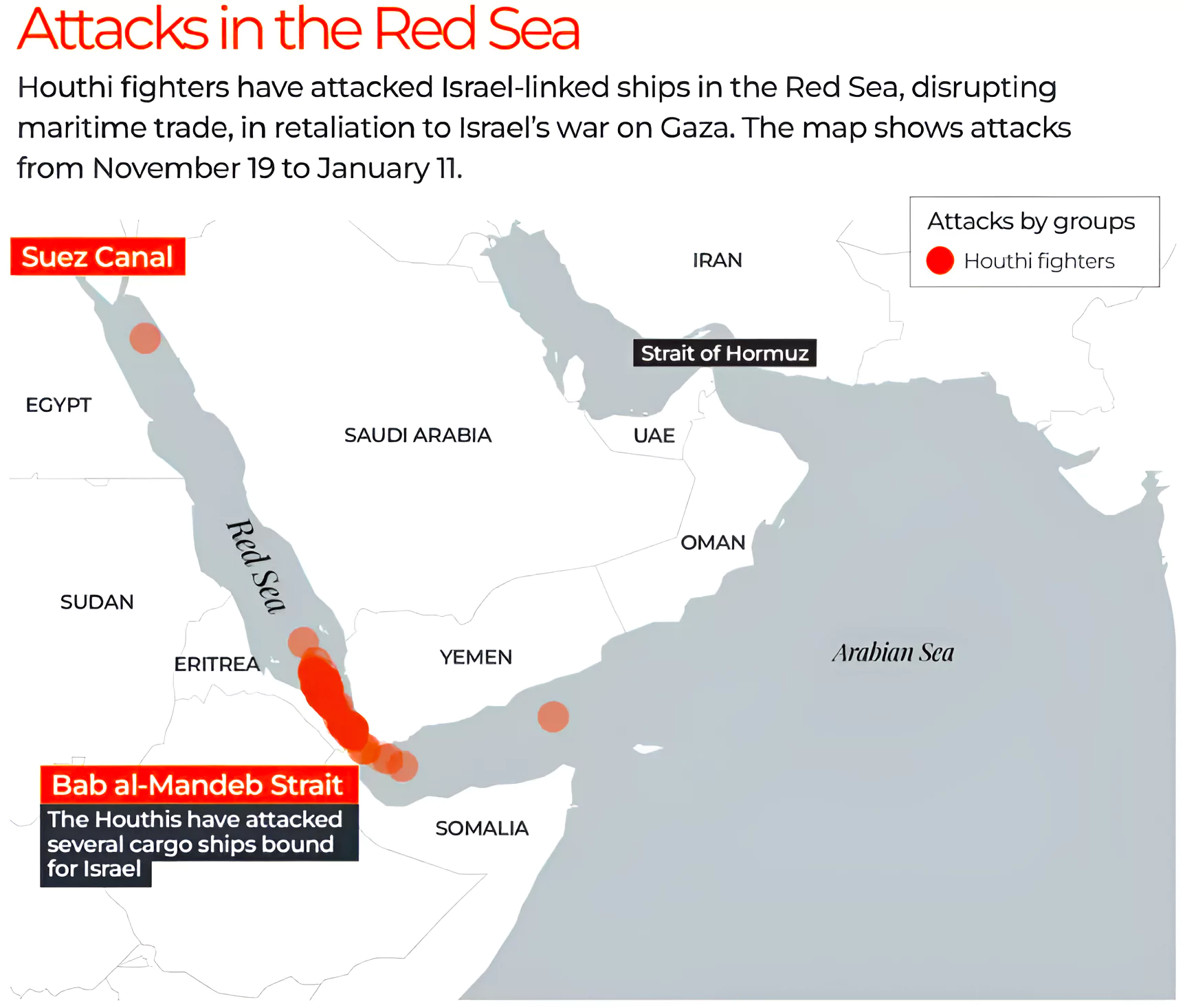 Mandate of the Operation: The mission will refrain from engaging in offensive actions on Yemeni territory for an initial duration of one year.
Mandate of the Operation: The mission will refrain from engaging in offensive actions on Yemeni territory for an initial duration of one year.
