| PSLV-C56 Places Seven Singapore Satellites Into Orbit | The Indian Space Research Organisation (ISRO) successfully launched PSLV rocket carrying seven Singaporean satellites from Satish Dhawan Space Centre in Sriharikota, Andhra Pradesh.
PSLV-C56 Mission:
|
| Worldcoin Project |
About the Worldcoin Initiative:
|
| ULLAS App |
About the ULLAS (Understanding Lifelong Learning for All in Society) :
|
Context:
About the Project:
What is a quantum-safe algorithm?
Post-quantum cryptography
Quantum cryptography:
News Source: The Hindu
Context:
About Wajid Ali Shah:
Contributions to music:
Contributions to dance:
Contributions to Hindustani Theatre:
Contribution to literature:
News Source : Indian Express
Context:
About Central African Republic:
 Image Credits: BBC
Image Credits: BBC
News Source: The Hindu
Context:
Recently, Indian military aircraft visited Australia’s Cocos (Keeling) Islands to enhance strategic reach and interoperability with Australia.
About Cocos Islands:
Strategic Significance:
News Source: The Hindu
Context:
Project Tiger and Project Elephant have been merged into a new division called the ‘Project Tiger and Elephant Division’ under the Ministry of Environment, Forest and Climate Change.
Reason for Merger:
Project Tiger:
Project Elephant:
Elephant Range States:
|
News Source: The Indian Express
Context:
As per a recent report by the World Meteorological Organization (WMO), Asia is the most disaster prone region in the world. In 2022, Asia faced 81 weather, climate, and water-related disasters.
About the ‘State of the Climate in Asia 2022’ Report:
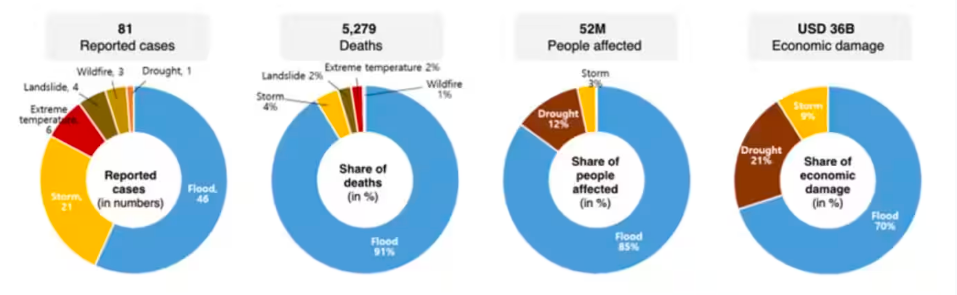 Image Source: DTE
Image Source: DTE
Key Takeaways from the Report:
| Year | Number of Deaths due to Natural Disasters | Number of People Affected by Disasters |
| 2021 | Approximately 3,800 | 48.3 million |
| 2022 | Approximately 5,879 (55% increase) | 52 million (increase from 2021) |
Reasons for Disasters :
India’s Initiatives to Tackle Climate Change
|
Way Forward:
World Meteorological Organization (WMO)
|
News Source: The Indian Express
Context: External affairs ministry has announced that India extended 308 lines of credit to partner countries amounting to $32.02 billion over the years as part of its development assistance program. Under India’s ‘Neighbourhood First policy, grant assistance projects have also been initiated in collaboration with nations such as Afghanistan, Bangladesh, Maldives, Myanmar, Nepal, Sri Lanka, and Bhutan.
Neighbourhood First Policy: India Extends 308 Lines Of Credit Worth Over $32 Billion
What is ITEC?
What is Line of Credit?
Source: Economic Times
SC Verdict on Newsclick Shows Adherence to Due Pro...
Stay Invested: On Chabahar and India-Iran Relation...
Credit Rating Agencies, Impact on India’s De...
Catapulting Indian Biopharma Industry
Globalisation Under Threat, US Import Tariffs Have...
Global Report on Hypertension, Global Insights and...
<div class="new-fform">
</div>
