Context: Nepal and India to establish a sister city relationship between Janakpur and Ayodhya.
Historic Agreement: Janakpur and Ayodhya to Become Twin Cities
What is a Sister City?
Janakpur- Ayodhya
Must Read: Punaura Dham Development Plan
News source: The Economic Times
Context: France President Emanuel Macron will attend the 75th Republic Day celebration 2024 as a chief guest.
Republic Day Chief Guest Protocol
Republic Day Chief Guest: Significance
India-France Relations: Bilateral, Strategic, Defence, Trade
Continue Reading: India-France Relationship
News source: The Indian Express
Context: New species of bacteria discovered by Visva- Bharati researchers being named after Nobel Laureate Rabindranath Tagore as “Pantoea Tagorei”.
Pantoea Tagorei: New Species Of Bacteria
About Pantoea Tagorei
|
About Rabindranath Tagore
|
|---|
Also Read: New Marine Amphipod Species Found In Chilika Lake
News Source: The Economic Times
Context: The Indian Government has issued the benchmark prices for non-torrefied biomass pellets to ensure faster procurement of biomass pellets for co-firing with coal in thermal power plants.
Fixed Benchmark Prices Boost Renewable Market Equity
What are Biomass Pellets?
Biomass Co-firing
Other Steps taken by the government for Renewable Energy:
Must Read: Renewable Energy Intermittency
Source: PIB
Context: India has voted in favour of another resolution at the UN General Assembly this week that backs the right of the Palestinian people to self determination.
Also Read: Understanding The Israel Palestine Conflict
What is the United Nations General Assembly (UNGA)?
Source: Economic Times
Context: External affairs ministry has announced that India extended 308 lines of credit to partner countries amounting to $32.02 billion over the years as part of its development assistance programme.
Source: Economic Times
Context: Kempegowda International Airport (KIA) Terminal 2, Bengaluru wins the UNESCO’s 2023 Prix Versailles award.
Kempegowda International Airport Terminal 2 Wins UNESCO’s 2023 Prix Versailles
About Prix Versailles
The United Nations Educational, Scientific and Cultural Organization (UNESCO)
Also Read: UNESCO’s World Heritage List, here. |
Terminal 2 or T2 of KIA
News source: The Hindu
Context: Every year, on December 22nd, the birth anniversary of legendary mathematician Srinivasa Ramanujan (1887-1920), is celebrated as National Mathematics Day.
About Srinivasa Ramanujan

|
“The Man Who Knew Infinity”:
Must Read: National Mathematics Day 2023, here. |
|---|
Srinivasa Ramanujan: A Chronology of his Achievements
Ramanujan: His Major Contributions to Mathematics
His Later Stage
News Source: The Indian Express
Context: Recently, the Lok Sabha passed the Press and Registration of Periodicals Bill 2023, which has already been passed by Rajya Sabha in the previous session.
Key Features of the Press and Registration of Periodicals Bill 2023
How the Press and Registration of Periodicals Bill 2023 differs from the Press and Registration of Books Act 1867?
Must Read: The Lok Sabha Passed The Post Office Bill 2023
News Source: PIB
Context: The Ministry of Youth Affairs & Sports announced the National Sports Awards 2023.
More on News:
National Sports Awards 2023 Winners List

|
About Tenzing Norgay National Adventure Award
|
|---|
News Source: PIB
Context: The International Organisation for Migration (IOM) launched Project PRAYAS (Promoting Regular & Assisted Migration for Youth and Skilled Professionals).
