Subject: GS-02: Polity and Governance
Context: The Delhi High Court recently granted requests to protect personality rights from potential misuse by third parties.
A trademark is a sign capable of distinguishing the goods or services of one enterprise from those of other enterprises. Trademarks are protected by intellectual property rights.
|
|---|
| Case of Anil Kapoor: The Delhi High Court granted an ex-parte, omnibus injunction restraining 16 entities from using Kapoor’s name, likeness, image, using technological tools like Artificial Intelligence, face morphing and even GIFs for monetary gain or commercial purpose. |
|---|
News Source: Indian Express
Context: During the 78th session of the United Nations General Assembly (UNGA) held recently, foreign ministers of the Quad reaffirmed the commitment to a “free and open” Indio-Pacific region.
United Nations Convention on the Law of the Sea(UNCLOS):
|
|---|
News Source: The Hindu
Context: The Department of Fisheries has sanctioned 732 artificial reef units for 10 coastal states with a total investment of Rs 126 crore under Pradhan Mantri Matsya Sampada Yojana (PMMSY) for rejuvenating coastal fisheries.

| Natural Reef:
The coral reef is the most familiar type of natural reef.
|
|---|
Despite the positives of building artificial reefs, we must preserve natural reefs.
Source: PIB
| AlphaMissense
|
AlphaMissense is a new tool based on AlphaFold that can identify harmful genome mutations.
How it works:
Potential benefits of AlphaMissense:
|
| AlphaFold | AlphaFold is an AI system developed by DeepMind (Google’s Subsdiry).
|
| India to be part of JP Morgan global bond index | JP Morgan decided to include Indian government bonds in its Government Bond Index-Emerging Markets with effect from June 2024.
Government Bonds:
|
| Dr Swati Nayak wins Norman Borlaug Field Award
|
Dr Swati Nayak ( ‘Bihana Didi’), an Indian scientist at the International Rice Research Institute (IRRI), has been named the 2023 recipient of the prestigious Norman E Borlaug Award for Field Research and Application, with the World Food Prize Foundation.
Contribution:
|
| Privilege Committee | Recently, opposition leaders wrote to the Lok Sabha Speaker, demanding that the matter concerning an MP’s use of unparliamentary language be referred to the Privileges Committee.
About Privilege Committee:
Parliamentary Privileges:
|
| Nasha Mukt Bharat Abhiyaan | Nasha Mukt Bharat Abhiyaan (NMBA) – MoU signed between Department of Social Justice & Empowerment and the All World Gayatri Pariwar.
Nasha Mukt Bharat Abhiyaan (NMBA):
|
Subject: GS:01: Art and Culture
Context: A Parliamentary panel observed that the requirement of a 100-meter prohibited and a 300-meter regulated zone around Archaeological Survey of India (ASI) protected monuments of India has created conflicts between local communities and the heritage sites.
News Source: The Hindu
Context:
According to NITI Aayog, the State Institute for Transformation (SIT) Aayogs are needed to support states to ensure the development goals are achieved.
More on News:
About SIT Aayog:
Role of NITI Aayog in Setting up SIT’s:
State Planning Commission vs SIT Aayog:
| Basis | State Planning Commission | SIT Aayog |
| Purpose | Historically it had a central role in formulating the state’s Five-Year Plans aimed at achieving balanced regional development, promoting economic growth etc. | Its main purpose is to facilitate policy development and transformational initiatives within the state’s context. |
| Decision-Making | It was responsible for drafting and approving state development plans. | It provides recommendations and guidance to the state government. |
| Relevance | Their relevance has diminished since the discontinuation of the Five-Year Plans at the national level. | They have gained prominence as they focus on addressing contemporary challenges and adapting to changing circumstances. |
| Functions: | They were primarily responsible for formulating development plans, assessing resource requirements, and coordinating the allocation of funds for various development projects. | They engage in a wide range of activities, including policy formulation, data analysis, capacity building, project monitoring, and resource mobilization. |
The discontinuation of five year plans, plaguing inefficiency and outdated working structure has led to initiation of scrutiny against the role of state planning commission, which has led to rise in demand for the SIT’s by various states in India.
Need for SIT Aayog:
Challenges Associated with SITs:
Way Forward:
Conclusion:
The SITs can help in improving the local economy and polity which can help improve India’s GDP growth and ensure making India “Viksit Bharat” (developed country) by 2047.
News Source: Mint
Context: Quantum computing is one of the most attractive investment avenues, both from the public and private sectors, reaching about US$35.5 billion globally in 2022.
More on News:
About Quantum Computing:
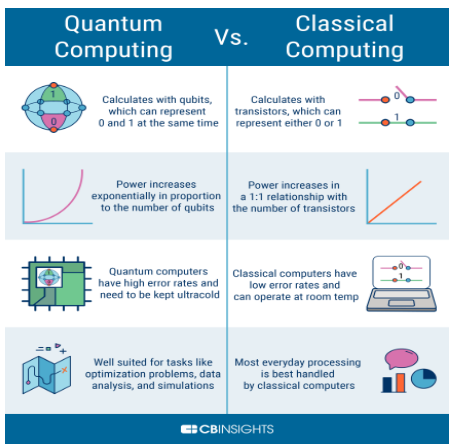
Application of Quantum Computing:
Government Initiatives:
Major international Quantum Computing Collaborations:
|
|---|
Limitations:
Way Forward:
SC Verdict on Newsclick Shows Adherence to Due Pro...
Stay Invested: On Chabahar and India-Iran Relation...
Credit Rating Agencies, Impact on India’s De...
Catapulting Indian Biopharma Industry
Globalisation Under Threat, US Import Tariffs Have...
Global Report on Hypertension, Global Insights and...
<div class="new-fform">
</div>
