The Prime Minister has inaugurated the refurbished Kochrab Ashram and unveiled the Master Plan for the Gandhi Ashram Memorial at the Mahatma Gandhi Ashram in Sabarmati, Ahmedabad, Gujarat.
| Name | Year | Place | Country |
| Phoenix Settlement | 1904 | Natal | South Africa |
| Tolstoy Farm | 1910 | Near Johannesburg | South Africa |
| Kochrab Ashram | 1915 | Ahmedabad | India |
| Sabarmati Ashram | 1917 | Ahmedabad | India |
| Sevagram Ashram | 1936 | Wardha | India |
Major Non-Violent protest: The Dandi March, also known as Salt March / Salt Satyagraha, was a major non-violent protest action led by Mahatma Gandhi in March-April 1930.
News Source: Indian Express
| Must Read | |
| NCERT Notes For UPSC | UPSC Daily Current Affairs |
| UPSC Blogs | UPSC Daily Editorials |
| Daily Current Affairs Quiz | Daily Main Answer Writing |
| UPSC Mains Previous Year Papers | UPSC Test Series 2024 |
The Department of Pharmaceuticals issued the UCPMP 2024 (Uniform Code for Pharmaceuticals Marketing Practices).
News Source: Business Standard
| Must Read | |
| NCERT Notes For UPSC | UPSC Daily Current Affairs |
| UPSC Blogs | UPSC Daily Editorials |
| Daily Current Affairs Quiz | Daily Main Answer Writing |
| UPSC Mains Previous Year Papers | UPSC Test Series 2024 |
Central Drugs Standard Control Organisation (CDSCO)
|
|---|
News Source: The Hindu
| Must Read | |
| NCERT Notes For UPSC | UPSC Daily Current Affairs |
| UPSC Blogs | UPSC Daily Editorials |
| Daily Current Affairs Quiz | Daily Main Answer Writing |
| UPSC Mains Previous Year Papers | UPSC Test Series 2024 |
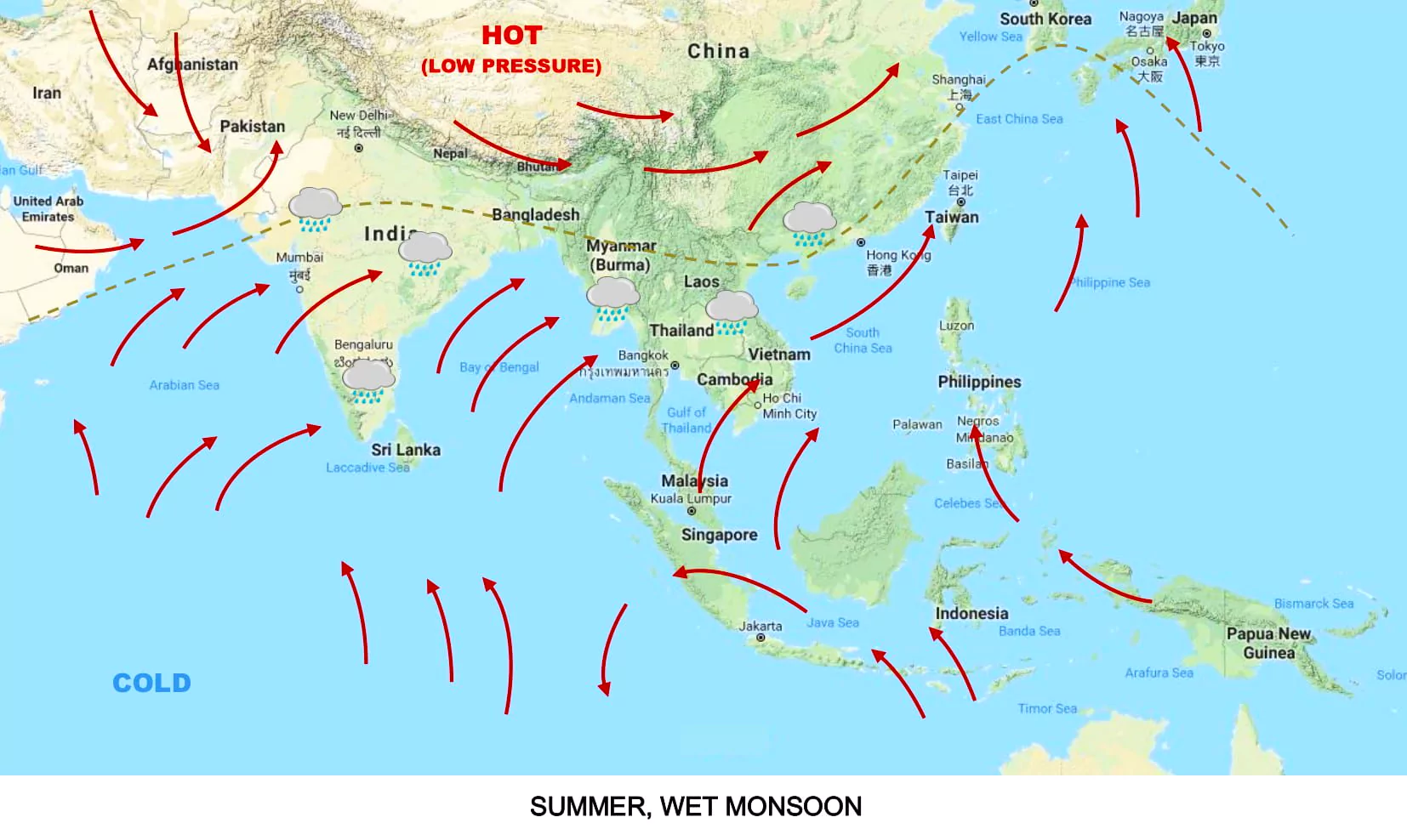
Recently, the first phase of the Atmospheric Research Testbed in Central India (ART-CI) was inaugurated in Sehore district in Bhopal.