About Project PRAYAS
|
About International Organisation for Migration (IOM)
Global Compact for Safe, Orderly and Regular Migration (GCM)
Migration Governance Framework (MiGOF)
Indian Council of World Affairs:
|
|---|
Must Read: International Migration Outlook 2023
News Source: Economic Times
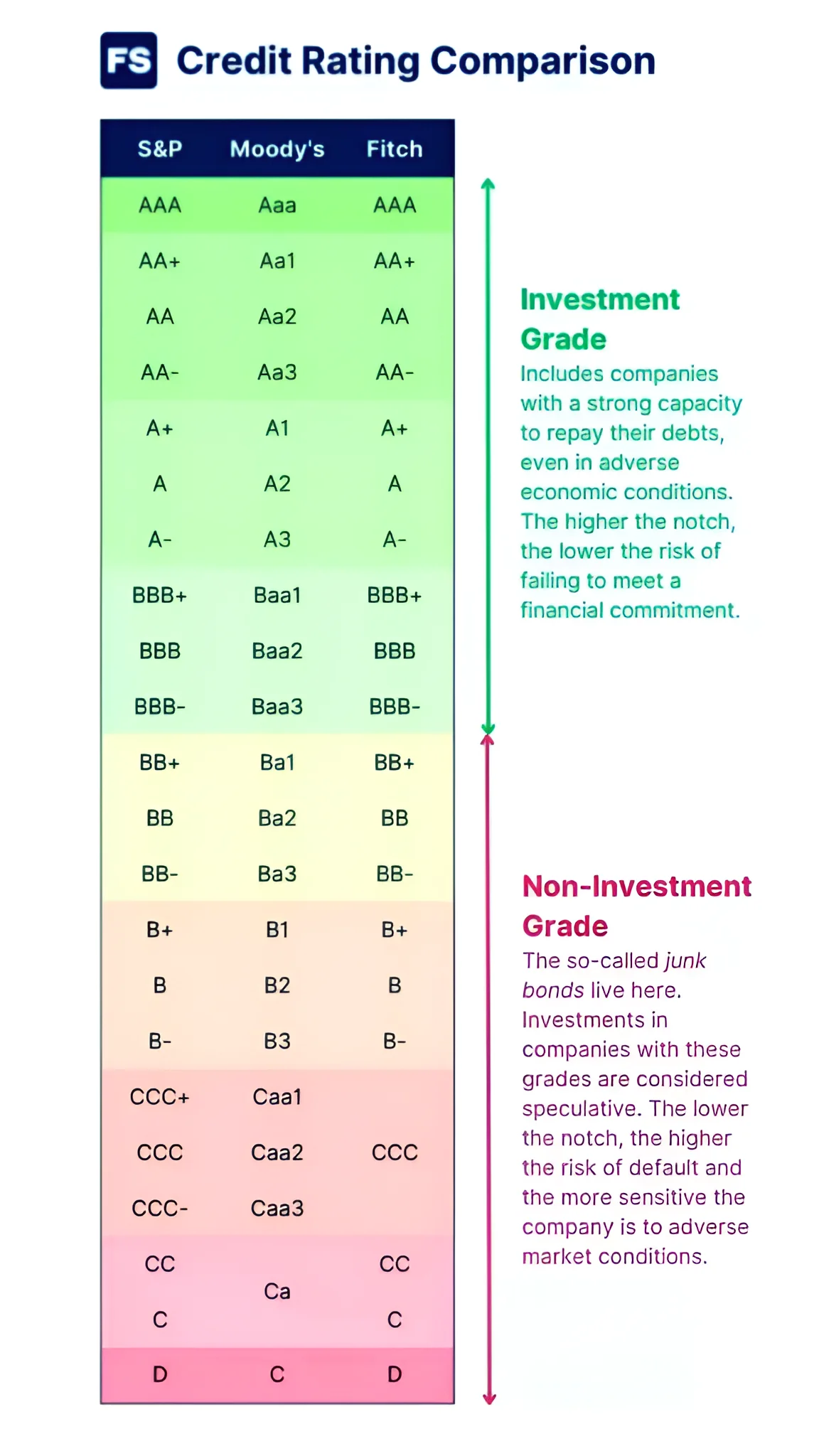
Context: This article is based on the news “Why has the Indian government criticised the methodologies of global credit rating agencies?” which was published in the Indian Express. The Finance Ministry released a document titled “Re-examining Narratives: A Collection of Essays,” to present alternative perspectives on various aspects of economic policy.
