Recently, Influenza A H5N1 was detected in dairy cows in six States in the U.S.
| Must Read | |
| NCERT Notes For UPSC | UPSC Daily Current Affairs |
| UPSC Blogs | UPSC Daily Editorials |
| Daily Current Affairs Quiz | Daily Main Answer Writing |
| UPSC Mains Previous Year Papers | UPSC Test Series 2024 |
The Department of Archaeology and Museums has unearthed a coin hoard at the Phanigiri Buddhist site in the Suryapet district (Telangana).
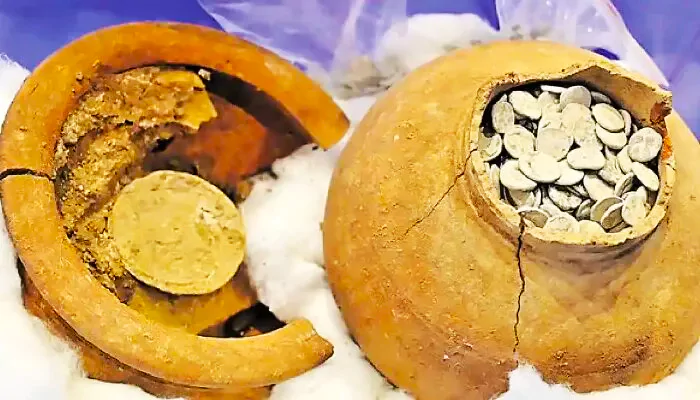

What are Toranas?
|
|---|
Vardhamanukota, Gajula Banda, Tirumalagiri, Nagaram, Singaram, Aravapalli, Ayyavaripalli, Arlagaddagudem, and Yeleswaram.
| Must Read | |
| NCERT Notes For UPSC | UPSC Daily Current Affairs |
| UPSC Blogs | UPSC Daily Editorials |
| Daily Current Affairs Quiz | Daily Main Answer Writing |
| UPSC Mains Previous Year Papers | UPSC Test Series 2024 |
According to the India TB Report 2024, 79% of presumptive TB testing was still carried out using 100-year-old sputum smear microscopy and just 21% of cases were detected using a molecular test.
| Presumptive TB refers to a patient presenting symptoms or signs suggestive of TB (previously known as a TB suspect). |
