Recently, the Centre has issued few directions to the states with regard to NOTTO (National Organ and Tissue Transplantation Organisation).
About National Organ and Tissue Transplant Organization (NOTTO)
|
|---|
| Must Read | |
| NCERT Notes For UPSC | UPSC Daily Current Affairs |
| UPSC Blogs | UPSC Daily Editorials |
| Daily Current Affairs Quiz | Daily Main Answer Writing |
| UPSC Mains Previous Year Papers | UPSC Test Series 2024 |
A Patient Safety Rights Charter was launched by WHO at the Global Ministerial Summit on Patient Safety.
The Sixth Global Ministerial Summit on Patient Safety:
|
|---|
National Patient Safety Implementation Framework 2018-2025
|
|---|
The 10 Fundamental Patient Safety Rights:
|
| Must Read | |
| NCERT Notes For UPSC | UPSC Daily Current Affairs |
| UPSC Blogs | UPSC Daily Editorials |
| Daily Current Affairs Quiz | Daily Main Answer Writing |
| UPSC Mains Previous Year Papers | UPSC Test Series 2024 |
The Union government has approved a policy to promote India as a manufacturing hub for electric vehicles (EVs)
About Electric Vehicle
|
|---|
| Must Read | |
| NCERT Notes For UPSC | UPSC Daily Current Affairs |
| UPSC Blogs | UPSC Daily Editorials |
| Daily Current Affairs Quiz | Daily Main Answer Writing |
| UPSC Mains Previous Year Papers | UPSC Test Series 2024 |
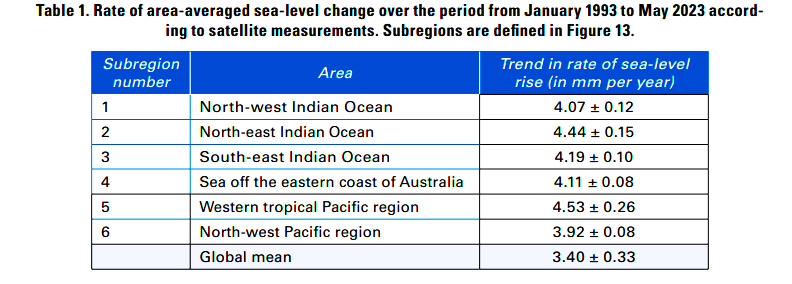
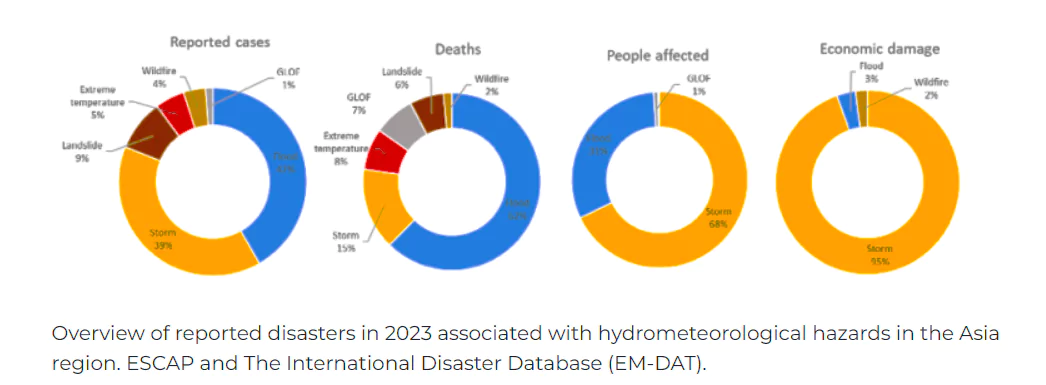
Recently, World Meteorological Organization’s (WMO) has published the report “State of the Climate in Asia 2023”.
| Must Read | |
| NCERT Notes For UPSC | UPSC Daily Current Affairs |
| UPSC Blogs | UPSC Daily Editorials |
| Daily Current Affairs Quiz | Daily Main Answer Writing |
| UPSC Mains Previous Year Papers | UPSC Test Series 2024 |
Recently, C-DOT, the premier Telecom R&D Centre of the Department of Telecommunications (DoT), Government of India and Indian Institute of Technology, Jodhpur (IIT-J) signed an agreement for “Automated Service Management in 5G and Beyond Networks Using Artificial Intelligence”.