Operation Prosperity Guardian
India’s Decision: Countries like India, Italy and France have sent ships to the region on their own initiative, distancing themselves from the U.S. umbrella. |
|---|
Source: Hindu
| Must Read | |
| NCERT Notes For UPSC | UPSC Daily Current Affairs |
| UPSC Blogs | UPSC Daily Editorials |
| Daily Current Affairs Quiz | Daily Main Answer Writing |
| UPSC Mains Previous Year Papers | UPSC Test Series 2024 |
Recently, a 5-day International Conference on Photonics, Quantum Information, and Quantum Communication, was organised by the Satyendra Nath Bose National Centre for Basic Sciences in Kolkata.
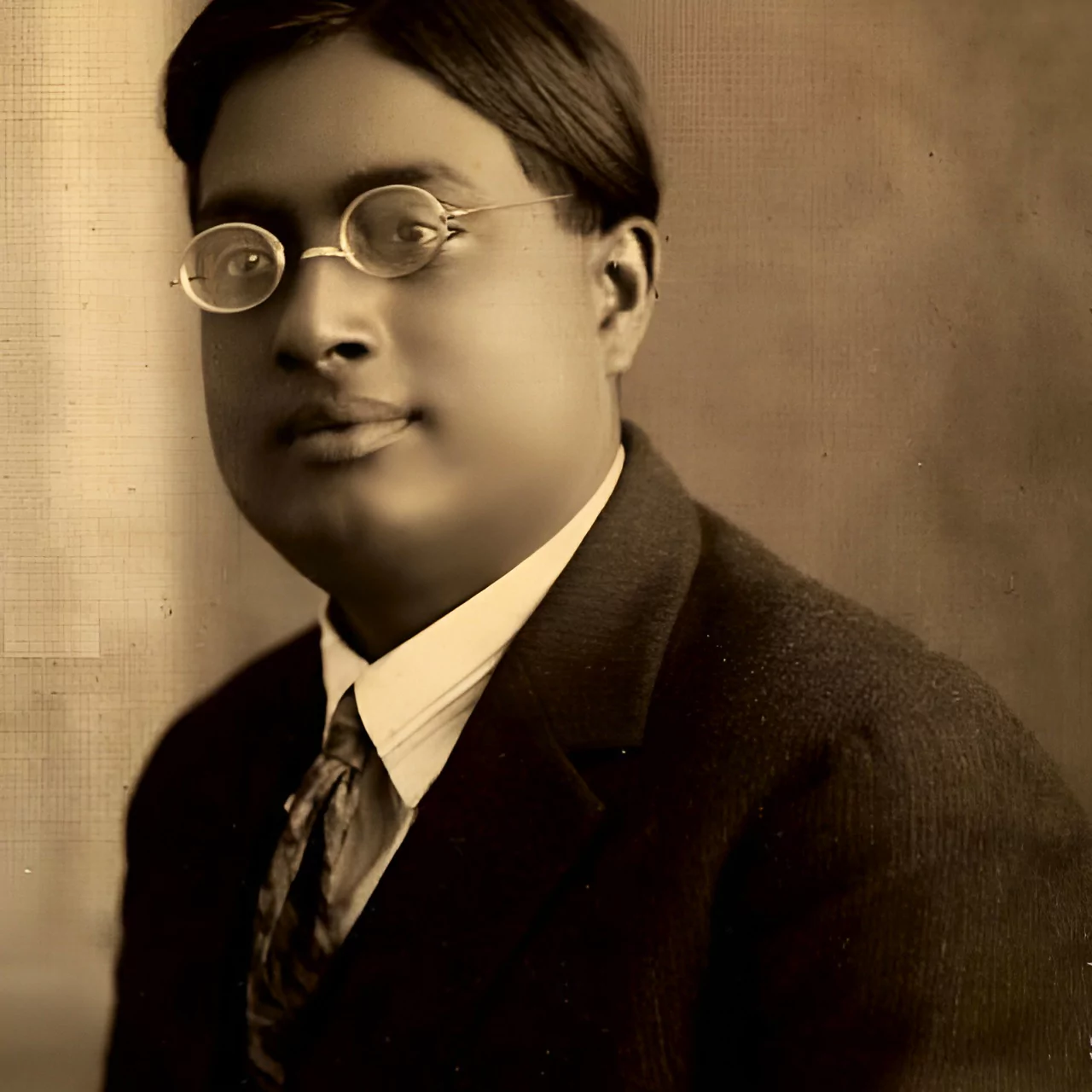

Satyendra Nath Bose was an Indian mathematician and physicist, an expert in theoretical physics. His contributions helped improve the Standard Model of Particle Physics.