Blue economy
|
|---|
News Source: Indianexpress
| Must Read | |
| NCERT Notes For UPSC | UPSC Daily Current Affairs |
| UPSC Blogs | UPSC Daily Editorials |
| Daily Current Affairs Quiz | Daily Main Answer Writing |
| UPSC Mains Previous Year Papers | UPSC Test Series 2024 |
The Union Health Secretary, introduced the National Action Plan for Prevention and Control of Snakebite Envenoming (NAP-SE) in India.

Snakebite envenoming
Snakebites cases in India
|
|---|
News Source: PIB
| Must Read | |
| NCERT Notes For UPSC | UPSC Daily Current Affairs |
| UPSC Blogs | UPSC Daily Editorials |
| Daily Current Affairs Quiz | Daily Main Answer Writing |
| UPSC Mains Previous Year Papers | UPSC Test Series 2024 |
Recently the Food and Agriculture Organization of the United Nations (FAO) and the Indian Council of Agricultural Research (ICAR) published the surveillance data of the Indian Network for Fishery and Animal Antimicrobial Resistance (INFAAR) for 2019-22.
| Isolates: a sample Collected for Anti-microbial Profiling. |
|---|
Multiple Drug Resistance (MDR):
|
|---|
Antimicrobial Resistance (AMR)
|
|---|
News Source: Down to Earth
| Must Read | |
| NCERT Notes For UPSC | UPSC Daily Current Affairs |
| UPSC Blogs | UPSC Daily Editorials |
| Daily Current Affairs Quiz | Daily Main Answer Writing |
| UPSC Mains Previous Year Papers | UPSC Test Series 2024 |
Archaeological Survey of India
|
|---|
News Source: PIB
| Must Read | |
| NCERT Notes For UPSC | UPSC Daily Current Affairs |
| UPSC Blogs | UPSC Daily Editorials |
| Daily Current Affairs Quiz | Daily Main Answer Writing |
| UPSC Mains Previous Year Papers | UPSC Test Series 2024 |
Recently, the Union Minister of State for Electronics and IT, Skill Development, Entrepreneurship inaugurated India’s first FutureLABS centre in C-DAC Thiruvananthapuram.
Centre for Development of Advanced Computing (C-DAC):
|
|---|
News Source: PIB
| Must Read | |
| NCERT Notes For UPSC | UPSC Daily Current Affairs |
| UPSC Blogs | UPSC Daily Editorials |
| Daily Current Affairs Quiz | Daily Main Answer Writing |
| UPSC Mains Previous Year Papers | UPSC Test Series 2024 |
Recently, the National Commission for Protection of Child Rights (NCPCR) celebrated its 19th Foundation Day.

Some Important Initiative by NCPCR:
|
|---|
News Source: PIB
| Must Read | |
| NCERT Notes For UPSC | UPSC Daily Current Affairs |
| UPSC Blogs | UPSC Daily Editorials |
| Daily Current Affairs Quiz | Daily Main Answer Writing |
| UPSC Mains Previous Year Papers | UPSC Test Series 2024 |
This Article is based on the news “PM witnesses ‘Bharat Shakti Exercise’ – a Tri-Services Firing and Manoeuvre Exercise in Pokhran, Rajasthan” which was published in the PIB. Recently, a tri-service military exercise “Bharat Shakti Exercise 2024” was held in Pokhran, Rajasthan.