|
Relevancy for Prelims: Global Credit Rating Agencies: Moody’s, Standard & Poor’s and Fitch, and Securities and Exchange Board of India (SEBI). Relevancy for Mains: Global Credit Rating Agencies and How do they rate firms from developing countries? |
|---|
Reforming Sovereign Credit Rating Process Need of the Hour
About Credit Rating Agencies (CRAs)
 Functions of Credit Rating Agencies:
Functions of Credit Rating Agencies:
SEBI Regulations, 1999
|
About Sovereign Credit Rating
|
|---|
Also Read: SEBI To Introduce T+0 Trading Settlement System, here.
Significance of Credit Rating Agencies
Issues with the methodologies used by the rating agencies
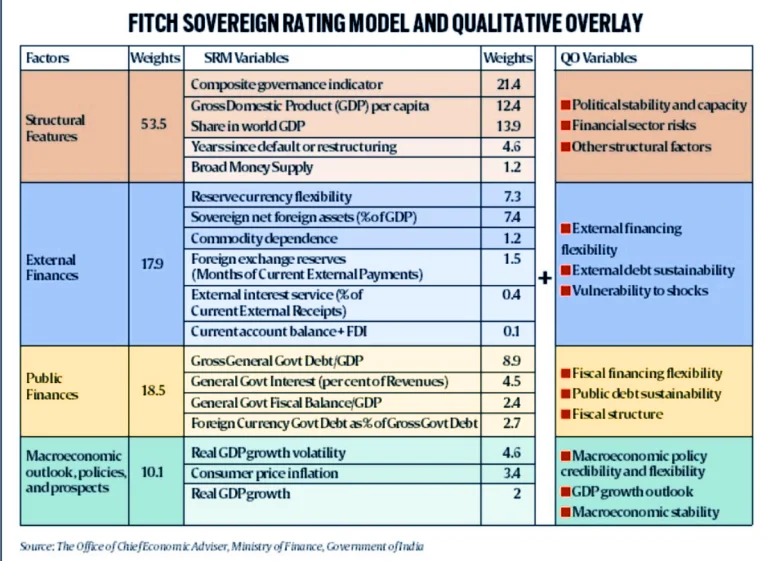
Other Challenges Faced by Credit Rating Agencies
|
About Infrastructure Leasing and Financial Services Limited (IL&FS) Crisis
|
|---|
Way Forward
Conclusion
The Indian government criticizes global credit rating agencies for biased methodologies, urging reforms and transparency to accurately assess developing economies and prevent conflicts of interest.
Context: Recently, the RBI Governor announced a proposal to establish data storage or Cloud Computing facilities for financial institutions in India.
