| Great Indian Bustard |
|
| Ecuador |
|
| Bharat (BH) Series |
|
| SATAT Scheme |
|
Context
The Centre has been pushing cell phone makers in India to make their instruments compatible with NavIC.
More about the news:
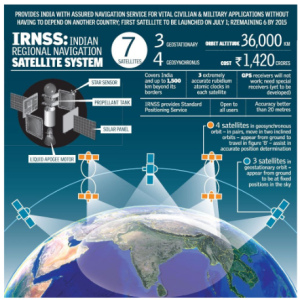 Currently the Aadhaar enrolment kits that are used to collect and verify personal details are linked to the American Global Positioning System (GPS).
Currently the Aadhaar enrolment kits that are used to collect and verify personal details are linked to the American Global Positioning System (GPS).About NavIC
Context:
The Monetary Policy Committee (MPC) of the Reserve Bank of India (RBI) decided to keep the main policy instrument (Repo rate) unchanged at 6.50%.
More about the news:
About Monetary Policy:
About Repo Rate:
News Source: The Hindu
Context:
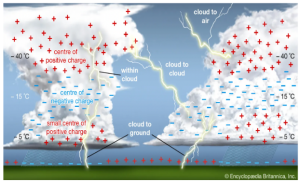
According to the Minister of Earth Sciences, nearly 2,880 people died due to lightning strikes in various states of the country in 2021.
More about the news:
Mechanism of Lightning Strikes
News Source: DTE,
Context:
During the financial years 2021-22 and 2022-23, a total of 45 projects costing Rs. 470.75 crore have been sanctioned by North Eastern Council (NEC) in Assam.
About North Eastern Council ( NEC):
Functions of the Council:
News Source: PIB,
Context:
More about the news:
Supreme Court Verdict in Anoop Baranwal v. Union of India:
Process of removal of Election Commissioners:
|
Features of the Bill:
Need of the bill:
Independence of Election Commission: Demand for an independent system for the appointment of members of the Election Commission goes back nearly 50 years. It has been repeatedly recommended by:
Addressing legal vacuum: Since there was no law made by Parliament as prescribed by the Constitution for the appointment of CEC and EC, the Bill now seeks to address this vacuum and set up a legislative process to make appointments to the EC.
Concerns with the Bill:
Article 324(2):
|
Challenges with functioning of Election Commission:
Way Forward:
| Additional Information:
Best practices from different nations in designating of Election Commissions:
|
News Source: Indian Express
Context:
Recently, International Day for the Conservation of the Mangrove Ecosystem was observed on July 26.
More on the News:
About Mangroves:
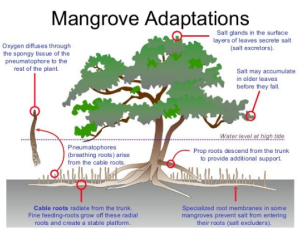 Mangroves have specialized adaptation to survive in the extreme conditions of the coastal environment.
Mangroves have specialized adaptation to survive in the extreme conditions of the coastal environment. India and Mangroves:
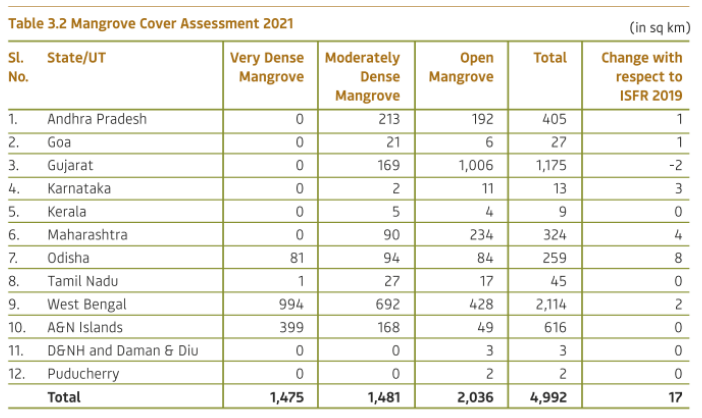
Significance:
Challenges faced by Mangrove Ecosystem:
Steps Taken for Conservation and Preservation of Mangrove
Way Forward
Conclusion
Global Effort to Protect and Preserve Mangrove
|
News Source: Livemint
SC Verdict on Newsclick Shows Adherence to Due Pro...
Stay Invested: On Chabahar and India-Iran Relation...
Credit Rating Agencies, Impact on India’s De...
Catapulting Indian Biopharma Industry
Globalisation Under Threat, US Import Tariffs Have...
Global Report on Hypertension, Global Insights and...
<div class="new-fform">
</div>