Birth: Calcutta (now Kolkata) in 1894.
Academic Life: By the age of 15, pursued a Bachelor of Science degree at the Presidency College
Inspired by: Jagdish Chandra Bose and Prafulla Chandra Ray.
Career: Lecturer at Calcutta University, along with astrophysicist Meghnad Saha.
Breakthrough: He had derived Planck’s law for black body radiation (which refers to the spectrum of light emitted by any hot object) without any reference to classical electrodynamics.
Death: February 4, 1974, after a severe heart attack at the age of 80.
Recognitions to Satyendra Nath Bose
|
|---|
Bharat Ratna Awards 2024: Award Winner List
News Source: The Hindu
| Must Read | |
| NCERT Notes For UPSC | UPSC Daily Current Affairs |
| UPSC Blogs | UPSC Daily Editorials |
| Daily Current Affairs Quiz | Daily Main Answer Writing |
| UPSC Mains Previous Year Papers | UPSC Test Series 2024 |
The recent study Published in the Elsevier Journal emphasised that besides local emissions, rapidly changing climate is a significant factor affecting air quality in India.
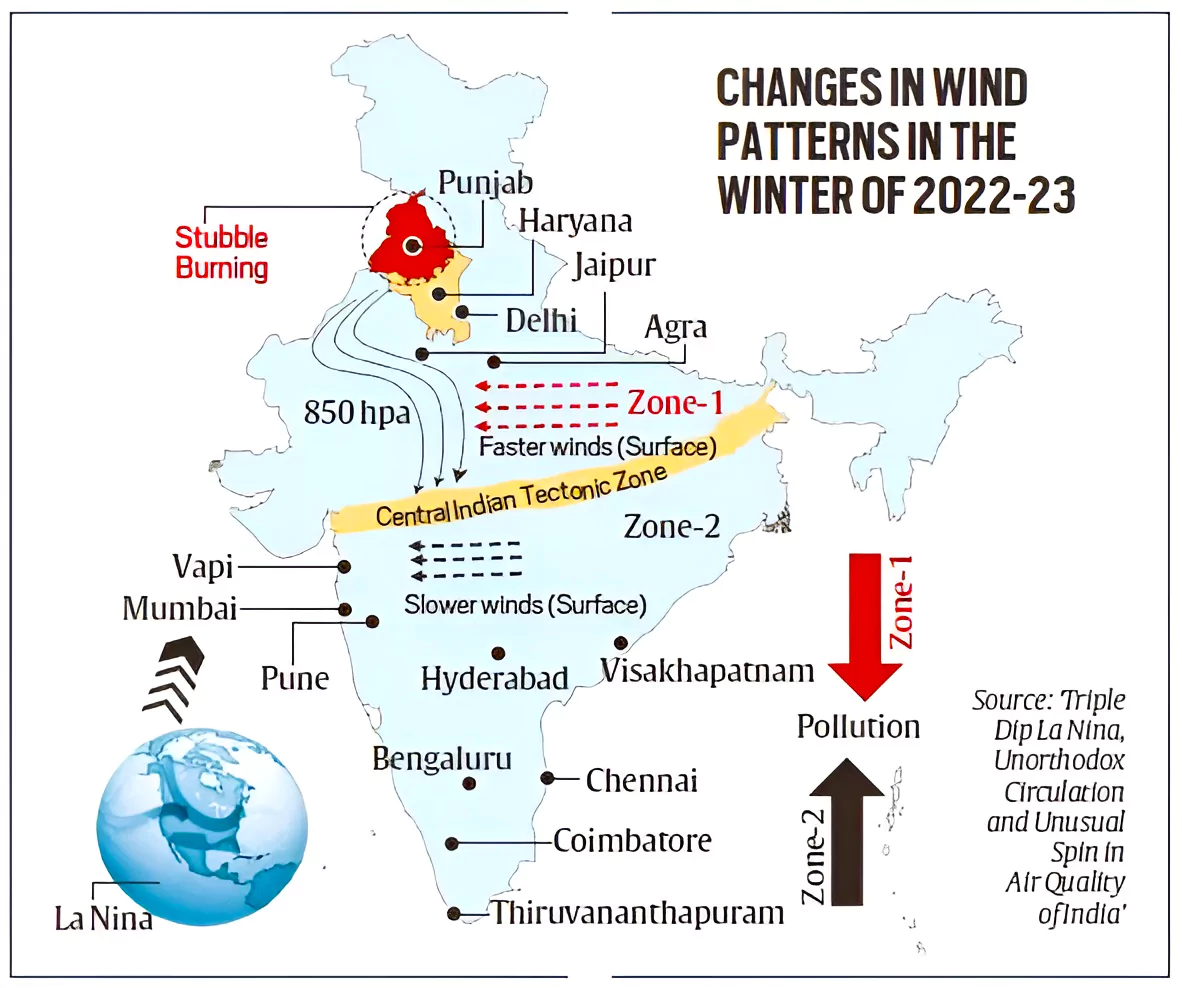
La Niña:
Triple Dip La-Nina:
Impact of Triple dip La Nina in India
|
|---|
News Source: Indian Express
| Must Read | |
| NCERT Notes For UPSC | UPSC Daily Current Affairs |
| UPSC Blogs | UPSC Daily Editorials |
| Daily Current Affairs Quiz | Daily Main Answer Writing |
| UPSC Mains Previous Year Papers | UPSC Test Series 2024 |
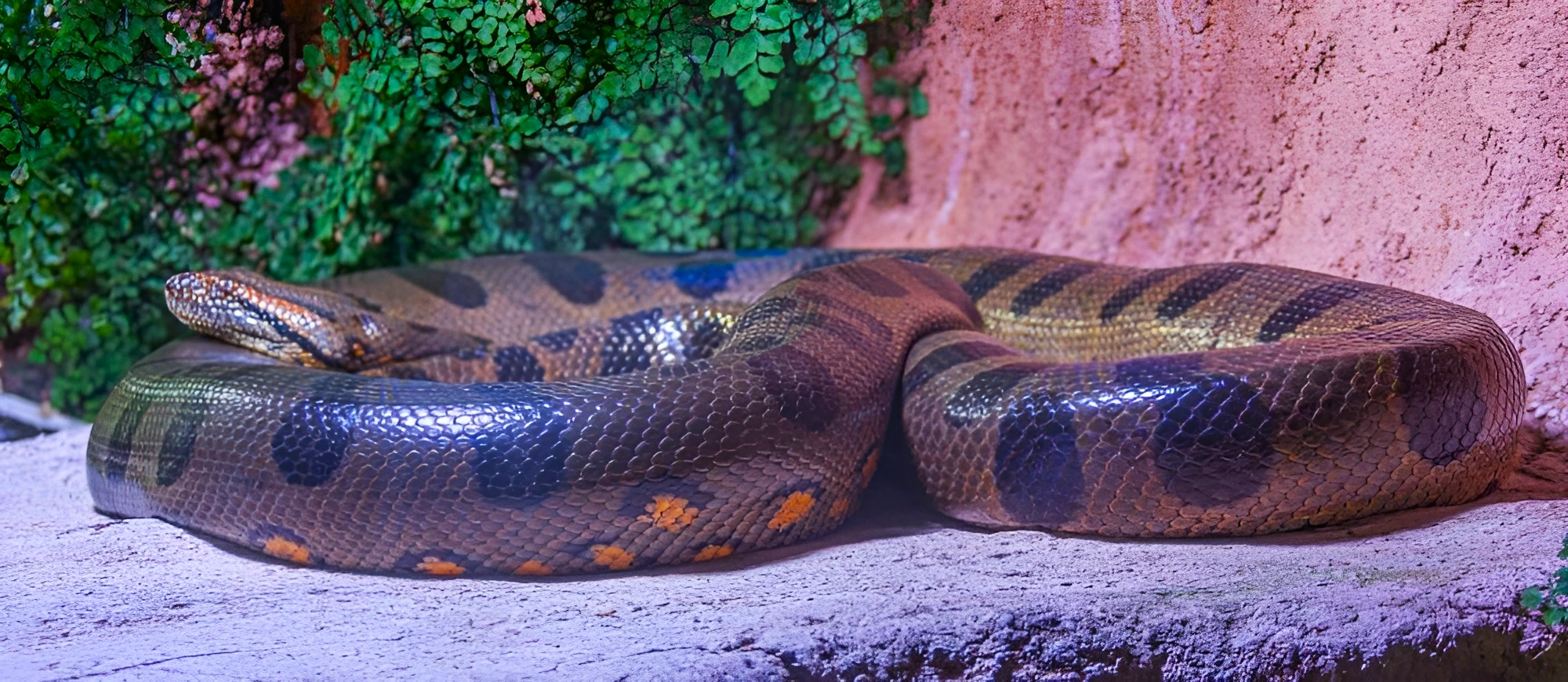
