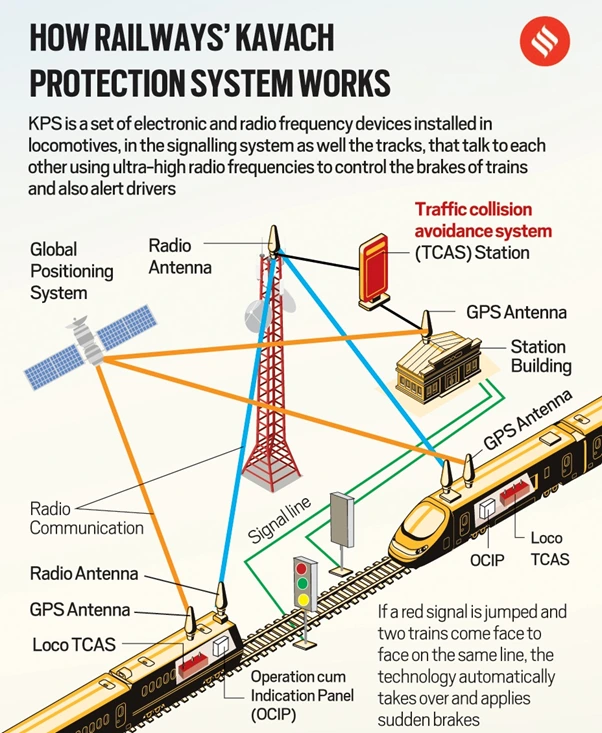
What are Safety Integrity Levels?
|
|---|
News Source: Live Mint
News Source: Economic Times
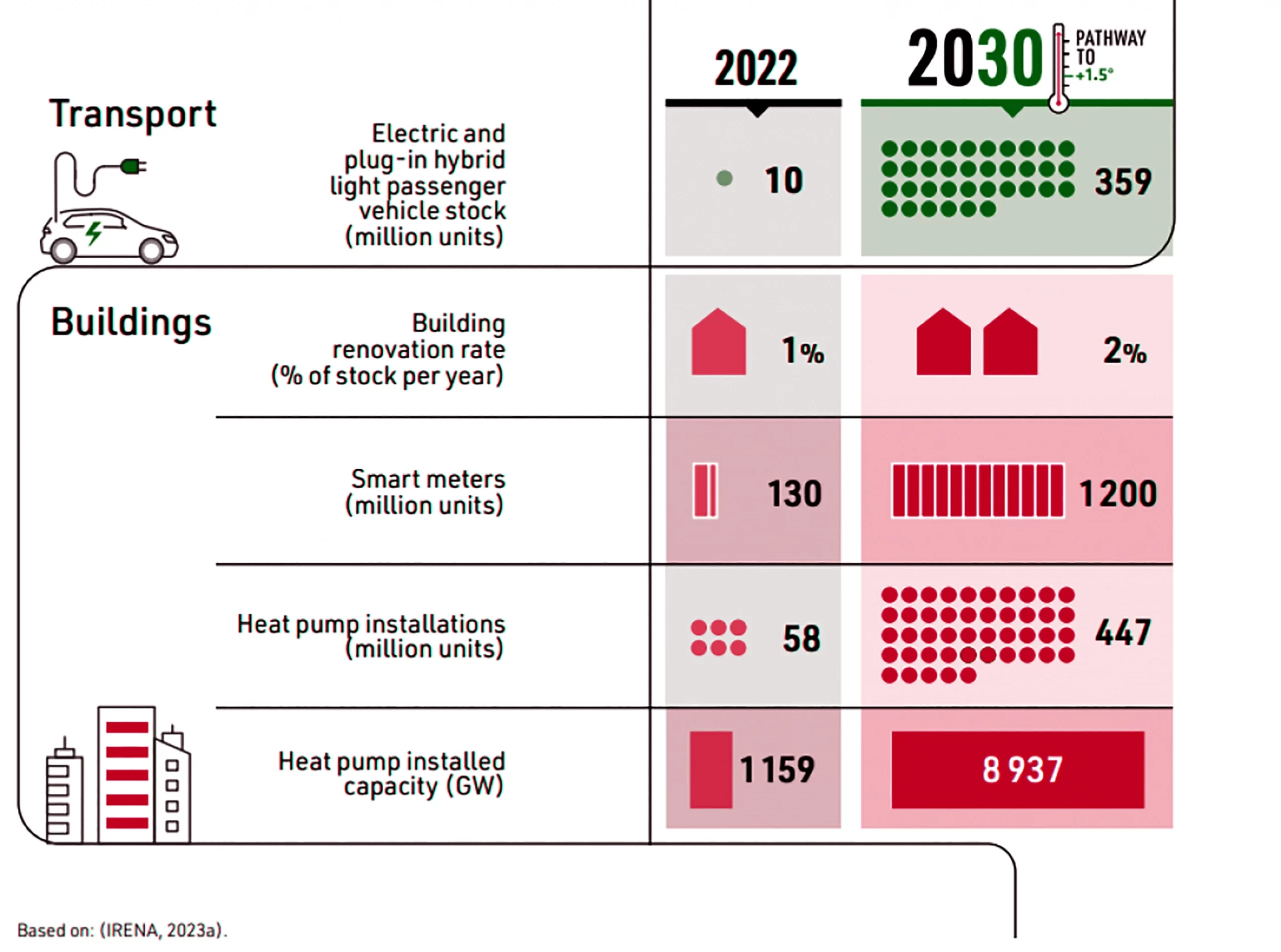
Global Stocktake
|
|---|
Source: Down to Earth
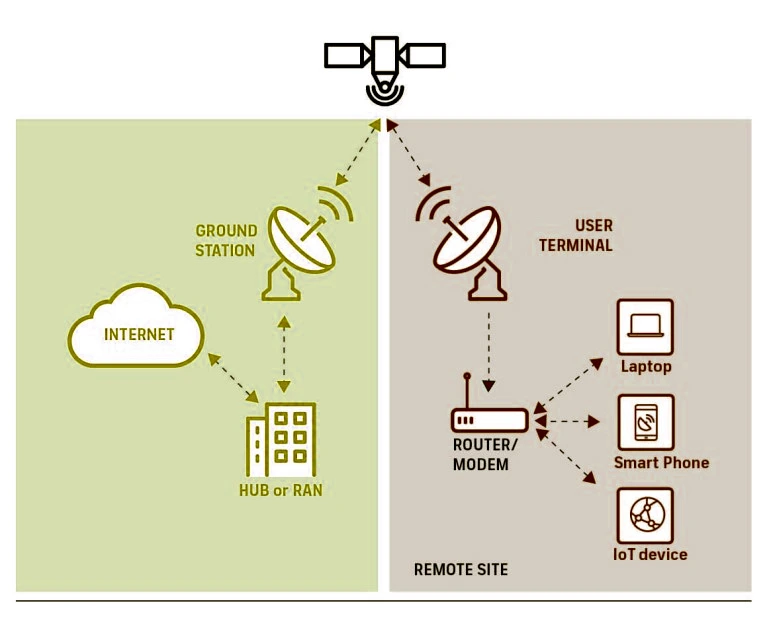
News Source: HinduBL
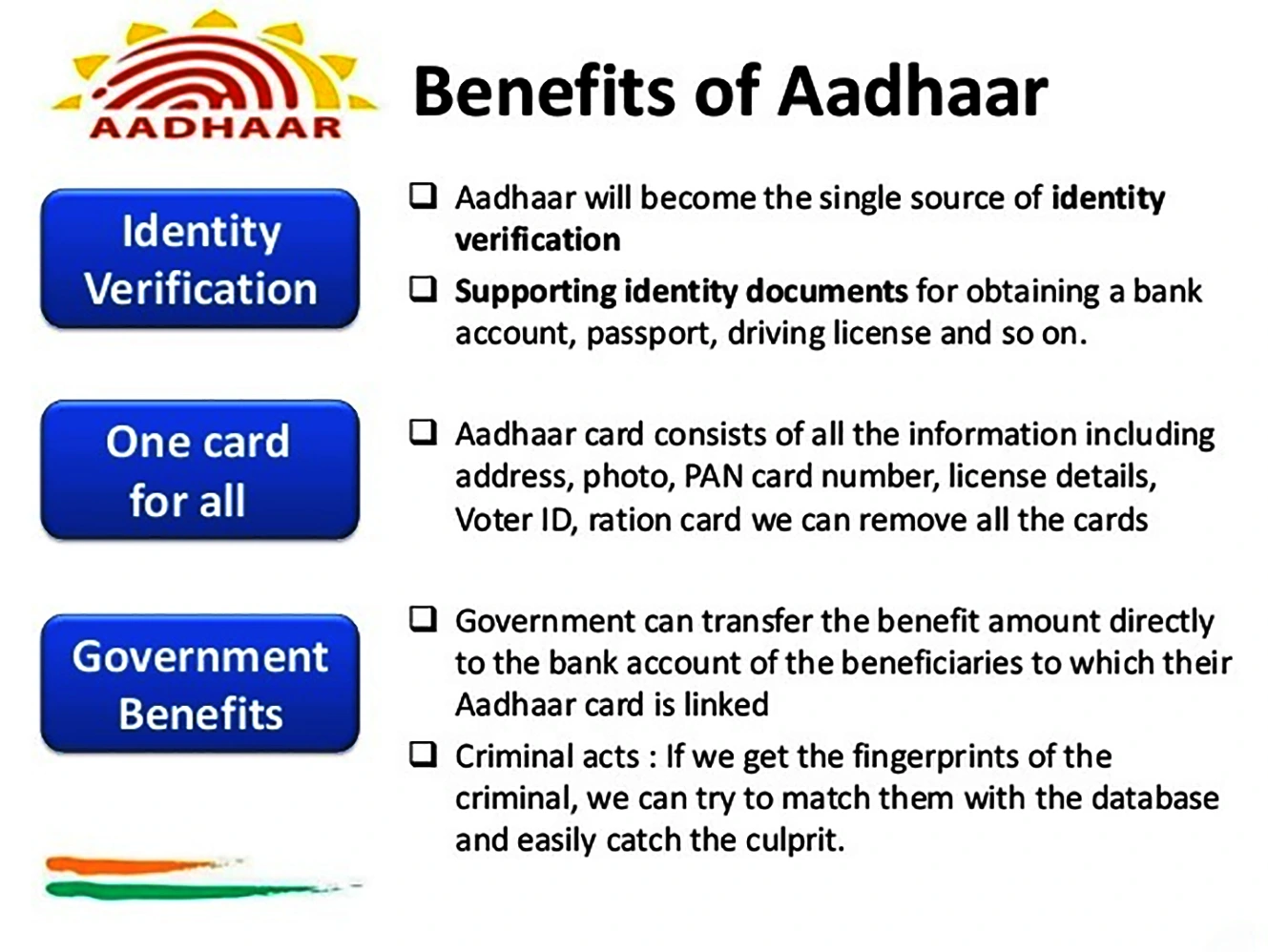
Unique Identification Authority of India (UIDAI)
|
|---|
Aadhaar-enabled Payment Services (AePS)
|
|---|
Also Read: Digital Personal DataProtection Bill 2023
The Aadhaar data breach highlights the importance of better security, oversight, and protective measures to safeguard personal information and ensure privacy rights.
| Prelims Question (2018)
