Context
Recently, the Standing Committee on External Affairs recommended the Ministry of External Affairs (MEA) on soft power projection and cultural diplomacy.
About Soft Power
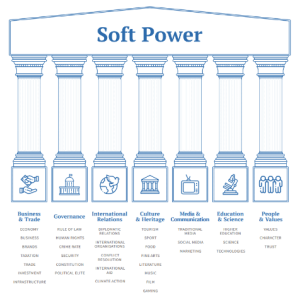 Culture: Where it is attractive to others. Ex: Hinduism, buddhism etc
Culture: Where it is attractive to others. Ex: Hinduism, buddhism etcIndia and it’s Soft Power
Significance of Soft Power for India:
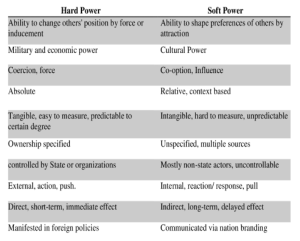 Global influence: Soft power can help India to enhance its image and reputation in the world, especially among its neighbors and strategic partners.
Global influence: Soft power can help India to enhance its image and reputation in the world, especially among its neighbors and strategic partners. Indian Council for Cultural Relations (ICCR)
Objectives of ICCR
Limitations Hindering India’s Soft Power Projection:
Global Soft Power Index
Recommendation by Standing Committee on Soft Power and Cultural Diplomacy:
Conclusion
News Source: The Print
Context:
The Parliamentary standing committee has called for addressing wage disparity under Mahatma Gandhi National Rural Employment Guarantee Act, 2005 (MGNREGA).
About MGNREGA:
Why was MGNREGA launched?
Key Features:
What is Social Audit?
|
.What types of works are taken up under MGNREGA ?
Key Achievements of MGNREGA:
Significance of MGNREGA:
Challenges:
Way Forward:
| Parliamentary Standing Committee over MGNREGA:
Observation:
Recommendations:
|
News Source: The Print
Context:
The Union Minister for Power and New & Renewable Energy has informed about the status of repayment of the bonds issued by the State Governments and the DISCOMs under the UDAY scheme.
About UDAY SCHEME:
Objectives of Scheme:
Key benefits for the states participating in UDAY:
Targets to be met by states under UDAY:
News Source: PIB
Context:
The Union Minister for Power and New & Renewable Energy has informed about the status of implementation and coverage of the SAUBHAGYA Scheme in the country.
About Saubhagya(Pradhan Mantri Sahaj Bijli Har Ghar Yojana) Scheme:
Objectives of Scheme:
Salient features:
News Source: PIB
Context:
Recently, the Government has set a deadline for mandatory implementation of the Good Manufacturing Practices (GMP), to bring them on par with World Health Organisation (WHO) standards.
More about the news:
Good Manufacturing Practice:
News Source: The Indian Express
Context:
Recently, an earthquake of 4.3 magnitude hit Andaman and Nicobar Islands.
Reason for earthquake in Andaman and Nicobar:
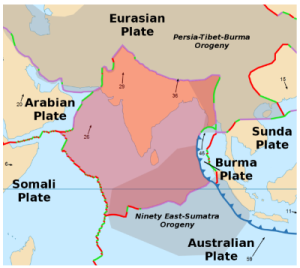 Tsunami 2004: Great Nicobar is not far from Banda Aceh in Indonesia, which was the epicentre of the December 2004 earthquake and tsunami that caused unprecedented damage.
Tsunami 2004: Great Nicobar is not far from Banda Aceh in Indonesia, which was the epicentre of the December 2004 earthquake and tsunami that caused unprecedented damage. About Tectonic Plate:
About Andaman and Nicobar Islands
Barren Island: Only Active Volcano of India
|
News Source: The Hindu
Contect:
Recently, South Korean researchers claimed that a lead-based compound they had developed, had shown superconducting properties at room temperature, under normal pressure conditions.
About Superconductivity:
Significance of Superconductivity:
News Source: Indian Express
| Antarctica’s sea ice at record low extent |
|
| Biomass Co-firing |
|
| Gender Inclusion Fund (GIF) |
|
SC Verdict on Newsclick Shows Adherence to Due Pro...
Stay Invested: On Chabahar and India-Iran Relation...
Credit Rating Agencies, Impact on India’s De...
Catapulting Indian Biopharma Industry
Globalisation Under Threat, US Import Tariffs Have...
Global Report on Hypertension, Global Insights and...
<div class="new-fform">
</div>
