Context:
The recent announcement of India-Middle East-Europe Economic Corridor (IMEC) has the potential to make India an Asian hub in global supply chains.
About Supply Chains:
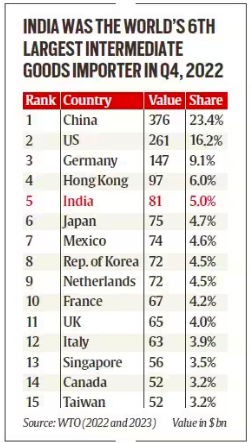
Factors Driving the Shift in Global Supply Chains Away from China:
India’s Emergence as an Attractive Supply Chain Hub:
Government Initiatives to Boost Manufacturing and Supply Chains
|
| China-Plus-One, or just Plus One refers to a strategy in which companies avoid investing only in China and diversify their businesses to alternative destinations. |
Benefits for South Asia:
Challenges in Integrating India into Global Value Chains:
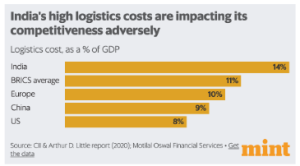 Inadequate access to essential information further hinders their integration into Global Value Chains (GVCs).
Inadequate access to essential information further hinders their integration into Global Value Chains (GVCs).Strategies for India’s Future in Supply Chains: Learn from China’s experience
Conclusion:
News Source: The Indian Express
Context:
UNICEF’s representative hailed India for making great progress in making plans and budgets more responsive.
More on News:
About Gender Responsive Budgeting:
GRB in India:
Significance of GRB:
Government Initiatives:
|
Challenges Still Remain:
International Best Practices:
|
Way Forward:
Conclusion:
News Source: The Economic Times
Context:
A recent study by Cornell University, United States, warns ‘Artificial Light Pollution’ affects Coastal Marine Ecosystems.
More On News:
Light Pollution: Light pollution, or artificial light at night, is the excessive or poor use of artificial outdoor light, and it has several forms:
Impact Of Light Pollution:
Marine Organisms:
Wild Life:
Humans:
Sky Glow Pollution:
Mitigation Measures:
Way Forward: To address Light Pollution it is essential to balance the need for outdoor lighting with the preservation of natural darkness for the benefit of both ecosystems and human well-being.
Source: DownTOEarth
Context:
Recently, the Union Ministry of Tribal Affairs (MoTA) issued guidelines for the conservation, management, and sustainable use of community forest resources (CFR) has raised concerns among experts.
More on News:
Community Forest Resources (CFR): defined in section 2 (a) of the FRA Act, means customary common forest, (including reserved forests, protected forests and protected areas).
Community Forest Resource rights
|
Concerns:
Way ahead: For effective forest conservation, reforestation and recovery, we must strengthen our local forest governance mechanisms.
Source: DownToEarth
Context:
A new Lancet Commission on TB reveals concerns about the global fight against tuberculosis, as TB deaths have increased for the first time in 20 years.
More on News
Major Highlights of report:
Major Recommendation Of Commission:
Way Forward: We need human-friendly, stigma-free, need-based psychosocial interventions along with clinical interventions as TB is not just a medical but a social disease as well.
Indian Government TB Elimination Strategy : On World TB Day 2023, Prime Minister Narendra Modi at One World TB Summit, announced initiatives to help the country meet the 2025 target.
|
Source: The Indian Express
| GOI and WOAH Collaborate to Strengthen One Health Approach |
Focus areas:
About World Organization for Animal Health(WOAH):
|
| Expansion of the Pradhan Mantri Ujjwala Yojana (PMUY) |
About PMUY:
|
| Dholera SIR all ready to Kickstart its Plug-and-Play Infrastructure |
About Dholera Special Investment Region(SIR):
Plug-and-Play Infrastructure:
|
| Special Session to Debate bill on ECs, discuss ‘Parliamentary Journey |
About the bill:
About special session of Parliament:
|
SC Verdict on Newsclick Shows Adherence to Due Pro...
Stay Invested: On Chabahar and India-Iran Relation...
Credit Rating Agencies, Impact on India’s De...
Catapulting Indian Biopharma Industry
Globalisation Under Threat, US Import Tariffs Have...
Global Report on Hypertension, Global Insights and...
<div class="new-fform">
</div>
