| News | Detail |
| Non-Convertible Debentures |
About Non-Convertible Debentures
Types of Non-Convertible Debentures:
|
| National Financial Reporting Authority (NFRA) | Recently, National Financial Reporting Authority (NFRA) has released a circular addressing the responsibilities of statutory auditors in reporting fraud within a company.
About NFRA
Role of the NFRA
Scope of the NFRA
|
| Agri-IKIGAI |
About Agri-IKIGAI
About Smallholder Farmers
|
| Kampala Ministerial Declaration on Migration, Environment and Climate Change (KDMECC) |
About KDMECC
|
| Onam Festival |
About Onam
|
Context:
According to recent study, up to 10,000 emperor penguin chicks across four colonies in Antarctica’s Bellingshausen Sea may have died as the sea ice underneath their breeding grounds melted and broke apart in late 2022.
About Emperor Penguins:
Reason for Failure of Breeding
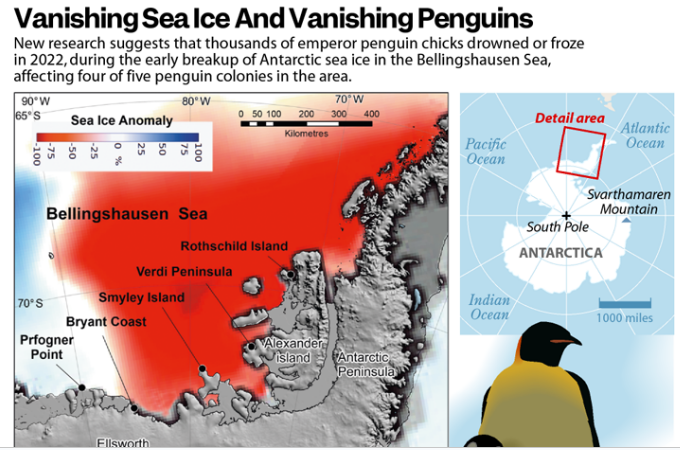 Impact: This puts more than 90% of emperor penguin colonies at risk as they may go extinct by the end of this century, if Earth continues to get warmer at the present rate.
Impact: This puts more than 90% of emperor penguin colonies at risk as they may go extinct by the end of this century, if Earth continues to get warmer at the present rate.Sea Around Antarctica
|
News Source: The Indian Express
Context:
Despite National Green Tribunal’s directions to the Government of Punjab, the state is yet to carry out Flood Plain zoning.
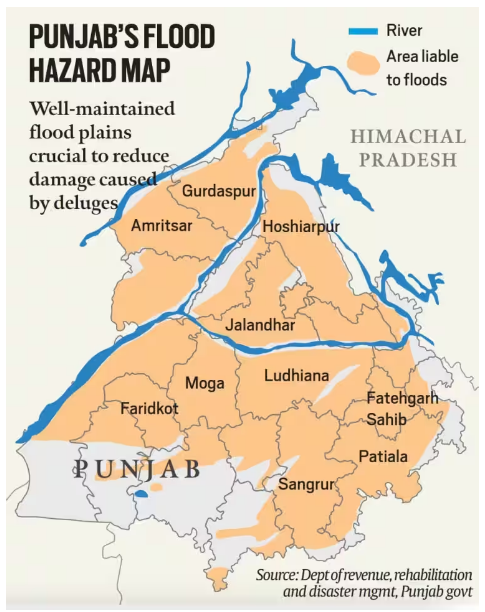
About Floodplains:
Characteristics of Floodplains:
Zoning of Flood Plains:
Significance of Zoning of FloodPlains
News Source: The Indian Express
Context:
Recently, the Supreme Court observed that Article 35-A of the Constitution has deprived people not residing in Jammu and Kashmir of some key constitutional rights.
About Article 35-A:
‘Permanent residents’ as per Article 35-A:
News Source: The Hindu
Context:
According to a report by Central Ground Water Board (CGWB), Delhi recharged more groundwater than it extracted in FY 2021-22.
About Groundwater:
Groundwater Exploitation
|
India’s Groundwater
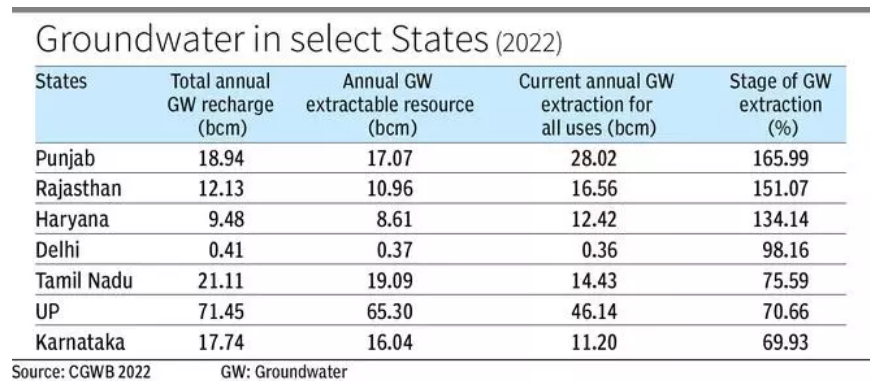
Ways to Improve Groundwater level:
News Source: The Hindubusinessline
Context:
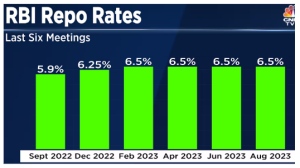
Recently, the Indian Finance Minister stressed the importance of taming inflation but cautioned against using interest rate hikes as the sole solution.
More on News:
| Pros | Cons |
|---|---|
|
Setting explicit inflation targets improves transparency and accountability. |
Ineffective for supply-side shocks and structural constraints. |
| Allows the central bank to adjust policies based on changing economic conditions. | Can lead to exchange rate fluctuations, especially in open economies. |
| Encourages a longer-term perspective in monetary policy. | Affects employment, income, and vulnerable populations. |
| Enhances the central bank’s credibility and stabilizes inflation expectations. | Relies on accurate and timely data, which may not be available everywhere. |
About Inflation Targeting:
Members of MPC
|
MPC and its role Inflation Targeting:
How CPI basket drives MPC inflation Target:
Challenges related to inflation targeting:
Suggestions to Improve Inflation Targeting:
Conclusion:
News Source: The Indian Express

Context:
The Prime Minister recently highlighted the significant contributions of female scientists and engineers towards the Chandrayaan-3 mission.
More about the news:
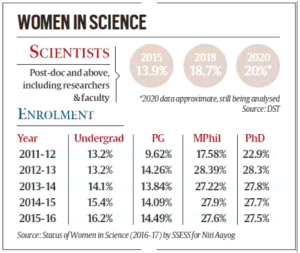 Global status: As per the recent Global Gender Gap Report 2023 by the World Economic Forum, women account for 27% of India’s STEM workforce, as compared to 32% of the non-STEM workforce.
Global status: As per the recent Global Gender Gap Report 2023 by the World Economic Forum, women account for 27% of India’s STEM workforce, as compared to 32% of the non-STEM workforce.
Significance of Women Participation in STEM:
News Source: The Hindu
SC Verdict on Newsclick Shows Adherence to Due Pro...
Stay Invested: On Chabahar and India-Iran Relation...
Credit Rating Agencies, Impact on India’s De...
Catapulting Indian Biopharma Industry
Globalisation Under Threat, US Import Tariffs Have...
Global Report on Hypertension, Global Insights and...
<div class="new-fform">
</div>
