Recently, The Federal Communications Commission of USA voted to reinstate Net Neutrality regulations.
Net Neutrality Regulations were first introduced under the Obama administration in 2015, but were repealed under President Donald J. Trump in 2017.
 Origin: It term was coined by Columbia University law professor Tim Wu in his 2003 paper titled “Network Neutrality, Broadband Discrimination”.
Origin: It term was coined by Columbia University law professor Tim Wu in his 2003 paper titled “Network Neutrality, Broadband Discrimination”.

Net Neutrality in IndiaIndia Prohibits differential pricing and explicitly upholds net neutrality with the strongest net neutrality regulations in the world, however there is no legislation or net neutrality yet.
|
|---|
| Must Read | |
| NCERT Notes For UPSC | UPSC Daily Current Affairs |
| UPSC Blogs | UPSC Daily Editorials |
| Daily Current Affairs Quiz | Daily Main Answer Writing |
| UPSC Mains Previous Year Papers | UPSC Test Series 2024 |
The Commonwealth Secretariat has recognized Centralised Public Grievance Redress and Monitoring System (CPGRAMS) of India as a best practice in Commonwealth Secretaries of Public Service meeting held at Marlborough House, London.
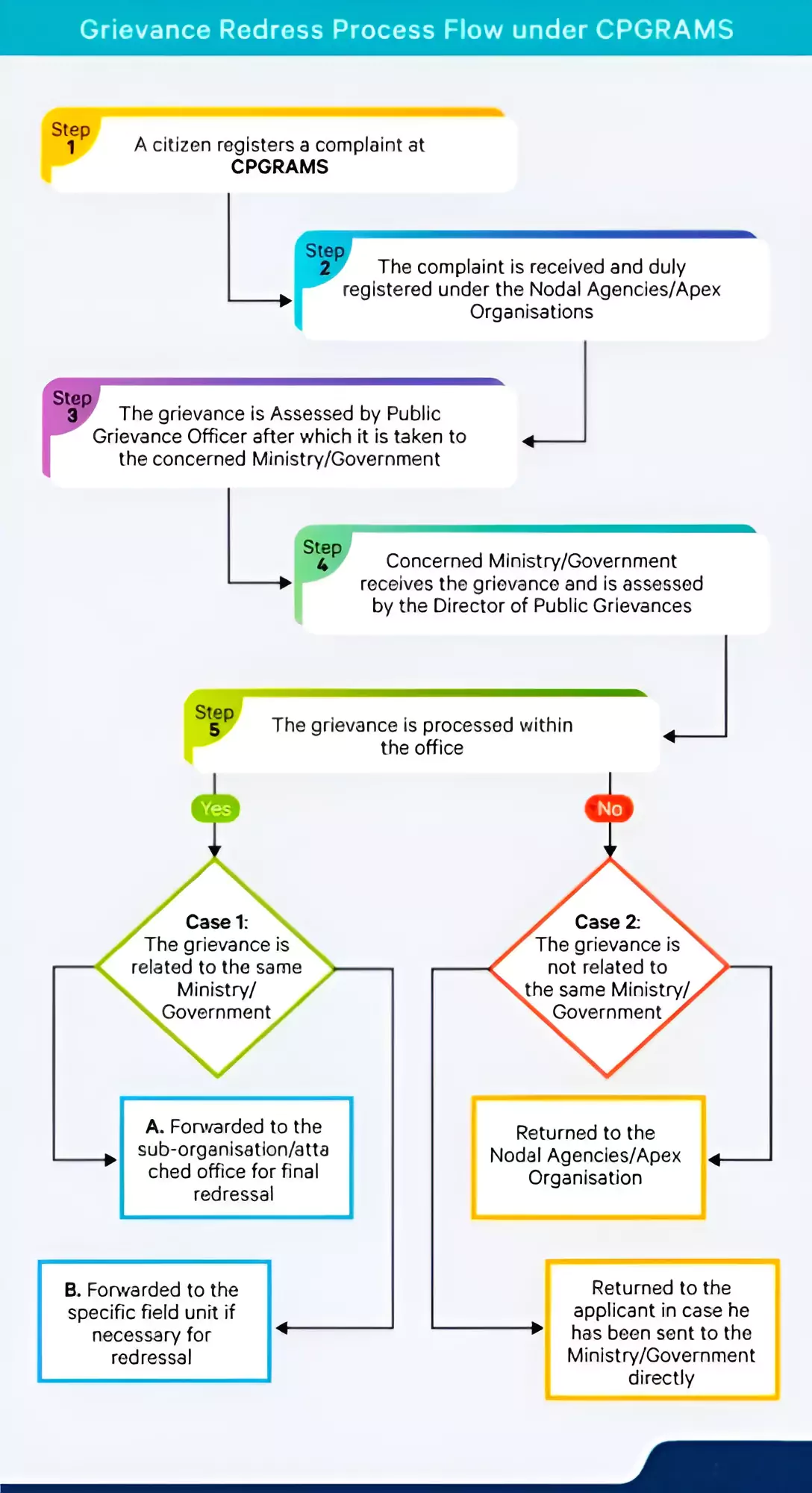 A stocktaking exercise: To conduct a stock taking exercise on the status of smart governance within the Commonwealth countries and to identify both the success stories as well as the gaps/demand for digital services.
A stocktaking exercise: To conduct a stock taking exercise on the status of smart governance within the Commonwealth countries and to identify both the success stories as well as the gaps/demand for digital services.
The CommonwealthThe Commonwealth is often described as a ‘family’ of nations. It is one of the world’s oldest political associations of states (beginning 1887) with roots in the British Empire.
|
|---|
| Must Read | |
| NCERT Notes For UPSC | UPSC Daily Current Affairs |
| UPSC Blogs | UPSC Daily Editorials |
| Daily Current Affairs Quiz | Daily Main Answer Writing |
| UPSC Mains Previous Year Papers | UPSC Test Series 2024 |
The Tamil Nadu government is considering denotifying a significant portion of the Pulicat bird sanctuary.

| Must Read | |
| NCERT Notes For UPSC | UPSC Daily Current Affairs |