|---|
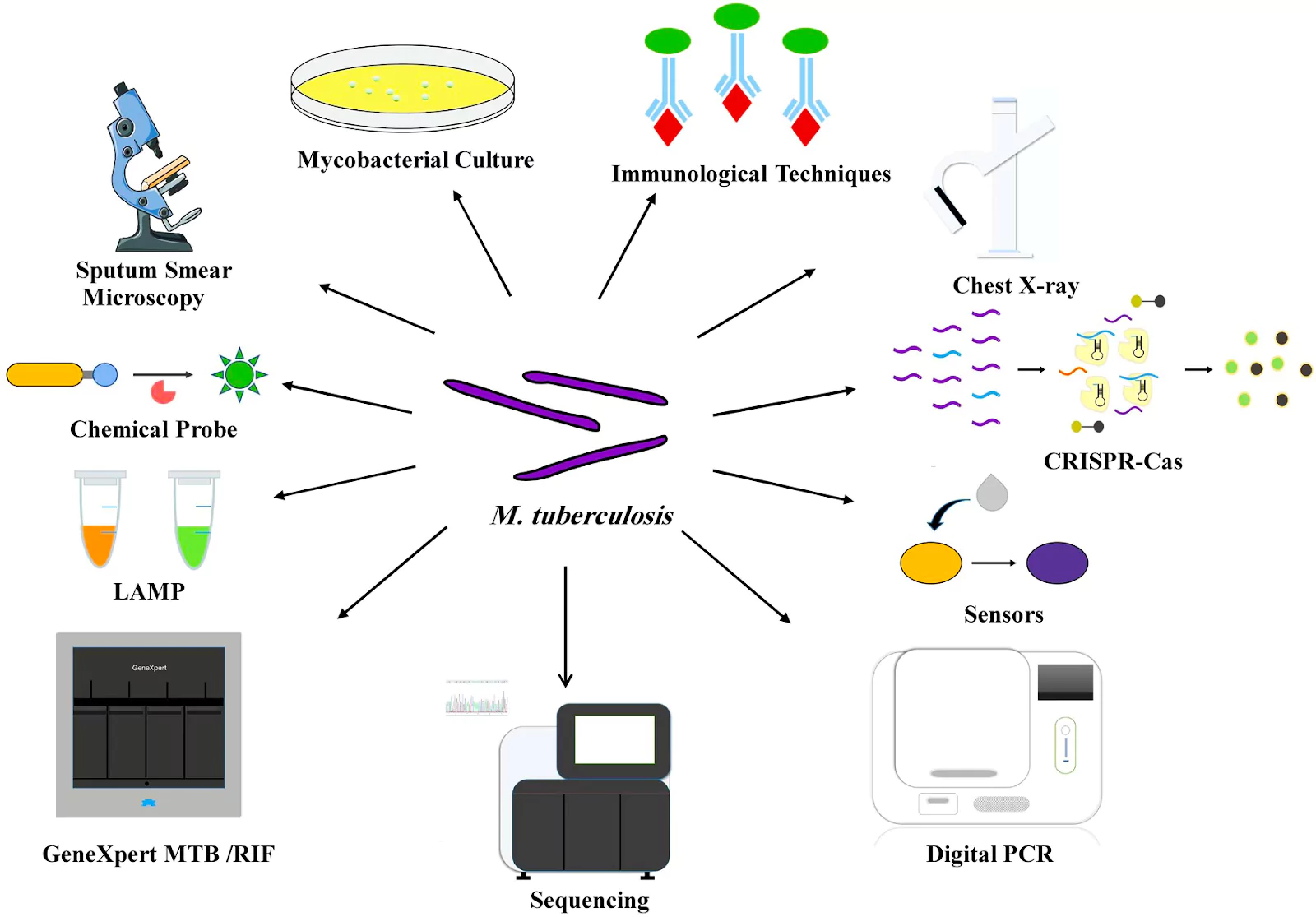 Hence, it has been an integral part of the global strategy for TB control.
Hence, it has been an integral part of the global strategy for TB control.
| Must Read | |
| NCERT Notes For UPSC | UPSC Daily Current Affairs |
| UPSC Blogs | UPSC Daily Editorials |
| Daily Current Affairs Quiz | Daily Main Answer Writing |
| UPSC Mains Previous Year Papers | UPSC Test Series 2024 |
Parcels of degraded forest land close to 3,853 hectares have been identified by 10 states to be made available to earn and potentially trade green credits.
What are Green Credits?
The Green Credits are Categorised into Eight key Areas:
|
|---|
Compensatory Afforestation Law
|
|---|
| Must Read | |
| NCERT Notes For UPSC | UPSC Daily Current Affairs |
| UPSC Blogs | UPSC Daily Editorials |
| Daily Current Affairs Quiz | Daily Main Answer Writing |
| UPSC Mains Previous Year Papers | UPSC Test Series 2024 |
India has emerged as the world’s fastest growing major economy in 2023, according to the United Nations.
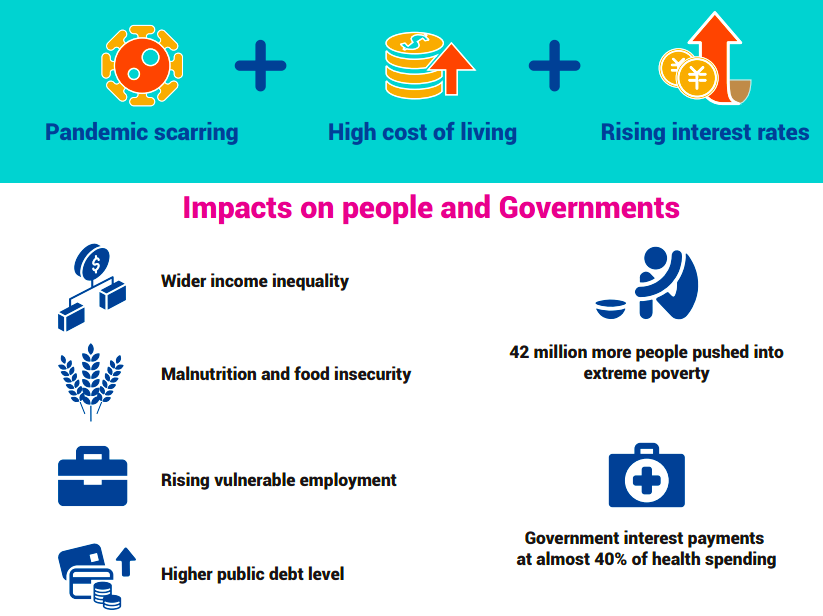 This happened at a time when food prices were already high due to weather issues caused by El Nino.