Scientific discovery has raised understanding about two genetically different species of green anaconda.
| Anacondas:
Anacondas, also known as water boas, belong to the genus Eunectes. They are a group of sizable snakes. Four different types of anacondas were identified in history.
Anacondas as Environmental Indicators:
|
|---|

News Source: Down to Earth
| Must Read | |
| NCERT Notes For UPSC | UPSC Daily Current Affairs |
| UPSC Blogs | UPSC Daily Editorials |
| Daily Current Affairs Quiz | Daily Main Answer Writing |
| UPSC Mains Previous Year Papers | UPSC Test Series 2024 |
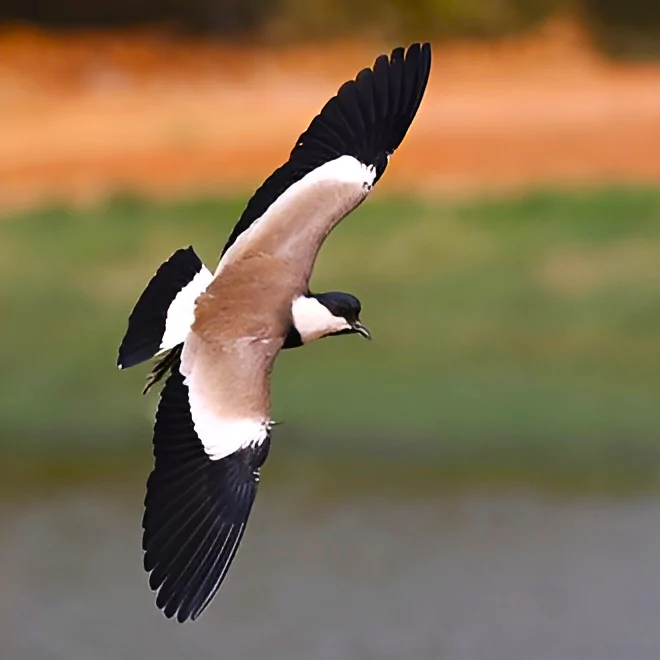
African-Mediterranean wader bird spur-winged lapwing has been spotted at Ammavaripet Lake near Warangal for the first time in India.