|
Relevancy for Prelims: RBI, Financial Institutions in India, Indian Financial Technology & Allied Services (IFTAS), and Unified Payments Interface (UPI). Relevancy for Mains: RBI’s Cloud Computing Facilities for Financial Institutions: Significance, Challenges, and Way Forward. |
|---|
Cloud Computing Facilities for Financial Institutions: RBI
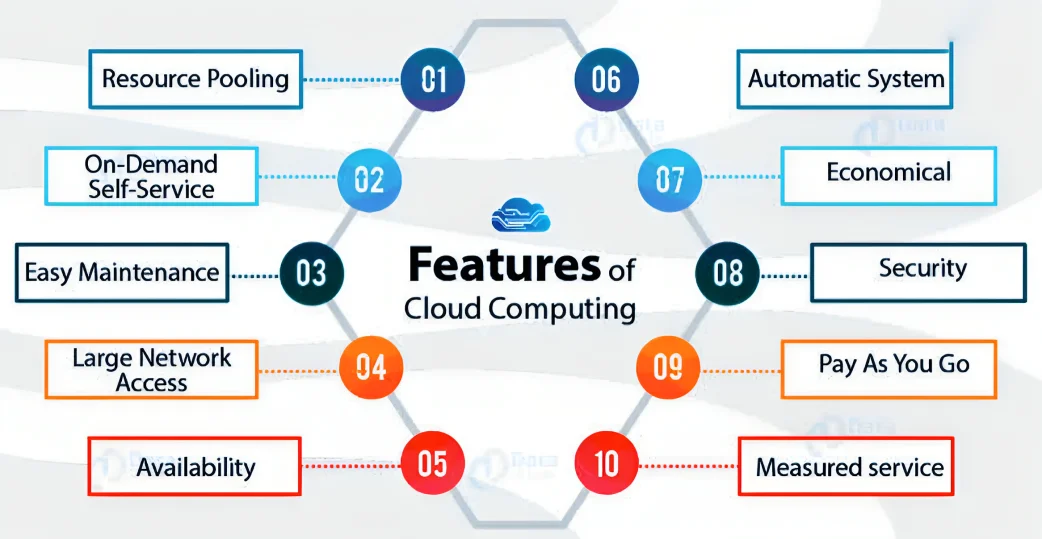
About Cloud Computing
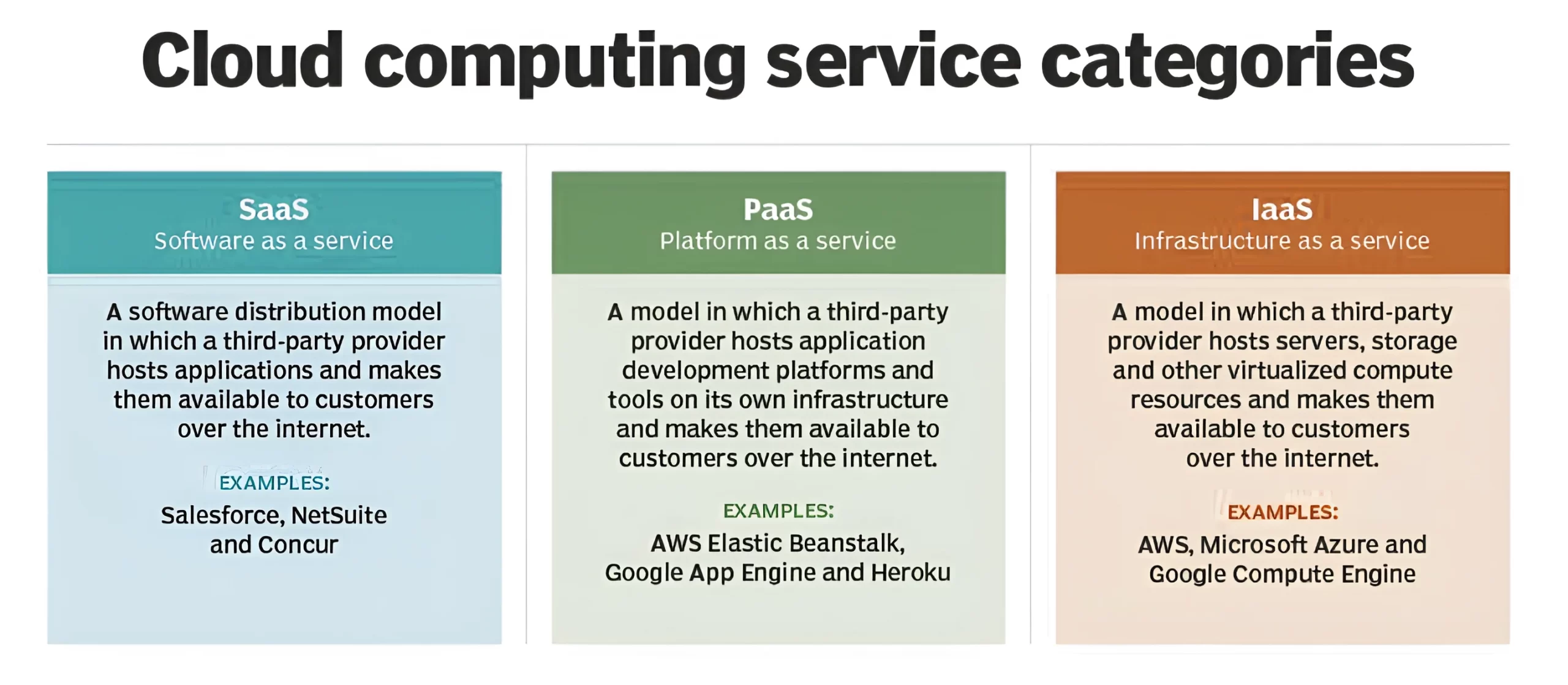
Must Read: RBI’s Direction To Credit Information Companies
Significance of Cloud Computing
Challenges Associated with Cloud Computing
|
Challenges: RBI and Cloud Computing
|
|---|
Way Forward
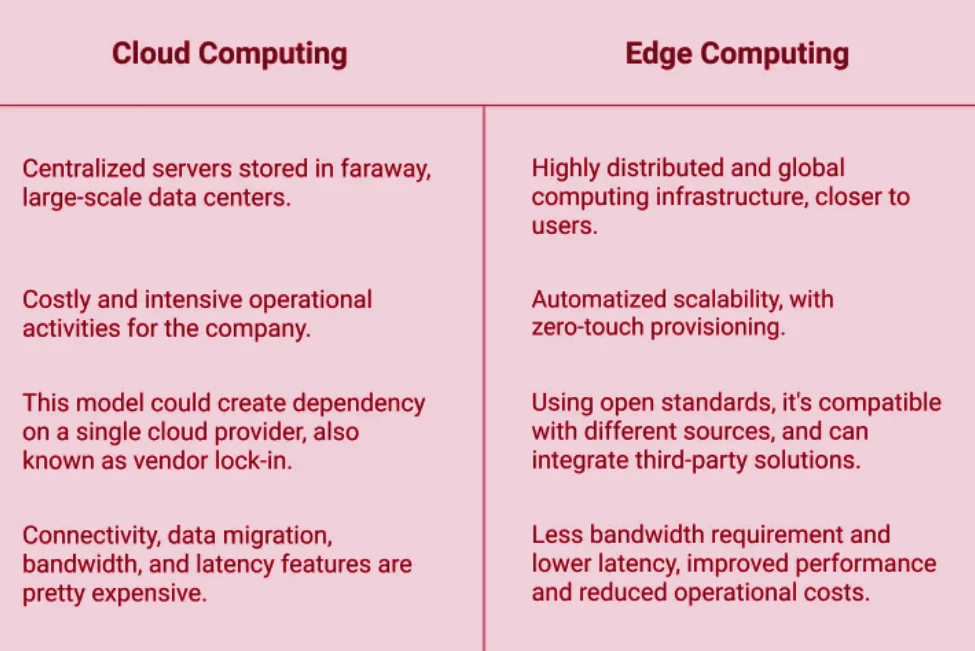
Conclusion
The RBI’s initiative to establish cloud computing facilities for financial institutions in India presents opportunities for enhanced data security, but challenges such as competition, security risks, and operational complexities need to be addressed through advanced security measures, integration with edge computing, and a focus on data governance and compliance.
SC Verdict on Newsclick Shows Adherence to Due Pro...
Stay Invested: On Chabahar and India-Iran Relation...
Credit Rating Agencies, Impact on India’s De...
Catapulting Indian Biopharma Industry
Globalisation Under Threat, US Import Tariffs Have...
Global Report on Hypertension, Global Insights and...
<div class="new-fform">
</div>