| UPSC Blogs | UPSC Daily Editorials |
| Daily Current Affairs Quiz | Daily Main Answer Writing |
| UPSC Mains Previous Year Papers | UPSC Test Series 2024 |
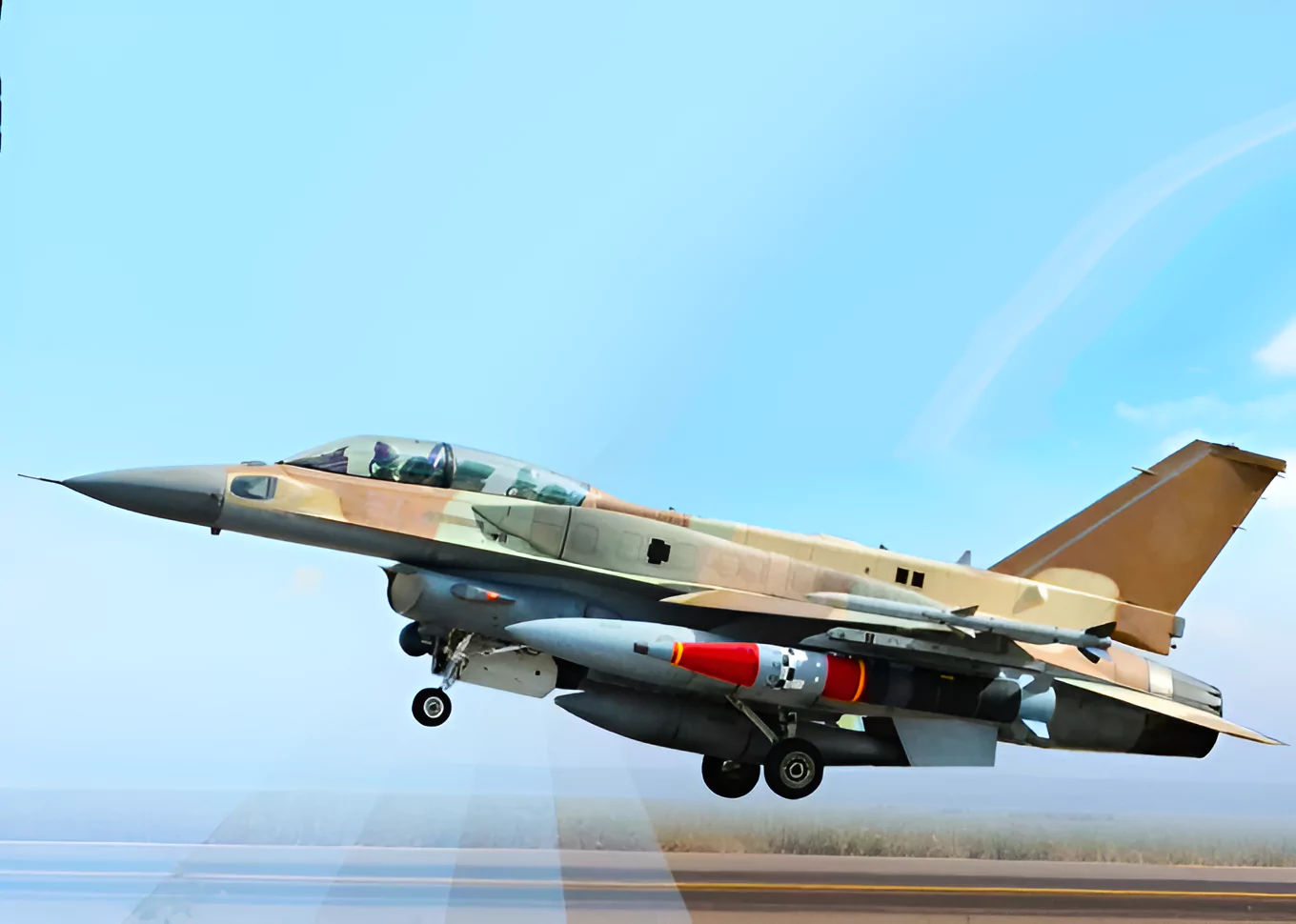

Recently, under the aegis of Strategic Forces Command a new version of Medium-Range Ballistic Missile successfully launched in the Andaman and Nicobar Islands.
Crystal Maze 2 is an extended stand-off range air-to-surface ballistic missile of Israeli origin, also known as ROCKS.
|
|---|
Significance for India: The Indian Air Force (IAF) has successfully conducted tests on this missile and aims to procure it in large numbers under the Make in India initiative. This move highlights India’s dedication to achieving self-sufficiency in defense manufacturing.
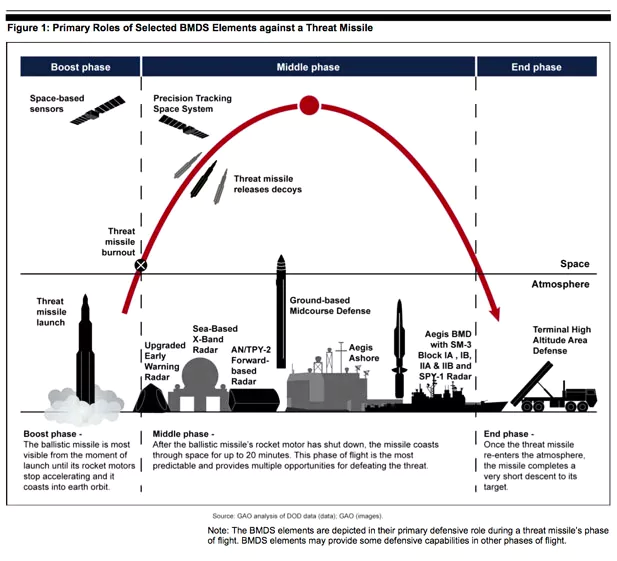
Strategic Forces Command (SFC):
|
|---|
| Must Read | |
| NCERT Notes For UPSC | UPSC Daily Current Affairs |
| UPSC Blogs | UPSC Daily Editorials |
| Daily Current Affairs Quiz | Daily Main Answer Writing |
| UPSC Mains Previous Year Papers | UPSC Test Series 2024 |
Bhutan’s government is organizing the Sustainable Finance for Tiger Landscapes Conference on Earth Day 2024.