Right to Privacy is protected as an intrinsic part of Right to Life and Personal Liberty. Which of the following in the Constitution of India correctly and appropriately imply the above statement? (a) Article 14 and the provisions under the 42nd Amendment to the Constitution (b) Article 17 and the Directive Principles of State Policy in Part IV (c) Article 21 and the freedoms guaranteed in Part III (d) Article 24 and the provisions under the 44th Amendment to the Constitution Ans: (c) |
|---|
| Mains Question: Examine the scope of Fundamental Rights in the light of the latest judgement of the Supreme Court on Right to Privacy. (250 words, 15 Marks) |
|---|
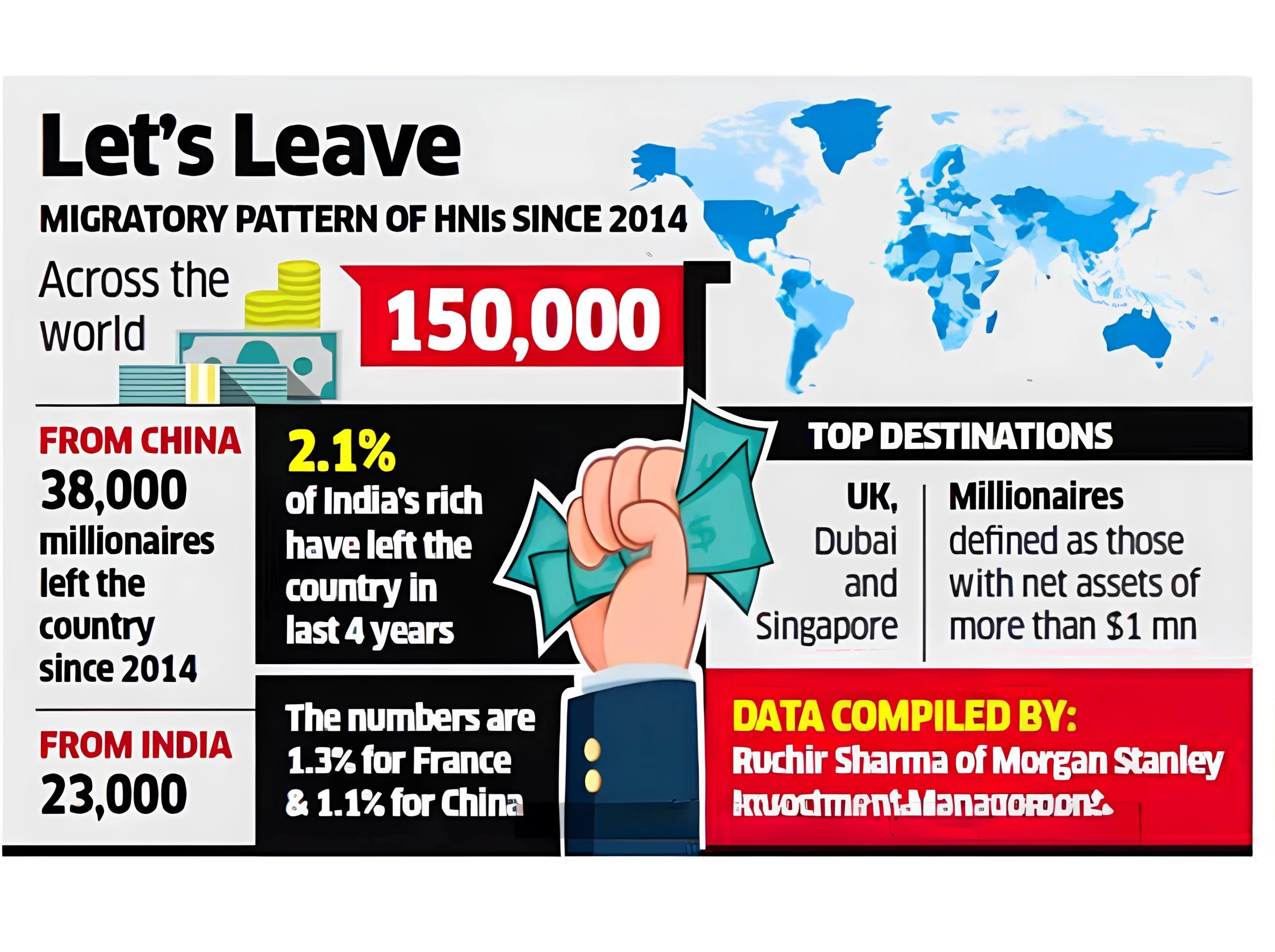
What is a Brain Drain?
Brain Drain V/S Brain Gain
|
|---|
There are several detrimental effects of brain drain on developing nations like India.
Government Initiative:
|
|---|
In addition to the above solutions, the government can also work to improve the overall quality of life in India. This includes investing in infrastructure, improving public services, and reducing corruption. By making India a more attractive place to live and work, the government can help to reduce brain drain and attract talent from around the world.
Also Read: International Migration Outlook 2023: Analysis of Trends, Impacts, and Challenges
Addressing the challenges of brain drain in India requires a comprehensive approach, encompassing investments in education, research, and innovation, along with favorable policies that create opportunities, improve quality of life, and ultimately transform the brain drain into a brain gain for the nation’s sustainable development.
| Mains Question: The Indian diaspora has scaled new heights in the West. Describe its economic and political benefits for India. |
|---|
SC Verdict on Newsclick Shows Adherence to Due Pro...
Stay Invested: On Chabahar and India-Iran Relation...
Credit Rating Agencies, Impact on India’s De...
Catapulting Indian Biopharma Industry
Globalisation Under Threat, US Import Tariffs Have...
Global Report on Hypertension, Global Insights and...
<div class="new-fform">
</div>
