Context:
Recently, flash floods and landslides caused by heavy rainfall have resulted in the blocking of the Chandigarh-Manali highway.
| PYQ:
Q. Major cities of India are becoming vulnerable to flood conditions. Discuss. (2016) |
About the News:
About Flash Floods:
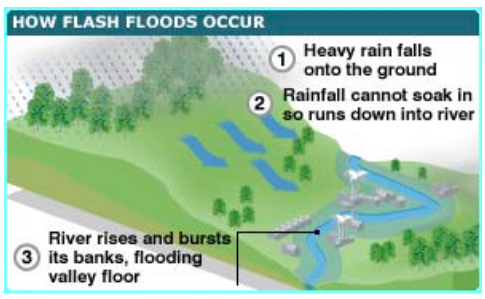
Image Credits: BBC
Characteristics of Flash Floods:
Causes of Flash Floods:
Impacts of Flash Floods:
Initiatives taken in this direction:
Way Forward:
| Additional Information:
About The National Disaster Management Authority (NDMA) guidelines on management of floods:
|
News Source: The Indian Express
Context:
| PYQ:
Q. What introduces friction into the ties between India and the United States is that Washington is still unable to find for India a position in its global strategy, which would satisfy India’s National self-esteem and ambitions” Explain with suitable examples. (2018) |
Key Highlights of the Visit:
Technology Partnership:
Defence Partnership:
| INDUS-X is a network of university, incubator, corporate, think tank, and private investment stakeholders. |
Promoting People-to People Ties:
Cooperation in the Indo-Pacific:
Energy Collaboration:
Terrorism:
Background:
Evolution of India and the US Relationship:
Areas of Cooperation between India-USA:
Challenges in the US-India relationship:
Way Forward:
| China-Plus-One refers to a strategy in which companies avoid investing only in China and diversify their businesses to alternative destinations. |
| Additional Information:
About State Visit:
|
News Source: The Indian Express
Fibonacci Spirals
Context:
A new study recently published in The Conversation challenged the viewpoint that Fibonacci spirals are found in each of the plant species.
Findings of the Study:
About Fibonacci Pattern/ Spiral:
News Source: The Hindu
Context:
Union Minister of Fisheries, Animal Husbandry & Dairying launched Nandi – NOC Approval for New Drug and Inoculation System portal.
About Nandi Portal:
News Source: pib
Context:
The Ministry of Power has set up a dedicated Centre of Excellence to accelerate industry adoption of clean technologies.
About UTPRERAK (Unnat Takniki Pradarshan Kendra):
News Source: pib
Context:
The Ministry of Finance has approved capital investment proposals of Rs. 56,415 crore in 16 States in the current financial year under ‘Special Assistance to States for Capital Investment 2023-24’ Scheme.
About the Scheme:
| Scheme Part | Objective |
| Part I | States have been allocated in proportion to their share of central taxes & duties as per the award of the 15th Finance Commission. |
| Part-II | Incentivizing scrapping of government vehicles by providing incentives to States. |
| Part-III | Encouraging reforms in urban planning. |
| Part-IV | Promoting reforms in urban finance. |
| Part-V | Increasing housing stock for police personnel in urban areas. |
| Part-VI | Promoting national integration and the “Make in India” concept through the construction of Unity Malls in each State. |
| Part-VII | Providing financial assistance for the establishment of libraries with digital infrastructure at the Panchayat and Ward levels. |
News Source: pib
Context:
Recently, the Manipur Chief Minister said that the Centre would ensure the implementation of the Suspension of Operations (SoO) agreement with Kuki insurgent groups in the hill area.
About Suspension of Operations (SoO) agreement:
Key Points under Suspension of Operations (SoO) agreement:
News Source: Indian Express
Context:
Recently, the Government in Madhya Pradesh launched the six-day Rani Durgavati Gaurav Yatra.
About Rani Durgavati:
News Source: Indian Express
SC Verdict on Newsclick Shows Adherence to Due Pro...
Stay Invested: On Chabahar and India-Iran Relation...
Credit Rating Agencies, Impact on India’s De...
Catapulting Indian Biopharma Industry
Globalisation Under Threat, US Import Tariffs Have...
Global Report on Hypertension, Global Insights and...
<div class="new-fform">
</div>