About 5G Network
About Network Slicing
About Telecom Technology Development Fund (TTDF) Scheme
|
|---|
| Must Read | |
| NCERT Notes For UPSC | UPSC Daily Current Affairs |
| UPSC Blogs | UPSC Daily Editorials |
| Daily Current Affairs Quiz | Daily Main Answer Writing |
| UPSC Mains Previous Year Papers | UPSC Test Series 2024 |
The World Crafts Council International (WCCI), has selected Srinagar, the picturesque city in Kashmir, for mapping its craft clusters.
 This registration status signifies its non-profit nature and international scope of operations.
This registration status signifies its non-profit nature and international scope of operations.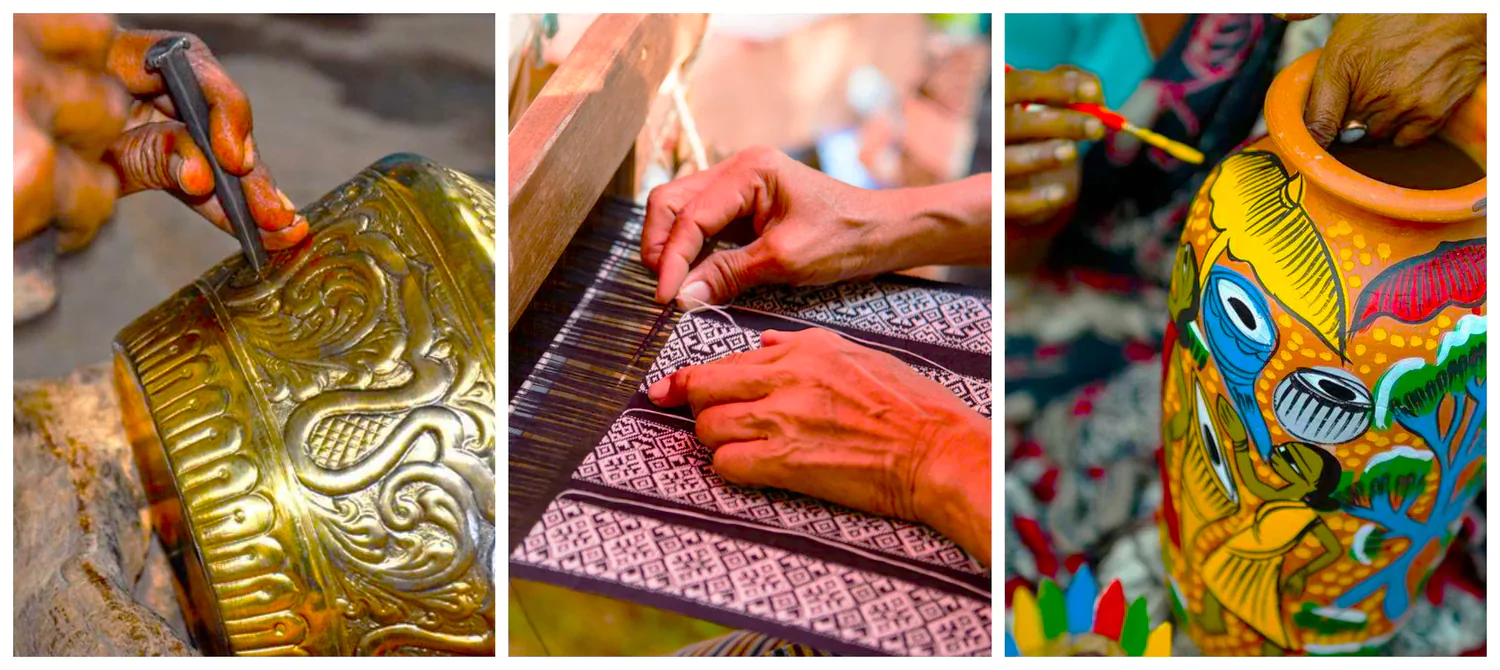 These craftsmen contribute approximately 1.76% to the total workforce of the area.
