Context: The modern sanitation system, designed to contain, convey, treat, and either dispose of or reuse the used water was built in London around the 1800s due to the emergence of industrialization-driven modern cities.
Sanitation Systems are usually determined based on the density of the population it is meant to serve.
Twin Pits:
|
Septic Tanks:
|
Sewage Treatment plant (STPs):
|
Faecal Sludge Treatment Plants (FSTPs):
|
News Source: The Hindu
Must Read: Progress on Household Drinking Water, Sanitation and Hygiene (WASH) 2000-2022
Context: Scientists’ predictions about how much dark energy is in the universe, based on their theories, are way off.
| Aspects | Dark Energy | Dark Matter |
| Proportion in Universe | Constitutes about 68% of the universe. | Makes up approximately 27% of the universe. |
| Role | Acts as a repulsive force, driving the expansion of the universe. | Exerts gravitational attraction, holding galaxies together. |
| Visibility | Cannot be directly observed; remains elusive. | Cannot be directly observed; detected through gravitational effects. |
| Discovery | Discovered in 1998, following observations of accelerating cosmic expansion. | Proposed as early as the 1920s based on gravitational effects |
Must Read: ISRO To Launch Chandrayaan 4 Mission
Source: The Hindu
Context: Experts are predicting that the disinvestment target for the current fiscal year is again likely to be missed due to the upcoming General Elections.
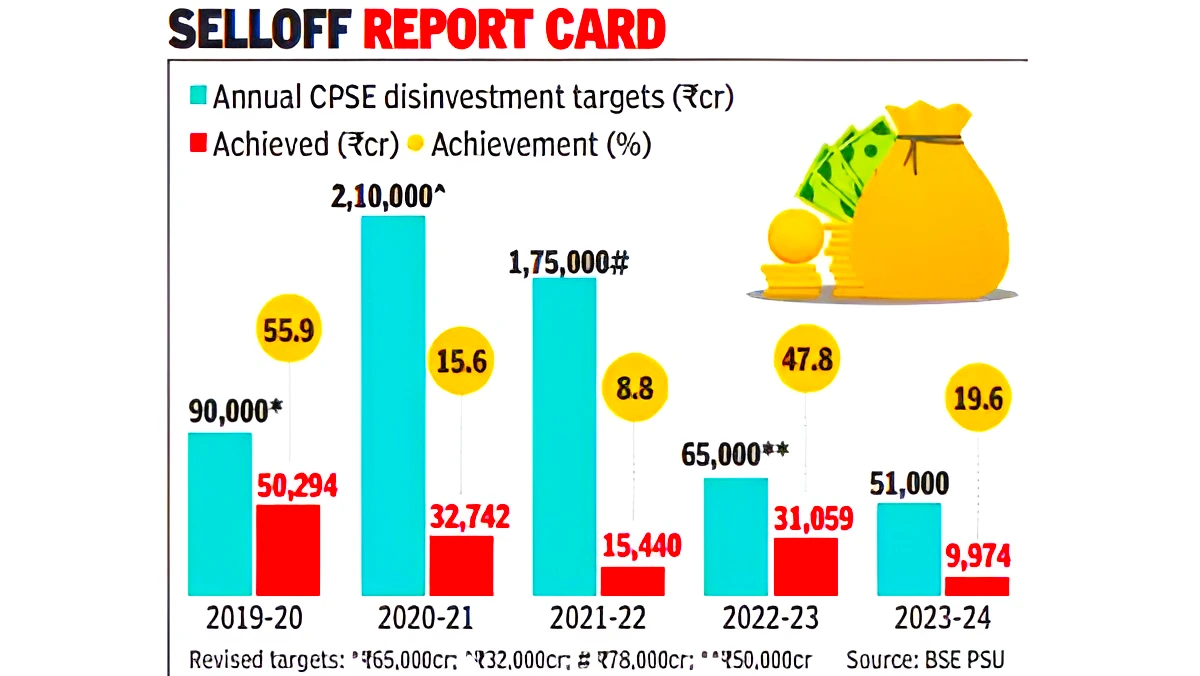 Most of the collection this financial year has been through minority stake sales via IPO (Initial Public Offering) and OFS (Offer For Sale).
Most of the collection this financial year has been through minority stake sales via IPO (Initial Public Offering) and OFS (Offer For Sale).Two-fold classification of economic sectors, to guide the policy for Disinvestment:
Must Read: Viksit Bharat @2047: Voice Of Youth Workshop
Source: The Hindu
Context: Veer Bal Diwas 2023: 26th December will be celebrated as ‘Veer Baal Diwas’ in honor of the 4 martyred sons of the 10th Sikh Guru, Guru Gobind Singh to pay homage to their courage and martyrdom.
Continue Reading: Veer Bal Diwas 2023
4 Sahibzades
About Guru Gobind Singh
|
|---|
News Source: The Hindu
Context: India and ASEAN will begin negotiations in February 2024 to modernize their old free trade agreement (FTA).
What is Free Trade Agreement (FTA)?
|
|---|
Read More about ASEAN-India Trade
Source: Business Line
Context: Chemical tanker MV Chem Pluto was hit by a drone attack roughly 200 nautical miles (370 km) off Gujarat coast.
