Context:
More about the news:
Salient Features of RTI Act:
|
Significance of the act:
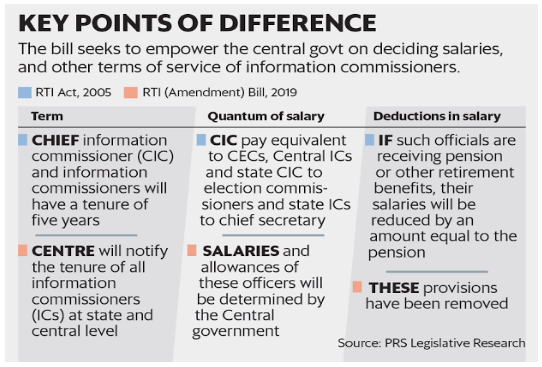
Challenges of the act:
RTI and political parties:
RTI vs Official Secrecy Act(OSA) 1923:
|
Way Forward:
News Source: The Hindu
Context:
According to a report and survey by the Indian Cellular and Electronic Association (ICEA) along with Accenture, around 206 million devices (smart phones and laptops) are lying idle with consumer households.
More on News:
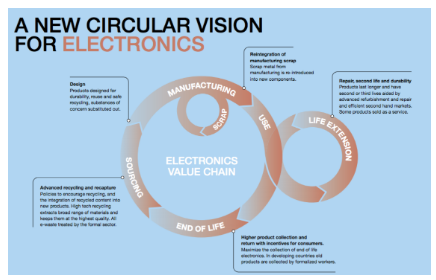
About e-Waste:
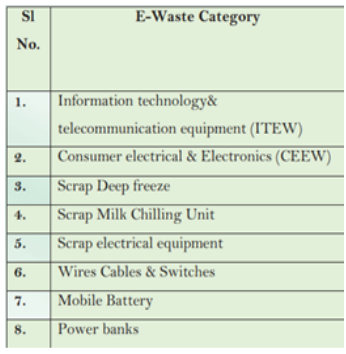
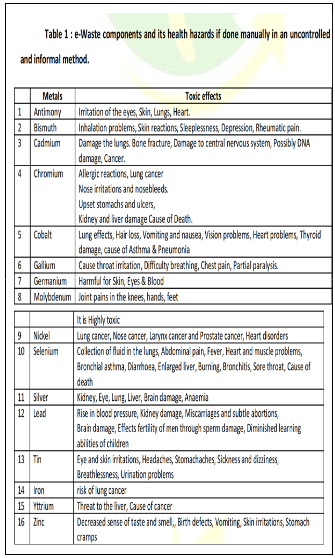
Challenges Related to E-Waste Management:
 |
 |
Way Forward:
Conclusion
Countries can work towards more effective and sustainable e-waste management, reducing the negative environmental and health impacts while maximizing the economic benefits of recycling and resource recovery.
News Source: Business Standard
Context:
Recently, the Indian Space Research Organisation (ISRO) launched Aditya L-1, its first space-based mission to study the Sun, from the Satish Dhawan Space Centre in Sriharikota.
About Aditya-L1 Mission:
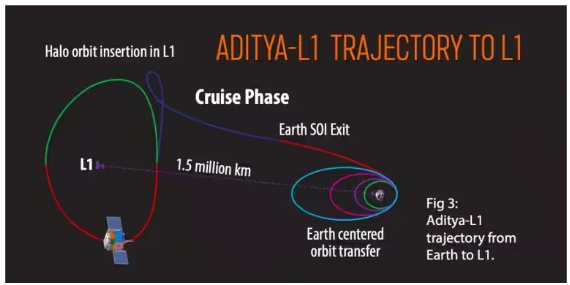 Image Credit: The Indian Express
Image Credit: The Indian Express
What is Space Weather?
|
Objectives of the Mission:
Sun’s Corona:
| Additional Information:
About Lagrange Points:
|
News Source: The Hindu
Context:
The Delhi High Court permitted two children with autism spectrum disorder (ASD) to undergo stem cell therapy for treatment of their condition.
About Stem Cell Therapy:
What are Stem cells?
Sources of Stem cells:
Applications of Stem Cell Therapy:
Autism Spectrum Disorder (ASD):
|
News Source: The Indian Express
Context:
The Competition Commission of India (CCI) approved the merger of Vistara with Air India as well as allowed Singapore Airlines to acquire 25.1% stake in the erstwhile national carrier.
About Competition Commission of India (CCI):
About Quasi-Judicial body:
|
News Source: The Hindu
Context:
About Simultaneous election/One Nation One Election:
Benefits of simultaneous elections:
Views of Reports in favour of Simultaneous Elections:
Challanges:
News Source: Hindustan times
Context:
Unified Payments Interface (UPI) recorded over 10 billion transactions in August, a historic milestone.
Consistent Month-on-Month Growth:
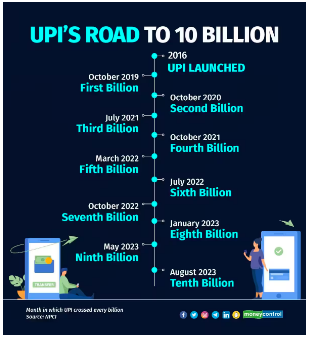
Expected Transaction Value Record:
National Payments Corporation of India (NPCI’s) Ambitious Target:
UPI’s Evolution and Growth Factors:
About Unified Payments Interface (UPI):
|
News Source: Economic Times
| Meri Maati Mera Desh campaign | The Union Home Minister and Minister of Cooperation inaugurated the ‘Amrit Kalash Yatra’ under the ‘Meri Maati-Mera Desh’ campaign.
About ‘Amrit Kalash Yatra’:
|
| G20 Culture Corridor | The G20 Culture Corridor is a special exhibition to be set up at the venue of the G-20 summit in New Delhi.
|
SC Verdict on Newsclick Shows Adherence to Due Pro...
Stay Invested: On Chabahar and India-Iran Relation...
Credit Rating Agencies, Impact on India’s De...
Catapulting Indian Biopharma Industry
Globalisation Under Threat, US Import Tariffs Have...
Global Report on Hypertension, Global Insights and...
<div class="new-fform">
</div>
