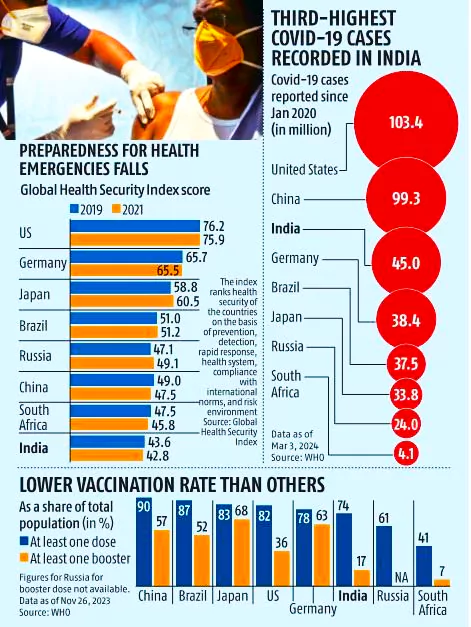
Recently, Asian Development Bank (ADB) released a report which highlighted the unpreparedness of nations across the world to tackle health emergencies even after the pandemic.
| Must Read | |
| NCERT Notes For UPSC | UPSC Daily Current Affairs |
| UPSC Blogs | UPSC Daily Editorials |
| Daily Current Affairs Quiz | Daily Main Answer Writing |
| UPSC Mains Previous Year Papers | UPSC Test Series 2024 |
Recently, Australia announced to contribute $3bn for construction of AUKUS nuclear powered submarines.

| Must Read | |
| NCERT Notes For UPSC | UPSC Daily Current Affairs |
| UPSC Blogs | UPSC Daily Editorials |
| Daily Current Affairs Quiz | Daily Main Answer Writing |
| UPSC Mains Previous Year Papers | UPSC Test Series 2024 |
According to the Ministry of Coal, there has been a reduction in the share of coal imports in the total coal consumption in the country.
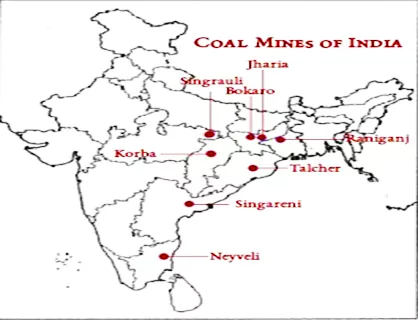 Gondwana coal, which is free from moisture and contains phosphorus and sulphur, makes up to 98% of the total coal reserves in India and 99% of the coal production in India.
Gondwana coal, which is free from moisture and contains phosphorus and sulphur, makes up to 98% of the total coal reserves in India and 99% of the coal production in India.
National Coal Index
|
|---|

With strategic focus on optimizing indigenous coal resources and leveraging innovative technological solutions, India continues its journey towards self-reliance or Atmanirbharta in energy security of the nation.
| Must Read | |
| NCERT Notes For UPSC | UPSC Daily Current Affairs |
| UPSC Blogs | UPSC Daily Editorials |
| Daily Current Affairs Quiz | Daily Main Answer Writing |
| UPSC Mains Previous Year Papers | UPSC Test Series 2024 |
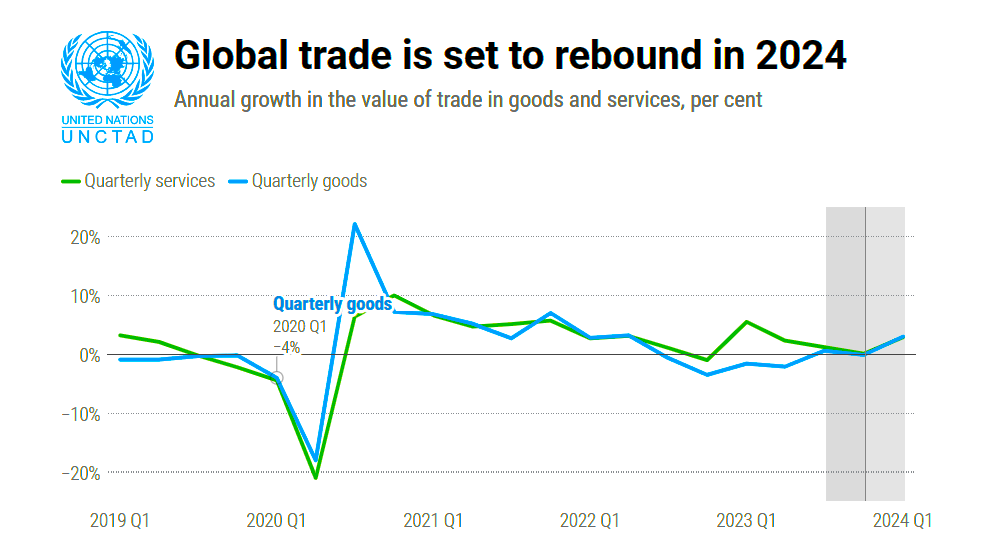
The United Nations Conference on Trade and Development (UNCTAD) predicts that global trade will improve in 2024.