These craftsmen contribute approximately 1.76% to the total workforce of the area.
| Must Read | |
| NCERT Notes For UPSC | UPSC Daily Current Affairs |
| UPSC Blogs | UPSC Daily Editorials |
| Daily Current Affairs Quiz | Daily Main Answer Writing |
| UPSC Mains Previous Year Papers | UPSC Test Series 2024 |
The Insurance Regulatory and Development Authority of India (IRDAI) has relaxed the restriction on applying for health insurance in India that allowed only individuals aged 65 and lower to purchase health covers.
| Must Read | |
| NCERT Notes For UPSC | UPSC Daily Current Affairs |
| UPSC Blogs | UPSC Daily Editorials |
| Daily Current Affairs Quiz | Daily Main Answer Writing |
| UPSC Mains Previous Year Papers | UPSC Test Series 2024 |
Recently, Bombay High Court in its verdict dismissed a suit challenging Syedna Mufaddal Saifuddin’s position as the 53rd religious leader of Dawoodi Bohra Community.
Power to excommunicate
|
|---|
Through Nass ( Conferment of Succession)
| Must Read | |
| NCERT Notes For UPSC | UPSC Daily Current Affairs |
| UPSC Blogs | UPSC Daily Editorials |
| Daily Current Affairs Quiz | Daily Main Answer Writing |
| UPSC Mains Previous Year Papers | UPSC Test Series 2024 |
Recently, Global leaders gathered (from 23 April-29 April 2024) in Ottawa, Canada for the 4th Session of Intergovernmental Negotiating Committee (INC) to discuss progress in drafting a first-ever global plastic treaty.

With Respect to restrictions and phase-outs, reuse policies, product design requirements, extended producer responsibility, and waste management etc
To rein in soaring plastic pollution by the end of the year. It could be the most significant deal relating to climate-warming emissions and environmental protection since the 2015 Paris Agreement, which got 195 parties to agree to keep global temperatures from rising beyond 1.5C.
| Must Read | |
| NCERT Notes For UPSC | UPSC Daily Current Affairs |
| UPSC Blogs | UPSC Daily Editorials |
| Daily Current Affairs Quiz | Daily Main Answer Writing |
| UPSC Mains Previous Year Papers | UPSC Test Series 2024 |
The National Human Rights Commission(NHRC) India organized the Statutory Full Commission meeting of all the seven National Commissions for ensuring the protection of Human Rights.
| Relevance For Prelims: Rights: Freedom, Responsibilities, And Human Dignity, Fundamental Rights (Article 12-35) , and National/State Human Rights Commission (NHRC).
Relevance For Mains: Human Rights Abuse in India: Status, Challenges, Initiatives, and Way Forward |
|---|
National Human Rights Commission (NHRC):
|
|---|
| Human Rights Report (HRR): The report, released by U.S. Secretary of State Anthony Blinken covers all countries receiving U.S. assistance and all UN member states, and assesses human rights practices as per the norms set forth in the Universal Declaration of Human Rights and other international agreements. |
|---|
| SC/ST Act, 1989: It aims to protect the marginalised communities against discrimination and atrocities. |
|---|
| Must Read | |
| NCERT Notes For UPSC | UPSC Daily Current Affairs |
| UPSC Blogs | UPSC Daily Editorials |
| Daily Current Affairs Quiz | Daily Main Answer Writing |
| UPSC Mains Previous Year Papers | UPSC Test Series 2024 |
<div class="new-fform">
</div>