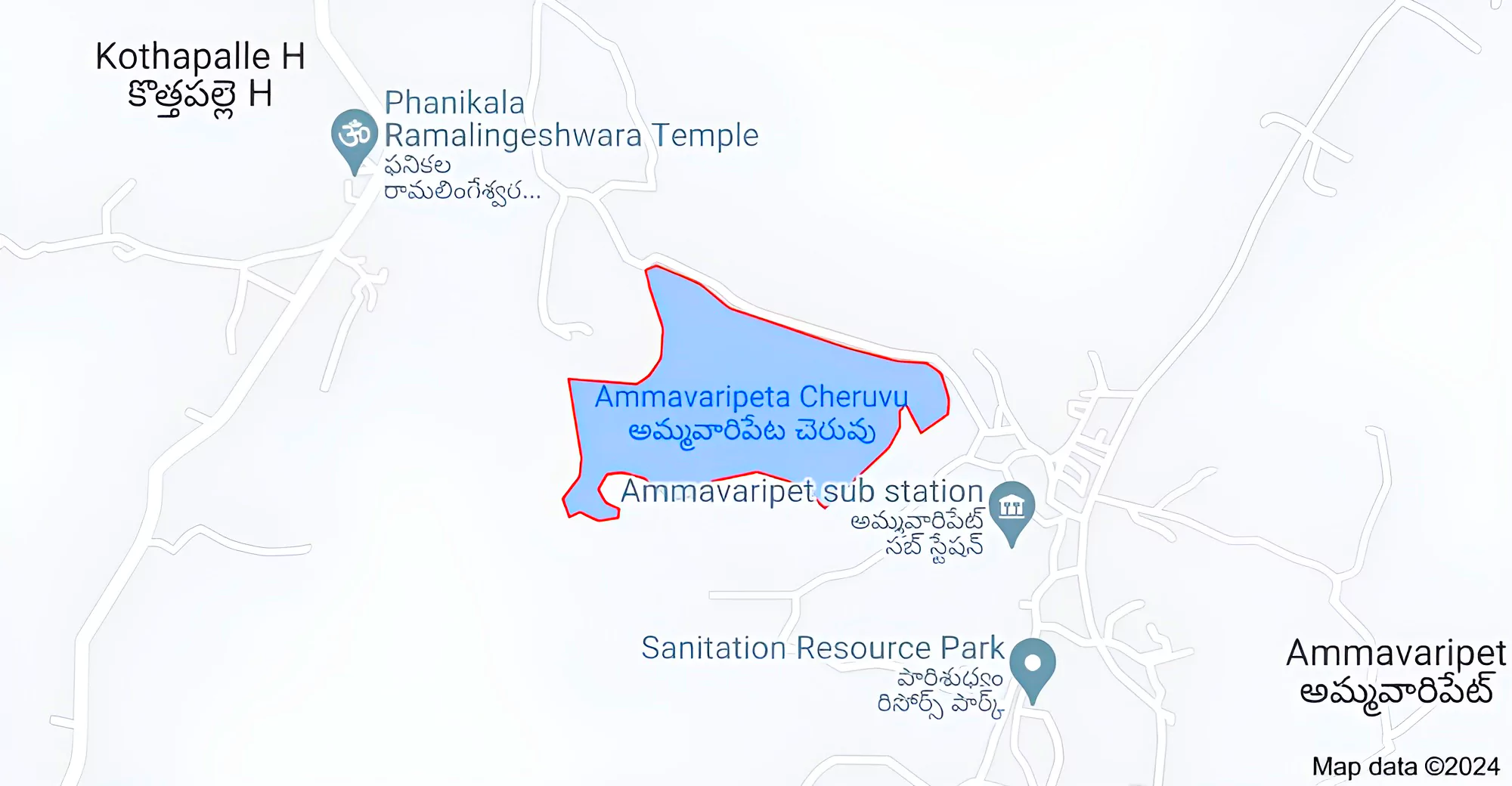
News Source: Thehindu
| Must Read | |
| NCERT Notes For UPSC | UPSC Daily Current Affairs |
| UPSC Blogs | UPSC Daily Editorials |
| Daily Current Affairs Quiz | Daily Main Answer Writing |
| UPSC Mains Previous Year Papers | UPSC Test Series 2024 |
Recently, the Union Government has increased the allocation of the ‘Sustainable & Inclusive Development of Natural Rubber Sector’ scheme for the next two financial years (2024-26) by 23% from Rs 576.41 crore to Rs 708.69 crore.