This happened at a time when food prices were already high due to weather issues caused by El Nino.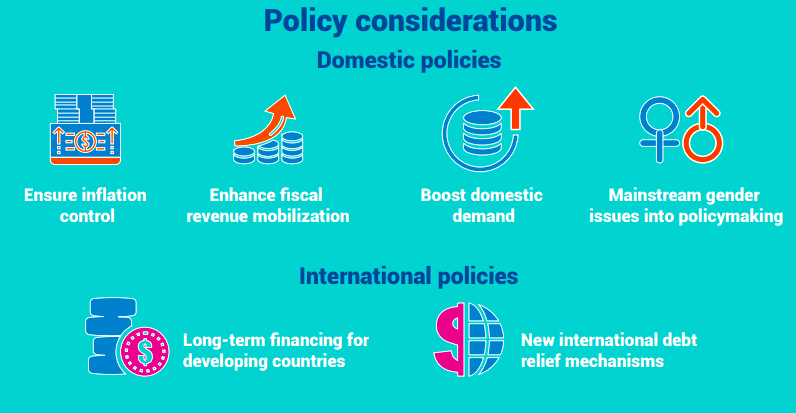
 ESCAP analysis: According to this analysis, there is a need to manage sustained macroeconomic and inflation stability, strong fiscal positions and financial market liquidity as these are crucial in keeping low borrowing rates.
ESCAP analysis: According to this analysis, there is a need to manage sustained macroeconomic and inflation stability, strong fiscal positions and financial market liquidity as these are crucial in keeping low borrowing rates. India has various challenges to face
| Must Read | |
| NCERT Notes For UPSC | UPSC Daily Current Affairs |
| UPSC Blogs | UPSC Daily Editorials |
| Daily Current Affairs Quiz | Daily Main Answer Writing |
| UPSC Mains Previous Year Papers | UPSC Test Series 2024 |
Nepal’s parliament has approved the BIMSTEC regional grouping’s charter.
 BIMSTEC charter can only be enforced after its endorsement by Parliament of a particular country.
BIMSTEC charter can only be enforced after its endorsement by Parliament of a particular country.
| Must Read | |
| NCERT Notes For UPSC | UPSC Daily Current Affairs |
| UPSC Blogs | UPSC Daily Editorials |
| Daily Current Affairs Quiz | Daily Main Answer Writing |
| UPSC Mains Previous Year Papers | UPSC Test Series 2024 |
The Institute for Human Development and the International Labour Organization (ILO) recently released the India Employment Report 2024.
Labour force Participation Rate:
|
|---|
| Must Read | |
| NCERT Notes For UPSC | UPSC Daily Current Affairs |
| UPSC Blogs | UPSC Daily Editorials |
| Daily Current Affairs Quiz | Daily Main Answer Writing |
| UPSC Mains Previous Year Papers | UPSC Test Series 2024 |
The United Nations Human Rights Council (UNHRC) has passed a resolution to protect the rights of intersex individuals.

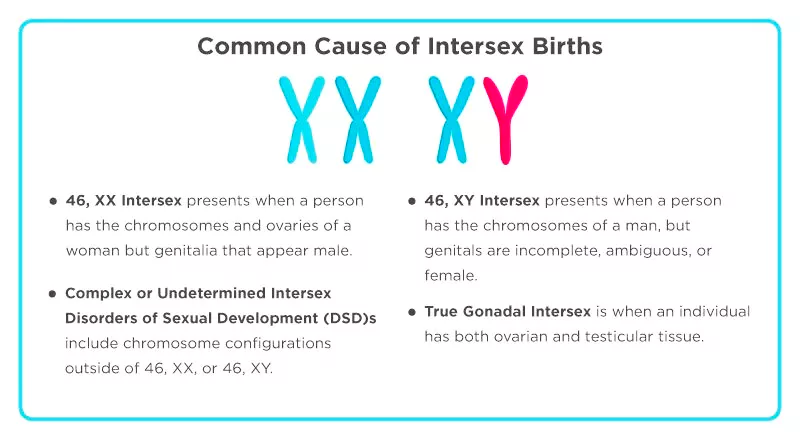 Currently, 1.7% of newborns are intersex.
