However, the Allahabad High Court ruled that ‘Sharing or retweeting a post would amount to “transmitting” under Section 67 of IT Act’ thereby attracting penal consequences.
Important provisions of IT Act are listed in table below;
| Section | Provisions |
|---|---|
| Section 43 |
Any act of destroying, altering or stealing a computer system/network or deleting data with malicious intentions without authorization from the owner of the computer is liable for the payment to be made to the owner as compensation for damages. |
| Section 43A | Any corporate body dealing with sensitive information that fails to implement reasonable security practices causing loss of another person will also be liable as a convict for compensation to the affected party. |
| Section 66 | Penalises Hacking of a Computer System with malicious intentions like fraud |
| Section 66 B, C, D | Penalises ‘Fraud or dishonesty’ using or transmitting information or identity theft |
| Section 66 E | Penalise ‘violation of privacy’ by transmitting image of private area |
| Section 66 F | This Section is on Cyber Terrorism affecting unity, integrity, security, sovereignty of India through digital medium is liable for life imprisonment. |
| Section 67 | Penalisese publishing obscene information or pornography or transmission of obscene content in public |
| Section 67A and 67B | Penalises publishing or transmission of material containing sexually explicit act in electronic form |
| Section 69 (A) | Under this section Centre has the power to “block for access by the public or cause to be blocked for access by the public any information generated, transmitted, received, stored or hosted in any computer resource”. |
| Section 79 | This section states that any intermediary shall not be held legally or otherwise liable for any third party information, data, or communication link made available or hosted on its platform. |
Source: The Hindu
Source: Indian Express
Source: PIB
National Food Security Act, 2013
|
|---|
Janani Suraksha Yojana
|
|---|
Source: PIB
Form Of Dark Patterns
|
|---|
Source: The Hindu
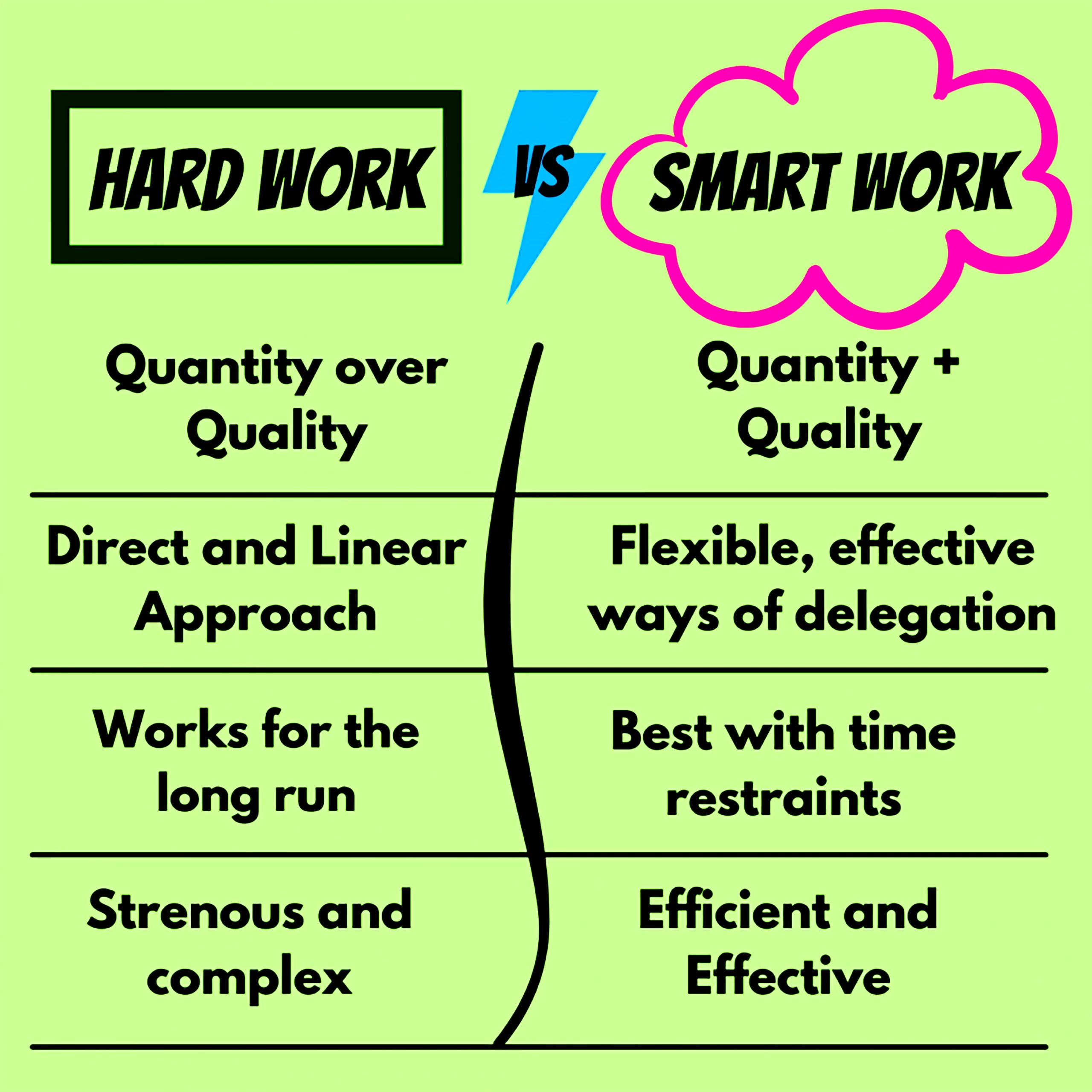
Now, India is aspiring to be a world leader. The mantra of Vivekananda ‘’Arise, awake, and stop not till the goal is reached.” is as, relevant and inspiring today as it was earlier for youth. In practice, combining hard work and smart work often yields the best results.
| Mains Question: What does ethics seek to promote in human life? Why is it all the more important in Public Administration? (150 words, 10 Marks) |
|---|
| Relevancy for Prelims: Fiscal Responsibility and Budget Management Act (FRBM Act), 2003, Fiscal Deficit, Fiscal Policy, and NK Singh Committee.