Largest Natural Rubber Producing Countries:
Largest Natural Rubber Producing States in India:
Zones of Rubber Cultivation:
|
|---|
About Natural Rubber
About Rubber Board of India
Government’s Initiatives Rubber Production In India
|
|---|
News Source: The Indian Express
| Must Read | |
| NCERT Notes For UPSC | UPSC Daily Current Affairs |
| UPSC Blogs | UPSC Daily Editorials |
| Daily Current Affairs Quiz | Daily Main Answer Writing |
| UPSC Mains Previous Year Papers | UPSC Test Series 2024 |
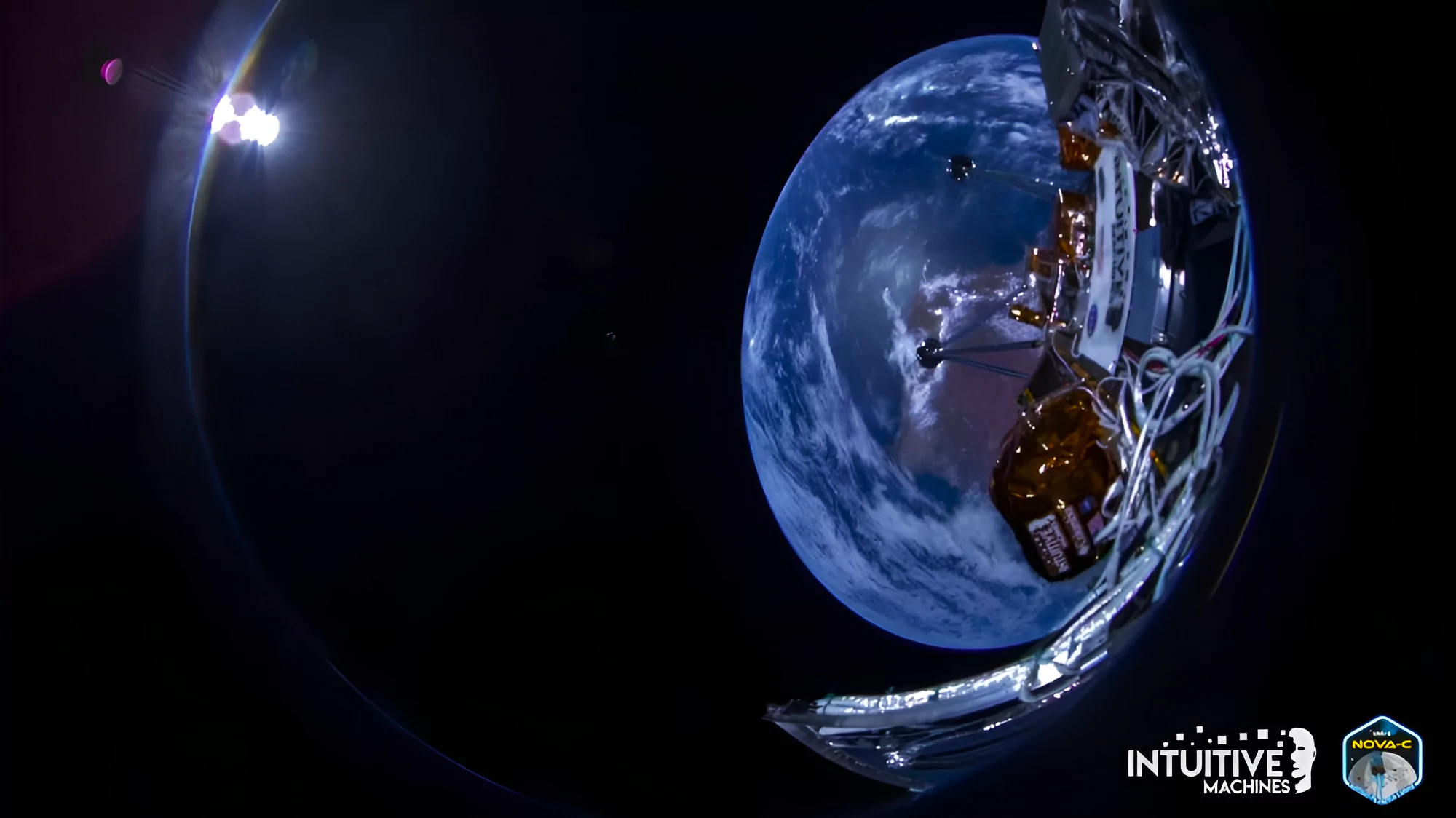
Recently, SpaceX launched Intuitive Machines’ IM-1 mission from the Kennedy Space Center in Florida carrying the private Odysseus moon lander built by Houston-based Intuitive Machines.

