Context:
Recently, the Department of Telecommunication (DoT) launched Bharat 6G Alliance to Drive Innovation and Collaboration in Next-Generation Wireless Technology (6G).
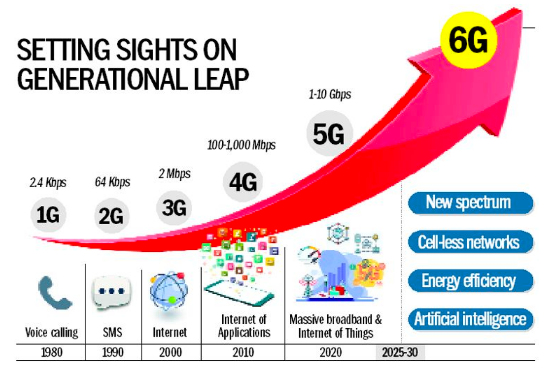
Background: Evolution from 1G to 6G
| Generation | Description |
| 1G |
|
| 2G |
|
| 3G |
|
| 4G |
|
| 5G |
|
| 6G |
|
About Bharat 6G Alliance (B6GA):
Bharat 6G Project:
Status of Digital ecosystem in India:
Government Initiatives:
Challenges Faced by the Telecom Sector:
Way Forward:
Difference between 5G and 6G:
| Aspect | 5G | 6G |
| Speed | Up to 10 Gbps | Up to 1 Tbps |
| Latency | Low latency (10 ms) | Ultra-low latency (<1 ms) |
| Spectrum (Major Frequency bands) | 24 GHz to 100 GHz | 95 GHz to 3 THz (Terahartz) can operate on a higher frequency than 5G |
| Use Cases | Accelerate adoption of cloud gaming, AV/VR technology, Internet of Things, etc. | Support high-performance computing, Remote-controlled factories, self-driven cars, smart wearables |
| Connectivity | Connecting billions of devices | Connectivity between virtual and physical world |
News Source: PIB
Context:
The Centre has asked e-commerce companies to not use “dark patterns” on their platforms that may deceive customers or manipulate their choices.
More on News:
About Dark Patterns:
Types of dark patterns identified the Consumer Affairs Ministry:
Steps taken by other governments
News Source: Indian Express
Context:
The CH3+ molecule, which is also known as methyl cation, has been detected in space for the first time by the James Webb Space Telescope (JWST).
About CH3+:
(Protoplanetary discs are discs of dense gas and dust surrounding young stars. The material in these discs eventually coalesces to form planets.)
| Additional Information
About James Webb Space Telescope
|
News Source: Indian Express
Context:
The Union government has decided to provide medical, financial and infrastructure support to victims in cases where the sexual assault results in pregnancies.
About the Scheme
| Additional Information
Nirbhaya Fund
|
About Mission Vatsalya Scheme:
News Source: The Hindu
Context:
Recently the Prime Minister congratulated new homeowners in Bengaluru’s first project under SWAMIH Fund which has helped more than 3000 families in owning their dream homes.
About SWAMIH Fund:
News Source: Indian Express , pib
Context:
Recently, the Union Minister of State for Panchayati Raj released Report on Panchayat Development Index at National Workshop on Panchayat Development Index.
About Panchayat Development Index (PDI):
News Source: pib
Context:
Recently, the NCP led by Sharad Pawar filed a disqualification petition against the nine NCP MLAs who joined the BJP-Sena government in Maharashtra.
Constitutional provisions for disqualifying the lawmakers:
Features of the Anti-Defection Law:
Recent Supreme Court Judgment:
The Supreme Court bench led by Chief Justice of India (CJI) DY Chandrachud in the May 11 verdict in Shiv Sena tussle case, laid down principles for the Speaker of the Assembly.
News Source: Indian Express
SC Verdict on Newsclick Shows Adherence to Due Pro...
Stay Invested: On Chabahar and India-Iran Relation...
Credit Rating Agencies, Impact on India’s De...
Catapulting Indian Biopharma Industry
Globalisation Under Threat, US Import Tariffs Have...
Global Report on Hypertension, Global Insights and...
<div class="new-fform">
</div>