 They also aim to mobilize sustainable financing for biodiversity conservation and utilization.
They also aim to mobilize sustainable financing for biodiversity conservation and utilization.Tigers are the largest wild cat species in the world.
Indian government Initiatives to Conserve Tigers
|
|---|
| Must Read | |
| NCERT Notes For UPSC | UPSC Daily Current Affairs |
| UPSC Blogs | UPSC Daily Editorials |
| Daily Current Affairs Quiz | Daily Main Answer Writing |
| UPSC Mains Previous Year Papers | UPSC Test Series 2024 |
A few days after Meta unveiled its Llama 3 Large Language Model (LLM), Microsoft unveiled the latest version of its ‘lightweight’ AI model – the Phi-3-Mini.
| Must Read | |
| NCERT Notes For UPSC | UPSC Daily Current Affairs |
| UPSC Blogs | UPSC Daily Editorials |
| Daily Current Affairs Quiz | Daily Main Answer Writing |
| UPSC Mains Previous Year Papers | UPSC Test Series 2024 |
Recently, the Embassy of Israel in India, in collaboration with a non-profit entity, has officially joined the ‘Million Miyawaki’ project as part of Earth Day celebrations.
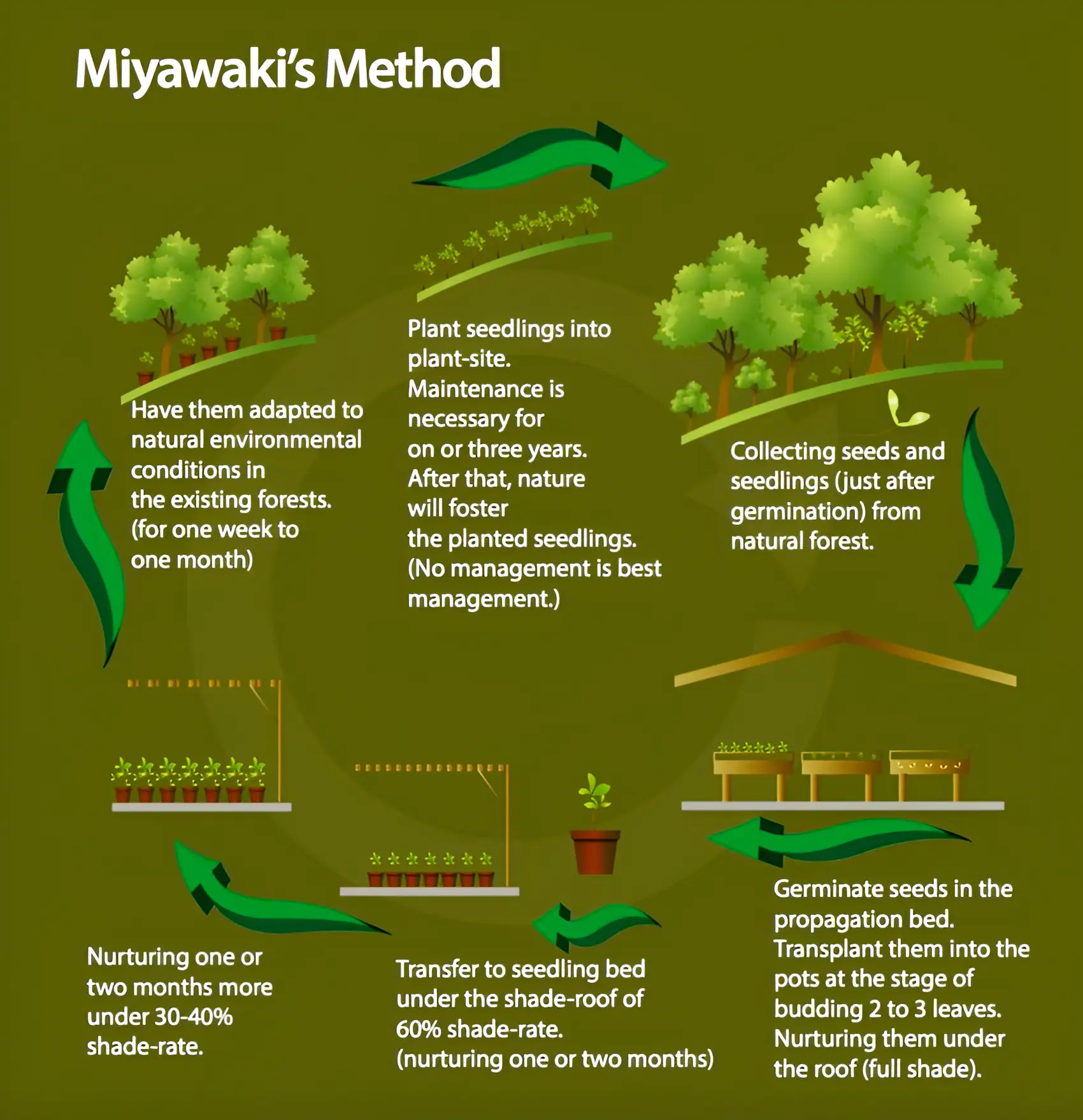
| Must Read | |
| NCERT Notes For UPSC | UPSC Daily Current Affairs |
| UPSC Blogs | UPSC Daily Editorials |
| Daily Current Affairs Quiz | Daily Main Answer Writing |
| UPSC Mains Previous Year Papers | UPSC Test Series 2024 |
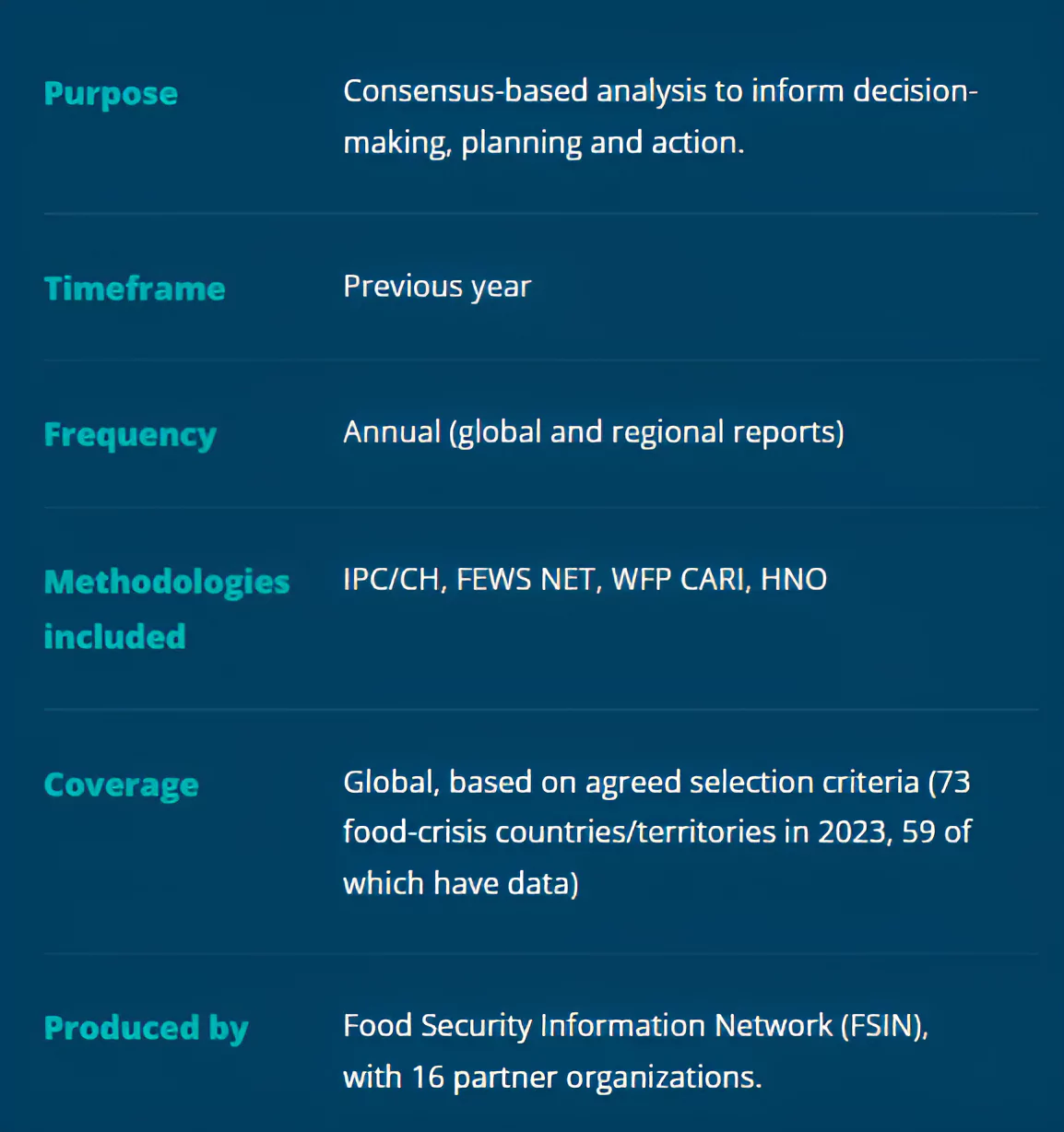
Recently, the 2024 Global Report on Food Crisis (GRFC) has been launched by the Global Network Against Food Crises.
| Relevance For Prelims: Food Security, Nutritional Security In India, India’s Food & Nutrition Security, Global Hunger Index 2023, Food Waste Index Report 2024 By UNEP, State Food Safety Index (SFSI) 2023, and Recent Food Inflation In India.
Relevance For Mains: Global Food Crisis: Status, Key Components, Challenges, Initiatives, and Way Forward. |
|---|
The Global Report on Food Crisis (GRFC) is the reference document for a comprehensive analysis of global, regional and country-level acute food insecurity.

Food Security Information Network:
Global Report on Food Crisis (GRFC):