| Positives | Negatives |
|
|
| Must Read | |
| NCERT Notes For UPSC | UPSC Daily Current Affairs |
| UPSC Blogs | UPSC Daily Editorials |
| Daily Current Affairs Quiz | Daily Main Answer Writing |
| UPSC Mains Previous Year Papers | UPSC Test Series 2024 |
India launched ‘Operation Indravati’ to evacuate its nationals from Haiti.
 There are between 75 and 90 Indians in Haiti and about 60 of them have registered with Indian authorities to return to India if need be.
There are between 75 and 90 Indians in Haiti and about 60 of them have registered with Indian authorities to return to India if need be.
| Must Read | |
| NCERT Notes For UPSC | UPSC Daily Current Affairs |
| UPSC Blogs | UPSC Daily Editorials |
| Daily Current Affairs Quiz | Daily Main Answer Writing |
| UPSC Mains Previous Year Papers | UPSC Test Series 2024 |
Recently, the principal bench of the National Green Tribunal (NGT) in New Delhi has initiated action on the Netravati Waterfront Promenade Development Project in Mangalore.
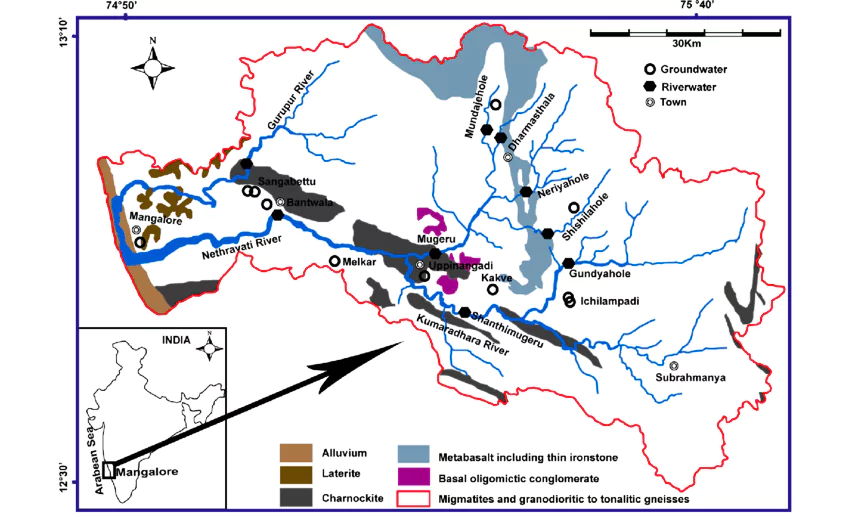
Waterfront Development
|
|---|
| Must Read | |
| NCERT Notes For UPSC | UPSC Daily Current Affairs |
| UPSC Blogs | UPSC Daily Editorials |
| Daily Current Affairs Quiz | Daily Main Answer Writing |
| UPSC Mains Previous Year Papers | UPSC Test Series 2024 |
In Iran, Baha’i Minority Faces Persecution Even After Death.
| Must Read | |
| NCERT Notes For UPSC | UPSC Daily Current Affairs |
| UPSC Blogs | UPSC Daily Editorials |
| Daily Current Affairs Quiz | Daily Main Answer Writing |
| UPSC Mains Previous Year Papers | UPSC Test Series 2024 |
Recently, the Zoological Survey of India published a book entitled, ‘An Illustrated Guide to the Lepidoptera of India’.