Relevancy for Mains: FRBM Act – Objectives, Key Features, and Challenges. |
|---|
What has FRBM Review committee recommended?
|
|---|
ALSO READ: BUDGET AND TAXATION
FRBM Act Exemptions/ Escape Clause: The option allows the government to widen the deficit by 0.5 percentage points in times of exigencies such as a war or calamities of national proportion.
The call to either repeal or revise the FRBM Act reflects the ongoing debate over its effectiveness, with challenges including fixed targets, escape clauses, and weak policy implementation. Policymakers advocate for a focus on flexible fiscal policies, emphasizing macroeconomic stability and a need for clear, accountable rules in the face of evolving economic dynamics.
| Prelims Question (2018)
Consider the following statements: 1. The Fiscal Responsibility and Budget Management (FRBM) Review Committee Report has recommended a debt to GDP ratio of 60% for the general (combined) government by 2023, comprising 40% for the Central Government and 20% for the State Governments. 2. The Central Government has domestic liabilities of 21% of GDP as compared to that of 49% of GDP of the State Governments. 3. As per the Constitution of India, it is mandatory for a State to take the Central Government’s consent for raising any loan if the former owes any outstanding liabilities to the latter. Which of the statements given above is/are correct? (a) 1 only (b) 2 and 3 only (c) 1 and 3 only (d) 1, 2 and 3 Ans: (c) |
|---|
| Mains Question: In the context of India’s evolving fiscal federalism, discuss the challenges and potential solutions to ensure equitable intergovernmental transfers. (250 words, 15 Marks) |
|---|
| Relevancy for Prelims: Qatar’s Controversial Verdict: Eight Former Indian Navy Officers Sentenced to Death Penalty, India Qatar Relations, Al Dahra Global Technologies and Consultancy Services, and International Court of Justice (ICJ).
Relevancy for Mains: India Qatar Relations, Significance of India Qatar relations, and Challenges are associated with India Qatar relations. |
|---|
Significance of India Qatar relations
|
|---|
Major Bilateral Trade Items
|
|---|
What challenges are associated with India Qatar relations?
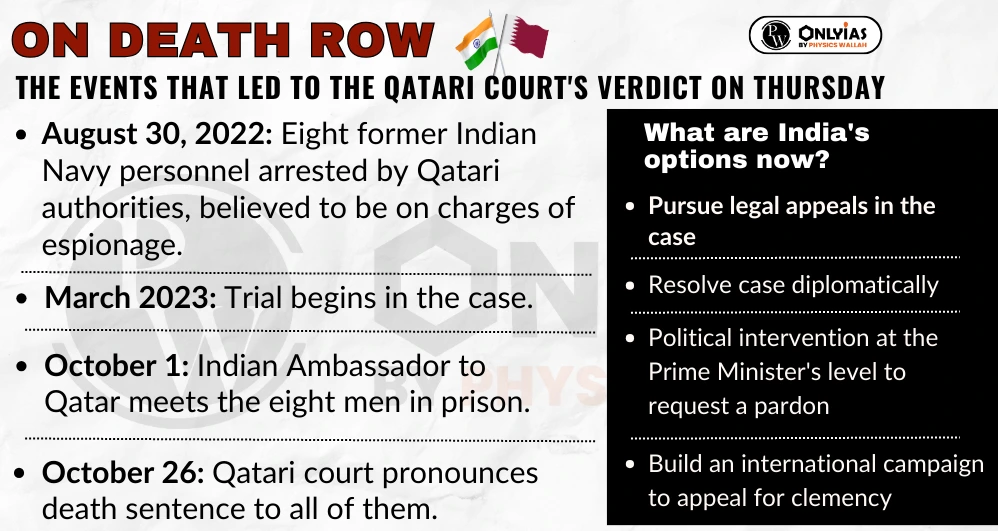
What can India do for 8 navy officers standing on the brink of death in Qatar?
|
|---|
Also read: India’s Diplomacy with West Asia Countries
In the context of India Qatar relations, these two nations need to resolve this complex and sensitive issue through diplomatic channels, reinforcing their enduring friendship. India’s approach exemplifies its commitment to diplomacy and the value it places on its relationships in the global arena.
| Prelims Question (2023)
Consider the following pairs: Regions often Reason for being in news 1. North Kivu and Ituri : War between Armenia and Azerbaijan 2. Nagorno-Karabakh : Insurgency in Mozambique 3. Kherson and Zaporizhzhia : Dispute between Israel and Lebanon How many of the above pairs are correctly matched ? (a) Only one (b) Only Two (c) All three (d) None Ans: (d) |
|---|
SC Verdict on Newsclick Shows Adherence to Due Pro...
Stay Invested: On Chabahar and India-Iran Relation...
Credit Rating Agencies, Impact on India’s De...
Catapulting Indian Biopharma Industry
Globalisation Under Threat, US Import Tariffs Have...
Global Report on Hypertension, Global Insights and...
<div class="new-fform">
</div>
