Chilka Lake
Nalabana Island (Nalabana Bird Sanctuary): Nalabana was declared a bird sanctuary in 1973 under the Wildlife Protection Act.
|
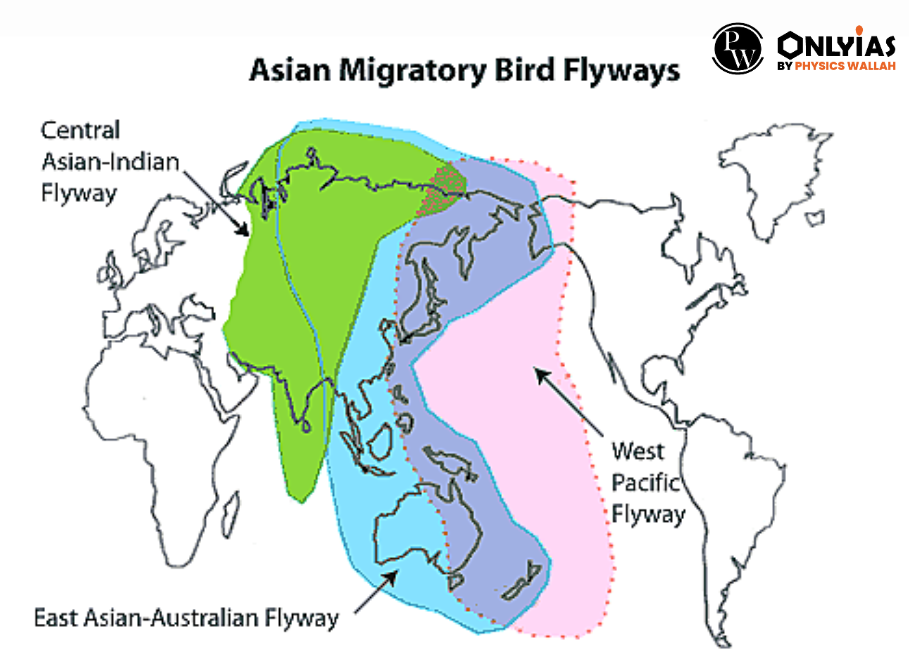
Source: Down to Earth
| Prelims Question:
Consider the following statements: 1. Asiatic lion is naturally found in India only. 2. Double-humped camel is naturally found in India only. 3. One-horned rhinoceros is naturally found in India only. Which of the statements given above is/are correct? (a) 1 only (b) 2 only (c) 1 and 3 only (d) 1, 2 and 3 Ans: (a) |
|---|
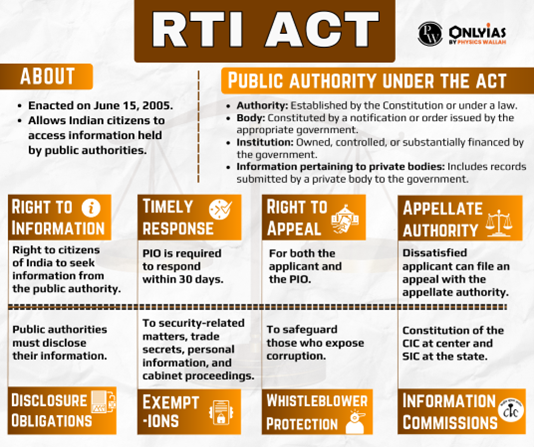
State information commissioners perform similar functions and their jurisdiction extends over all state public authorities of respective states.