Lepidopterology
|
|---|
 Features:
Features:
| Must Read | |
| NCERT Notes For UPSC | UPSC Daily Current Affairs |
| UPSC Blogs | UPSC Daily Editorials |
| Daily Current Affairs Quiz | Daily Main Answer Writing |
| UPSC Mains Previous Year Papers | UPSC Test Series 2024 |
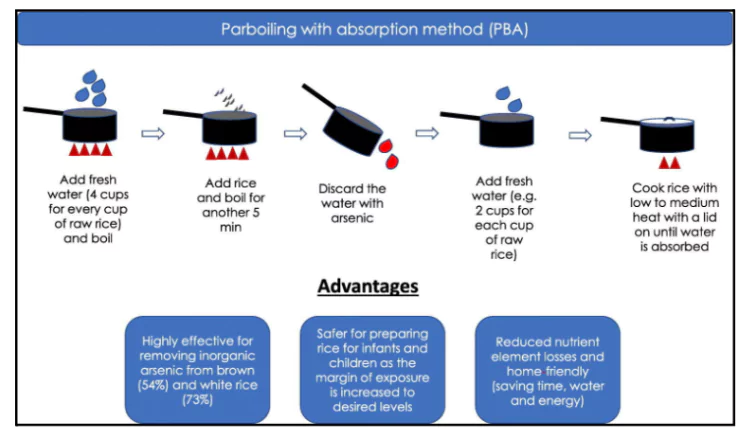
A recent study by the University of Sheffield has highlighted the risks of using water contaminated with arsenic to cook rice.

 Cancer (like skin, lung, bladder, and kidney cancer), heart diseases, and diabetes.
Cancer (like skin, lung, bladder, and kidney cancer), heart diseases, and diabetes.Monitoring Drinking Water Quality
|
|---|
| Must Read | |
| NCERT Notes For UPSC | UPSC Daily Current Affairs |
| UPSC Blogs | UPSC Daily Editorials |
| Daily Current Affairs Quiz | Daily Main Answer Writing |
| UPSC Mains Previous Year Papers | UPSC Test Series 2024 |
UNESCO led the development of the United Nations World Water Development Report 2024 on World Water Day (March 22, 2024).
| Relevancy for Prelims: World Water Day, State Of Global Water Resources Report 2022, Jal Jeevan Mission (JJM), Water Resources, Groundwater Crisis In Indian Cities, Water Conservation, How Can India Balance Its Water Demand And Supply?, and Pradhan Mantri Krishi Sinchayee Yojana (PMKSY).
Relevancy for Mains: United Nations World Water Development Report 2024: Key Highlights. |
|---|
World Water Day
|
|---|
Water-related mechanisms for Peace:
|
|---|
Concept of Water Diplomacy:
|
|---|
How Can Water be Used as a Tool for Peace?
|
|---|
To build resilience against climate change and to serve a growing population equitably and sustainably, an integrated and inclusive approach, centred on human rights, and based on sound, trusted data, must be taken to managing this finite resource.
| Must Read | |
| NCERT Notes For UPSC | UPSC Daily Current Affairs |
| UPSC Blogs | UPSC Daily Editorials |
| Daily Current Affairs Quiz | Daily Main Answer Writing |
| UPSC Mains Previous Year Papers | UPSC Test Series 2024 |
Recently, the Delhi Chief Minister was arrested by the Enforcement Directorate (ED) on charges of corruption and money laundering in the formulation and execution of the Delhi government’s excise policy for 2021-22, which was later scrapped.
| Relevancy for Prelims: Money Laundering, Questionable Searches Under The Money Laundering Act, Enforcement Directorate (ED), and Enforcement Directorate-States Tussle.
Relevancy for Mains: Issues Related to Corruption in India. |
|---|
Judicial Custody
|
|---|
| Earlier Such Cases
In February 2024, Jharkhand Mukti Morcha (JMM) leader and then CM Hemant Soren was arrested by the ED in a money-laundering case. Soren resigned as CM after his arrest, and Seraikela MLA Champai Soren replaced him. Similarly, in 2001, Tamil Nadu CM J Jayalalithaa was arrested in a disproportionate assets case, and O Paneerselvam replaced her till she obtained bail. This was repeated in 2014, when she was convicted and charged in the same case. Paneerselvam resigned in both 2001 and 2014 after she obtained bail and a stay of her conviction, respectively. |
|---|
About the S. Ramachandran versus V. Senthil Balaji Case
|
|---|
Role of Lieutenant Governor (LG)- A Unique Scheme for Delhi:
|
|---|
About Delhi Excise Policy 2021-22
|
| Must Read | |
| NCERT Notes For UPSC | UPSC Daily Current Affairs |
| UPSC Blogs | UPSC Daily Editorials |
| Daily Current Affairs Quiz | Daily Main Answer Writing |
| UPSC Mains Previous Year Papers | UPSC Test Series 2024 |
<div class="new-fform">
</div>