News Source: The Indian Express
| Must Read | |
| NCERT Notes For UPSC | UPSC Daily Current Affairs |
| UPSC Blogs | UPSC Daily Editorials |
| Daily Current Affairs Quiz | Daily Main Answer Writing |
| UPSC Mains Previous Year Papers | UPSC Test Series 2024 |
This article is based on the news “Forest (Conservation) Amendment Act 2023: States, UTs must act as per definition in TN Godavarman judgement, says SC ” which was published in the Down To Earth. The Supreme Court, in an interim order, said that ‘’the states and Union territories (UT) must act according to the definition of forest as laid down in the landmark TN Godavarman Thirumalpad v. Union of India judgement issued in 1996.
| Relevancy for Prelims: Supreme Court, Forest Conservation, Forest (Conservation) Amendment Bill 2023, and Forest Rights Act 2006 And Rights Of Forest Dwellers.
Relevancy for Mains: Amendment to the Forest Conservation Act 2023: Features, Significance, Challenges and Way Forward. |
|---|
Genesis of Godavarman Judgement:
Recognition of Zoo Mentioned in Section 38H of Wildlife Protection Act 1972 |
|---|
The forest conservation architecture in India:
|
|---|
| Impact & Significance of Godavarman Case 1996:
On Forest Conservation Laws:
Enhanced Judicial Involvement in Environmental Governance:
Protection and Preservation of Forest Lands:
Recognition of Rights for Forest Dwellers and Tribal Communities:
Establishment of various committees to ensure adherence to its directives:
|
|---|
The amendments to the forest conservation Act pushed the ground for diverting more forest land for non-forest activities. It endangers not only forests and wildlife, but also the well-being and livelihoods of forest-dwelling communities. Therefore Current ruling of the Supreme Court on the definition of Forest & Permission for Zoo & Safari Creation is a welcome step.
| Must Read | |
| NCERT Notes For UPSC | UPSC Daily Current Affairs |
| UPSC Blogs | UPSC Daily Editorials |
| Daily Current Affairs Quiz | Daily Main Answer Writing |
| UPSC Mains Previous Year Papers | UPSC Test Series 2024 |
This article is based on the news “Union Home Minister and Minister of Cooperation Shri Amit Shah says in order to build a disaster resilient India, Prime Minister Shri Narendra Modi ji has introduced a multi-dimensional Disaster Management Plan” which was published in the PIB Recently, the Prime Minister has introduced a multi-dimensional Disaster Management Plan.
| Relevancy for Prelims: Disasters and Natural Hazards, Disaster Management In India, Disaster Risk Index And Reduction, and National Policy On Disaster Management 2009.
Relevancy for Mains: Multi-Dimensional Disaster Management Plan: Objectives, Need, and Significance, and Way Forward. |
|---|
Sendai Framework
|
|---|
International Cooperation for Disaster Risk Reduction:
|
|---|
The changing environmental landscape coupled with anthropogenic impacts will make the disasters more dynamic in nature. This will require a multi-dimensional approach integrated with technological advancements to predict, mitigate and rehabilitate the vulnerable communities.
| Prelims PYQ (2017):
With reference to ‘Global Climate Change Alliance’, which of the following statements is/are correct? 1. It is an initiative of the European Union. 2. It provides technical and financial support to targeted developing countries to integrate climate change into their development policies and budgets. 3. It is coordinated by World Resources Institute (WRI) and World Business Council for Sustainable Development (WBCSD). Select the correct answer using the code given below: (a) 1 and 2 only (b) 3 only (c) 2 and 3 only (d) 1, 2 and 3 Ans: (a) |
|---|
| Must Read | |
| NCERT Notes For UPSC | UPSC Daily Current Affairs |
| UPSC Blogs | UPSC Daily Editorials |
| Daily Current Affairs Quiz | Daily Main Answer Writing |
| UPSC Mains Previous Year Papers | UPSC Test Series 2024 |
<div class="new-fform">
</div>