Currently, 1.7% of newborns are intersex.
Intersex Rights Movement in India
Intersex Asia:
|
|---|
| Must Read | |
| NCERT Notes For UPSC | UPSC Daily Current Affairs |
| UPSC Blogs | UPSC Daily Editorials |
| Daily Current Affairs Quiz | Daily Main Answer Writing |
| UPSC Mains Previous Year Papers | UPSC Test Series 2024 |
Marine researchers along the Visakhapatnam coastline in Andhra Pradesh reported an occurrence of a bloom of venomous jellyfish.
 Common Names: mauve stinger or purple-striped jellyfish
Common Names: mauve stinger or purple-striped jellyfish| Factor affecting Jellyfish blooms | Explanation |
| Natural Cycles | Jellyfish populations naturally fluctuate. Blooms can occur due to these variations. |
| Ocean Temperature Rise | Warmer waters can be ideal for jellyfish reproduction and growth, increasing their populations. |
| Eutrophication | Excess nutrients from runoff can lead to plankton blooms, which jellyfish feed on. This can indirectly boost jellyfish numbers. |
| Overfishing | Overfishing of natural predators of jellyfish can lead to a decrease in those populations, allowing jellyfish to thrive without competition. |
| Habitat Modification | Coastal development and changes in water flow can disrupt ecosystems, favoring jellyfish over other species. |
| Must Read | |
| NCERT Notes For UPSC | UPSC Daily Current Affairs |
| UPSC Blogs | UPSC Daily Editorials |
| Daily Current Affairs Quiz | Daily Main Answer Writing |
| UPSC Mains Previous Year Papers | UPSC Test Series 2024 |
World Health Day which is observed every year on April 7 emphasizing on the issue of health equity for global health and justice.
| Relevance For Prelims: World Health Day 2024, Health, DISEASES, Role Of Government In Health, ADB Report On Health Emergency Preparedness, The Impact Of Climate Change On Health, Global Initiative On Digital Health (GIDH), and India’s Health Care Journey.
Relevance For Mains: Health Equity in India: Significance, Challenges, Government Initiatives, and Way Forward. |
|---|
Interlinkage of Health and Development
|
|---|
Constitutional Provision: The Directive Principles of State Policy in Part IV of the Constitution provides a basis for the right to health.
|
|---|
| National Health Policy 2017:It articulates “the attainment of the highest possible level of good health and well-being, and universal access to good quality health care services without anyone having to face financial hardship as a consequence” as its goal, which aligns with the UHC target. |
|---|
Role of Private Sector in Health Equity:
|
|---|
Global Best Practices:
|
|---|
Prioritising good health and well-being is critical for achieving sustainable development goals at both the local and global levels. It not only improves the quality of life for individuals but also contributes to creating more equitable, resilient, and sustainable communities. In an interconnected world, it is essential to recognise the importance of global collaboration in healthcare. With the collective knowledge, resources, and best practices of various nations, we can achieve a sustainable future for all.
| Prelims PYQ (2023):
Consider the following statements: Statement-I: India’s public sector health care system largely focuses on curative care with limited preventive, promotive and rehabilitative care. Statement-II: Under India’s decentralized approach to health care delivery, the States are primarily responsible for organizing health services. Which one of the following is correct in respect of the above statements? (a) Both Statement-I and Statement-II are correct and StatementII is the correct explanation for Statement-I (b) Both Statement-I and Statement-II are correct and StatementII is not the correct explanation for Statement-I (c) Statement-I is correct but StatementII is incorrect (d) Statement-I is incorrect but Statement-II is correct Ans: (b) |
|---|
| Must Read | |
| NCERT Notes For UPSC | UPSC Daily Current Affairs |
| UPSC Blogs | UPSC Daily Editorials |
| Daily Current Affairs Quiz | Daily Main Answer Writing |
| UPSC Mains Previous Year Papers | UPSC Test Series 2024 |
<div class="new-fform">
</div>