About Pokhran:
|
|---|
It highlights the resilience, innovation, and strength of India’s domestic defense capabilities on the global stage towards realizing the idea of Aatmanirbharta in defense.
| Must Read | |
| NCERT Notes For UPSC | UPSC Daily Current Affairs |
| UPSC Blogs | UPSC Daily Editorials |
| Daily Current Affairs Quiz | Daily Main Answer Writing |
| UPSC Mains Previous Year Papers | UPSC Test Series 2024 |
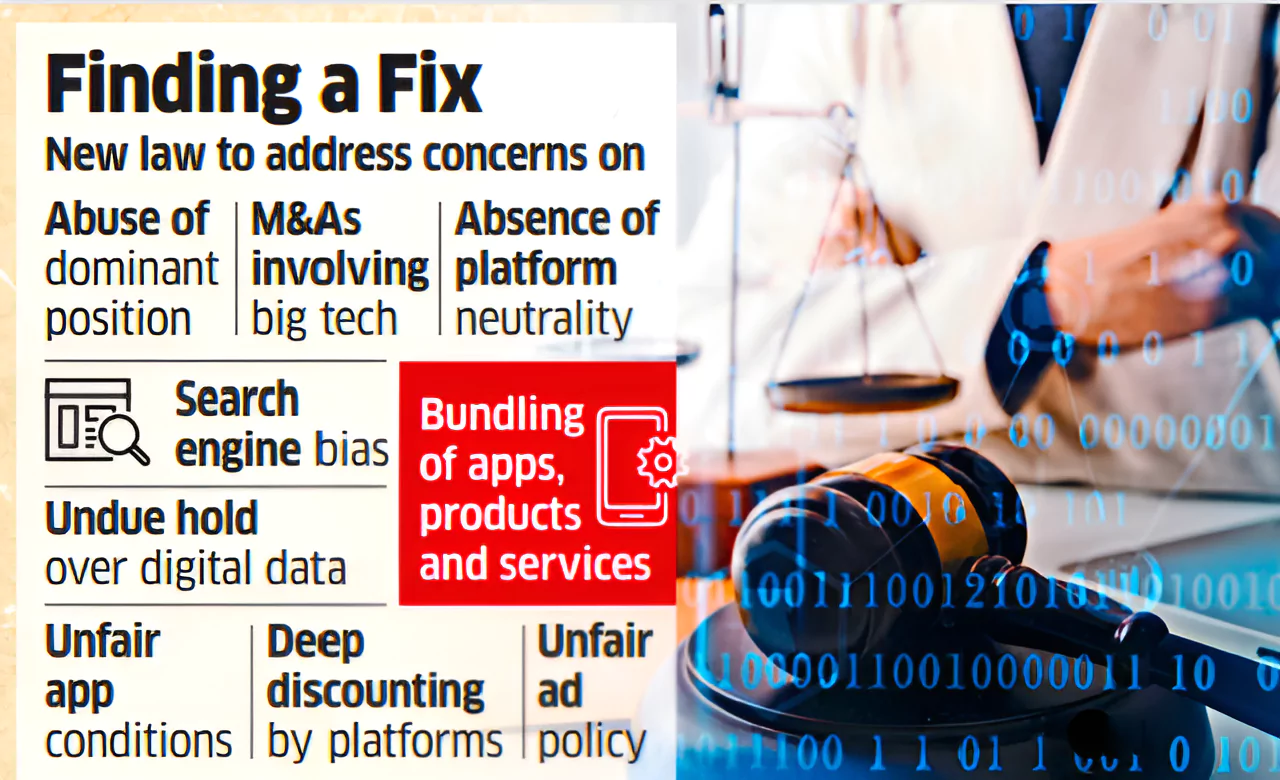
This Article is based on the news “Panel recommends law to regulate Big Tech firms” which was published in the Hindu. Recently, the Committee on Digital Competition Law (CDCL), formed by the Ministry of Corporate Affairs (MCA) last February, released its report, recommending legislation to regulate the market power of Big Tech firms like Google and Meta.
| Relevancy for Prelims: Information Technology, Competition Commission Of India (CCI), CCI Report On Iron Ore, and MCA Unveils The “Leniency Plus” Regime.
Relevancy for Mains: Recommendations by the Committee on Digital Competition Law (CDCL) On Regulating Big Tech Companies in India: Need, Significance, Challenges, and Way Forward. |
|---|

| The network effect is a business principle that illustrates the idea that when more people use a product or service, its value increases. |
|---|
About Competition Commission of India:
|
|---|
Such ex-ante regulation could potentially stifle innovation by imposing burdensome regulations on tech companies.
Ex-ante Provisions:
|
|---|
In the world of global diplomacy and technological advancements countries need to recognize the new dynamic of bargaining power between State and Big Tech firms and these big tech firms need to build efficient and effective compliance processes, addressing regulation at scale while keeping costs under control and maintaining the ability to innovate at pace.
| Must Read | |
| NCERT Notes For UPSC | UPSC Daily Current Affairs |
| UPSC Blogs | UPSC Daily Editorials |
| Daily Current Affairs Quiz | Daily Main Answer Writing |
| UPSC Mains Previous Year Papers | UPSC Test Series 2024 |
SC Verdict on Newsclick Shows Adherence to Due Pro...
Stay Invested: On Chabahar and India-Iran Relation...
Credit Rating Agencies, Impact on India’s De...
Catapulting Indian Biopharma Industry
Globalisation Under Threat, US Import Tariffs Have...
Global Report on Hypertension, Global Insights and...
<div class="new-fform">
</div>