Integrated Food Security Phase Classification (IPC):
|
|---|

Rise in Acute Food Insecurity: Overall, 1 in 5 people assessed were in need of critical urgent action.
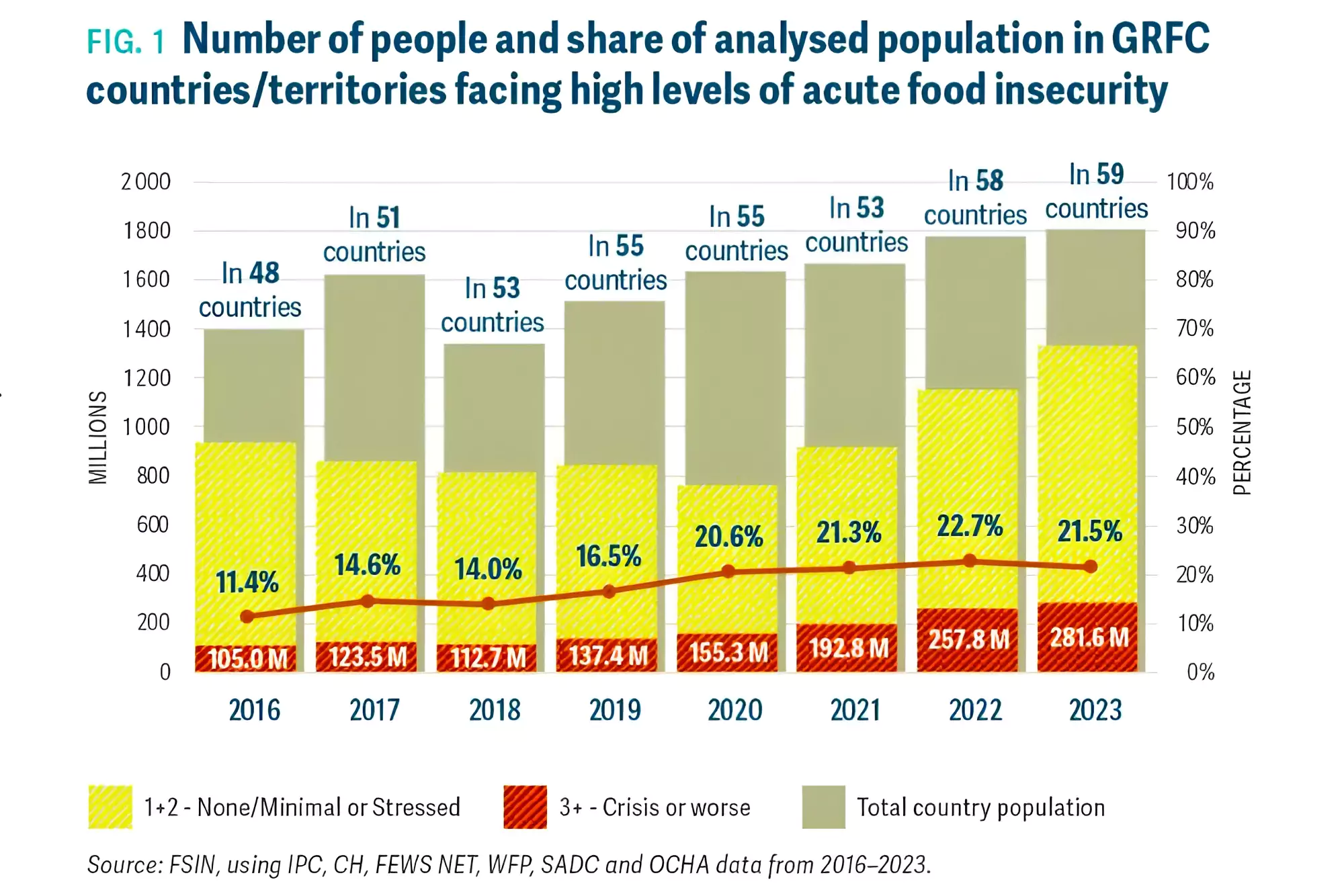 Year-on-year Increase: It was mainly explained by increased analysis coverage, as well as deterioration in some countries / territories outweighing improvements in others.
Year-on-year Increase: It was mainly explained by increased analysis coverage, as well as deterioration in some countries / territories outweighing improvements in others.
 Interconnection between Displacement & Acute Food Insecurity: In both Sudan and Gaza, the number of forcibly displaced people reached 90 million in the 59 countries, the highest in eight years of GRFC reporting, highlighting the high correlation between displacement and acute food insecurity.
Interconnection between Displacement & Acute Food Insecurity: In both Sudan and Gaza, the number of forcibly displaced people reached 90 million in the 59 countries, the highest in eight years of GRFC reporting, highlighting the high correlation between displacement and acute food insecurity.
Food SecurityWorld Food Summit of 1996: It defined food security as “when all people, at all times, have physical and economic access to sufficient, safe and nutritious food that meets their dietary needs and food preferences for an active, and healthy life”.
|
|---|
Intensifying conflict and insecurity, the impacts of economic shocks, and the effects of extreme weather events are accelerating the acute food insecurity.
Key Drivers of Food Crises |
Impact Observed |
| Conflict/Insecurity |
|
| Extreme Weather Events |
|
| Economic Shocks |
|
| Mains Question: Discuss the consequences of climate change on the food security in tropical countries. (150 words, 10 Marks) |
|---|
| Must Read | |
| NCERT Notes For UPSC | UPSC Daily Current Affairs |
| UPSC Blogs | UPSC Daily Editorials |
| Daily Current Affairs Quiz | Daily Main Answer Writing |
| UPSC Mains Previous Year Papers | UPSC Test Series 2024 |
<div class="new-fform">
</div>