Source: The Economic Times
| Mains Question: The Right to Information or RTI Act is not all about citizens’ empowerment alone, it essentially redefines the concept of accountability.” Discuss. (GS Paper 2; UPSC Mains 2018) |
|---|
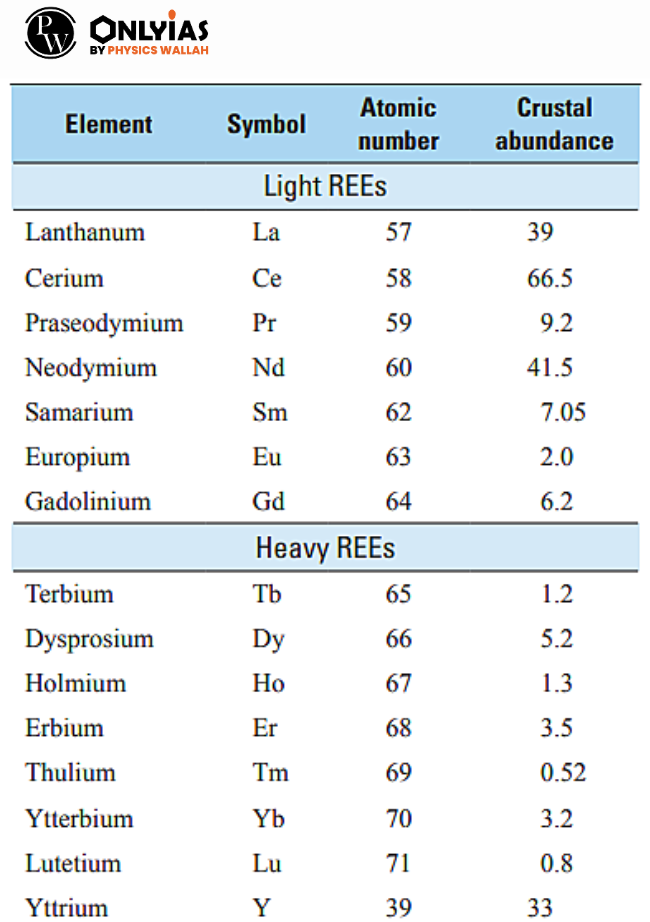
Source: livemint
| Prelims Question
With reference to the management of minor minerals in India, consider the following statements: 1. Sand is a ‘minor mineral’ according to the prevailing law in the country. 2. State Governments have the power to grant mining leases of minor minerals, but the powers regarding the formation of rules related to the grant of minor minerals lie with the Central Government. 3. State Government have the power to frame rules to prevent illegal mining of minor minerals. Which of the statements given above is/are correct? (a) 1 and 3 only (b) 2 and 3 only (c) 3 only (d) 1, 2 and 3 Ans: (a) |
|---|
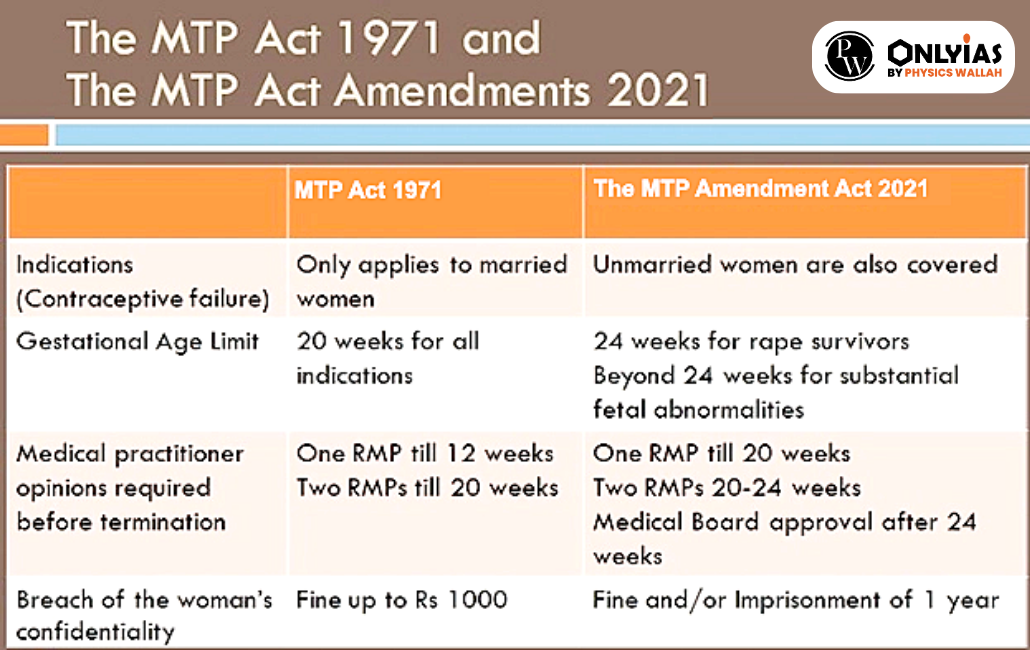
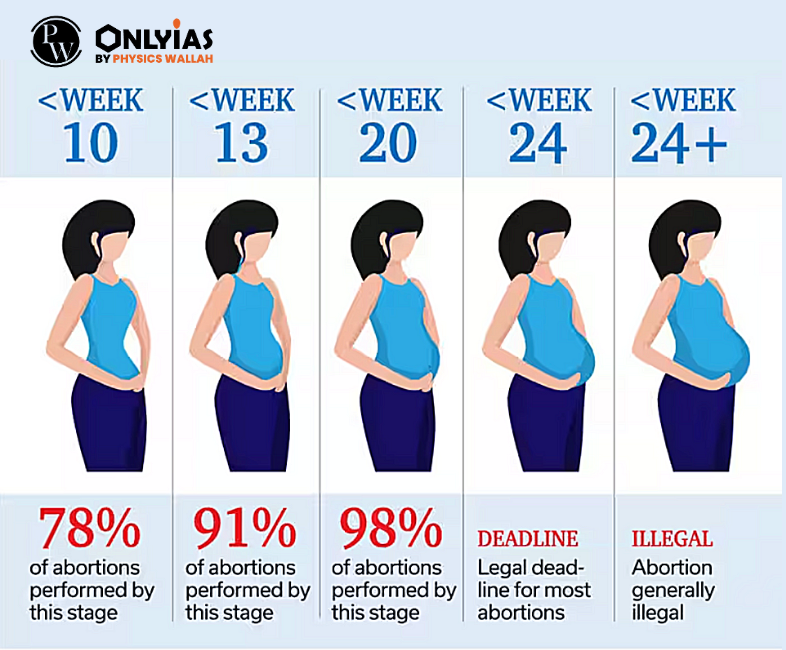
| Relevancy for Prelims: Supreme Court, Unborn Child Rights, Medical Termination of Pregnancy or MTP Act, WHO, National Human Rights Commission, UN Guidance call to protect Children’s Rights.
