Context: The government has approved amendments to the Mines and Minerals (Development And Regulation) Act allowing commercial mining of lithium and a few other minerals.
Proposed Amendments:
Need for amendment:
What are critical minerals?
|
Additional Information
|
Context:
Recently, Sri Lanka said that it will back the resolution proposed by Pakistan at the UNHRC condemning the Sweden government’s action to allow the burning of the Quran.
About UNHRC:
Mandate:
Membership of the Council:
News Source: The Hindu
Context: Minister of Ports, Shipping and Waterways, recently inaugurated the indigenous Differential Global Navigation Satellite System (DGNSS) called ‘SAGAR SAMPARK’.
About Sagar Sampark:
| Additional Information
What is Differential GNSS?
|
News Source: pib
Context: Geologists have said that sediments at Crawford Lake in Canada’s Ontario have provided evidence of the beginning of the Anthropocene epoch.
About Anthropocene epoch:
Crawford Lake in Canada and recent study
Earth’s geological time scale
News Source: Indian Express
Context: Recently, NASA celebrated the anniversary of the James Webb telescope by sharing a new image of sunlike stars being born. The picture is of the Rho Ophiuchi cloud complex, the nearest stellar nursery to Earth.

Image credit: The Hindu
About James Webb Telescope:
News Source: BBC
Context: In a recently concluded NATO summit held at Vilnius, Lithuania , members strengthened their commitment to defence and investment. They also agreed to bring Ukraine closer to NATO, and deepen partnerships around the world.
About NATO:
News Source: livemint
Context: The Ministry of Social Justice and Empowerment introduced Atal Vayo Abhyuday Yojana (AVYAY) to empowering senior citizens in India
About Atal Vayo Abhyuday Yojana:
| Additional Information:
About Integrated Programme for Senior Citizens (IPSrC):
Rashtriya Vayoshri Yojana:
|
News Source: pib
Context:
Recently, the Goods and Services Tax (GST) Council decided to levy a uniform 28 per cent tax on full face value for online gaming, casinos and horse-racing.
About Online Gaming:
| Games of skill | Games of chance or luck |
|
|
India’s Online Gaming Potential
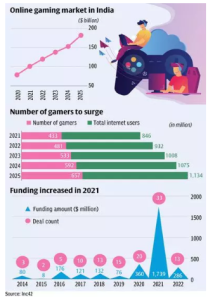
Reason for Growth of Online Gaming In India
Benefits of Online Gaming:
Concerns Associated with Online Gaming:
Regulation of Online Gaming in India:
Government Initiatives to Promote Safe Online Gaming in India:
Online Gaming Regulation Globally:
Way Forward:
Conclusion:
Related Information:
About Goods and Services Tax (GST) Council:
|
News Source: Indian Express
Context:
Key Highlights:
What is Cryptocurrency?
How Does Cryptocurrency Work?
Benefits Of Cryptocurrency:
Challenges of cryptocurrency:
What Is Digital Currency?
Central Bank-backed Digital Currency (CBDC):
Difference between cryptocurrency and digital money:
|
Cryptocurrency regulation in India:
Arguments in favour of regulating cryptocurrency in India.
Arguments against regulating cryptocurrency in India:
Way Forward:
News Source: TOI
SC Verdict on Newsclick Shows Adherence to Due Pro...
Stay Invested: On Chabahar and India-Iran Relation...
Credit Rating Agencies, Impact on India’s De...
Catapulting Indian Biopharma Industry
Globalisation Under Threat, US Import Tariffs Have...
Global Report on Hypertension, Global Insights and...
<div class="new-fform">
</div>