Relevancy for Mains: MTP Act; Right to Abortion v/s. Right to Life of the unborn child, Evolution of Abortion Law in India: MTP Act, Global abortion laws, Supreme Court’s arguments on medical termination of pregnancy. |
|---|

Global Abortion Statistics by WHO
|
|---|
The recent Supreme Court case highlights the ongoing debate over the Medical Termination of Pregnancy or MTP Act, underscoring the challenge of balancing women’s rights to abortion within the legal framework.
| Prelims Question
Which of the following gives ‘Global Gender Gap Index’ ranking to the countries of the world? (a) World Economic Forum (b) UN Human Rights Council (c) UN Women (d) World Health Organization Ans: (a) |
|---|
| Mains Question: Explain the constitutional perspectives of Gender Justice with the help of relevant Constitutional Provisions and case laws. |
|---|
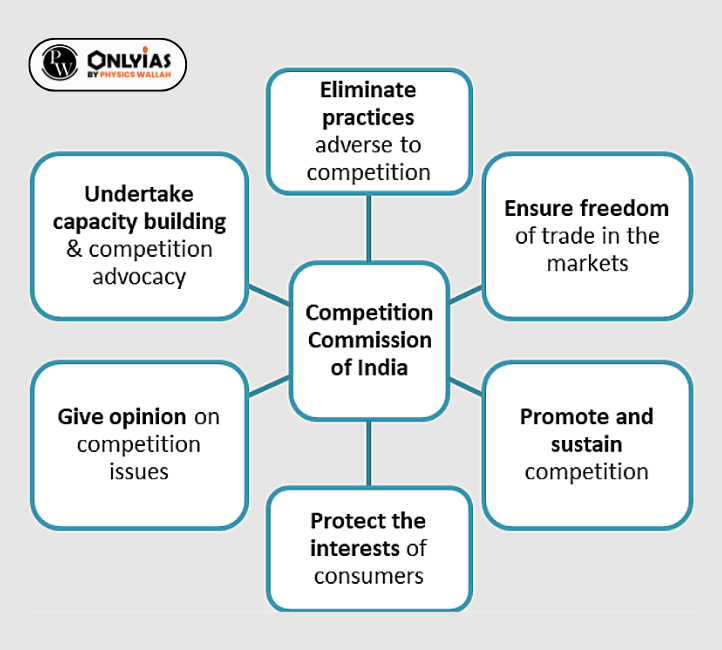
| Relevancy for Prelims: Competition Commission of India, Tribunals, National Company Law Appellate Tribunal, Competition Act, 2002, Competition (Amendment) Act, 2023 Transparency And Accountability.
Relevancy for Mains: Competition Commission of India had ordered detailed investigations against Google, Misuse of Data by Tech-Giants, Data Privacy, and some significant cases handled by the Competition Commission of India to promote healthy competition. |
|---|
Misuse of Data by Tech-Giants
|
|---|
Also read: Introduction To The Digital Personal Data Protection Bill
NCLAT– Appellate Authority
|
|---|
Also read: World Investment Report
Competition Commission of India will soon do a market study to understand the possible impact of Artificial Intelligence so that they can understand the market better. CCI is looking at the possibility of any anti-competitive practices, and how they can be addressed. Going by global experience, it is still early days for the competition regulator in India. Challenges are to be expected and overcoming them will be key to having a healthy, competitive environment in the Indian business ecosystem.
| Prelims Question:
‘Broad-based Trade and Investment Agreement (BTIA)’ is sometimes seen in the news in the context of negotiations held between India and (a) European Union (b) Gulf Cooperation Council (c) Organization for Economic Cooperation and Development (d) Shanghai Cooperation Organization Ans: (a) |
|---|
| Mains Question: Discuss the role of the Competition Commission of India in containing the abuse of dominant position by the Multi-National Corporations in India. Refer to the recent decisions. |
|---|
SC Verdict on Newsclick Shows Adherence to Due Pro...
Stay Invested: On Chabahar and India-Iran Relation...
Credit Rating Agencies, Impact on India’s De...
Catapulting Indian Biopharma Industry
Globalisation Under Threat, US Import Tariffs Have...
Global Report on Hypertension, Global Insights and...
<div class="new-fform">
</div>