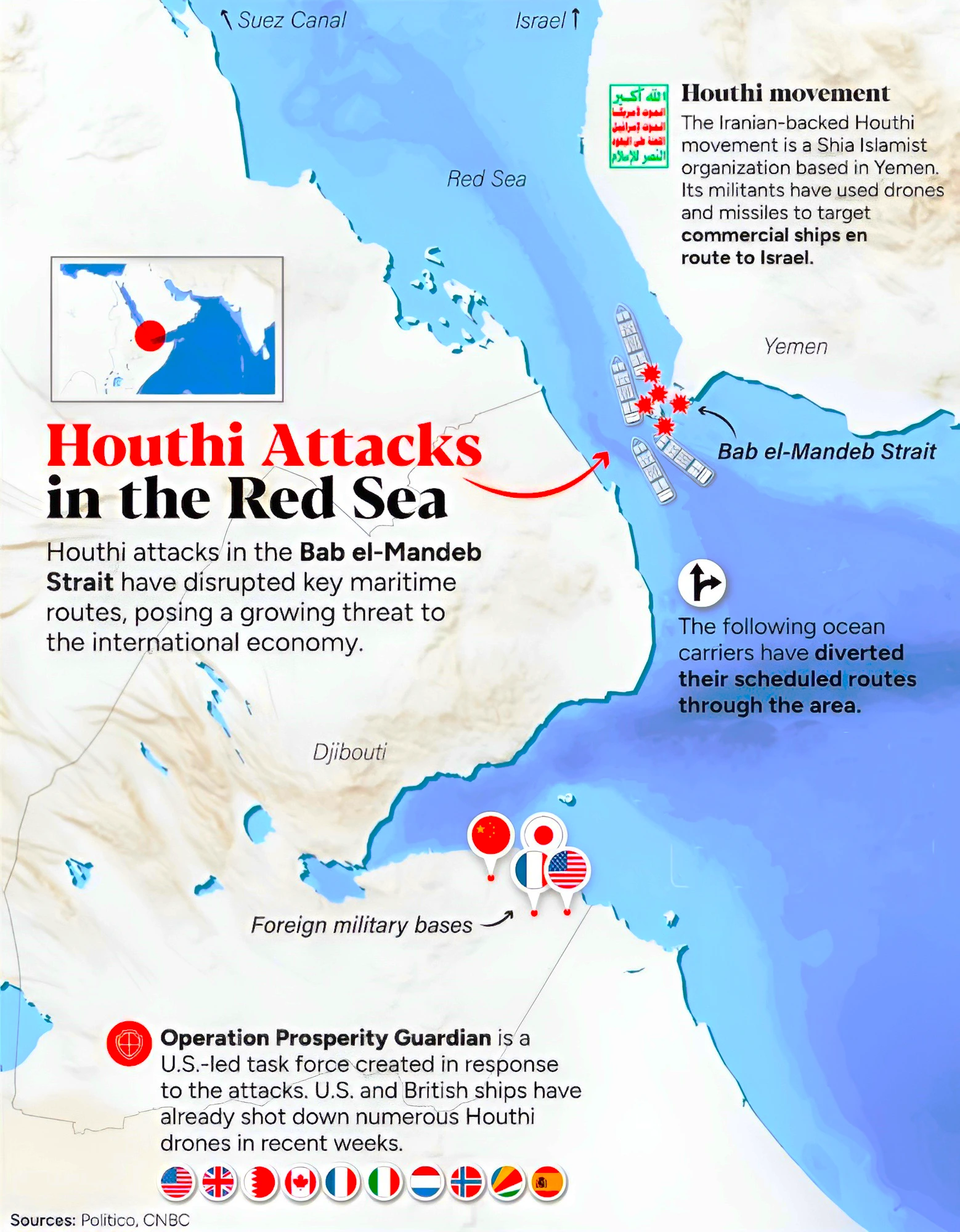
Continue Reading: How Are Houthi Attacks On Ships In The Red Sea Affecting Global Economy?
About Suez Canal
About Operation Prosperity Guardian
|
|---|
News Source: Indian Express
Context: First Rupee Payment for Oil to UAE: Recently, the Indian Oil Corporation (IOC) paid Indian rupees for the purchase of a million barrels of crude oil from Abu Dhabi National Oil Company (ADNOC).
Continue Reading: Internationalisation Of Rupee
News Source: Financial Express
Context: Union Minister Dr Jitendra Singh launched the Extended Version of Mission Karmayogi on Good Governance Day.
Good Governance Day
Continue Reading: Good Governance Day 2023, here. |
|---|
| About Mission Karmayogi
The National Programme for Civil Services Capacity Building (‘NPCSCB’) – “Mission Karmayogi” was launched to enhance governance through Civil Service Capacity Building. It has six pillars:-
Institutional framework and programme implementation
Continue Reading: Mission Karmayogi, here. |
|---|
News Source: PIB
Context: In a research paper recently published by RBI officials, they have claimed that the risk of stagflation in India has further lowered to 1%, compared to 3% in August.
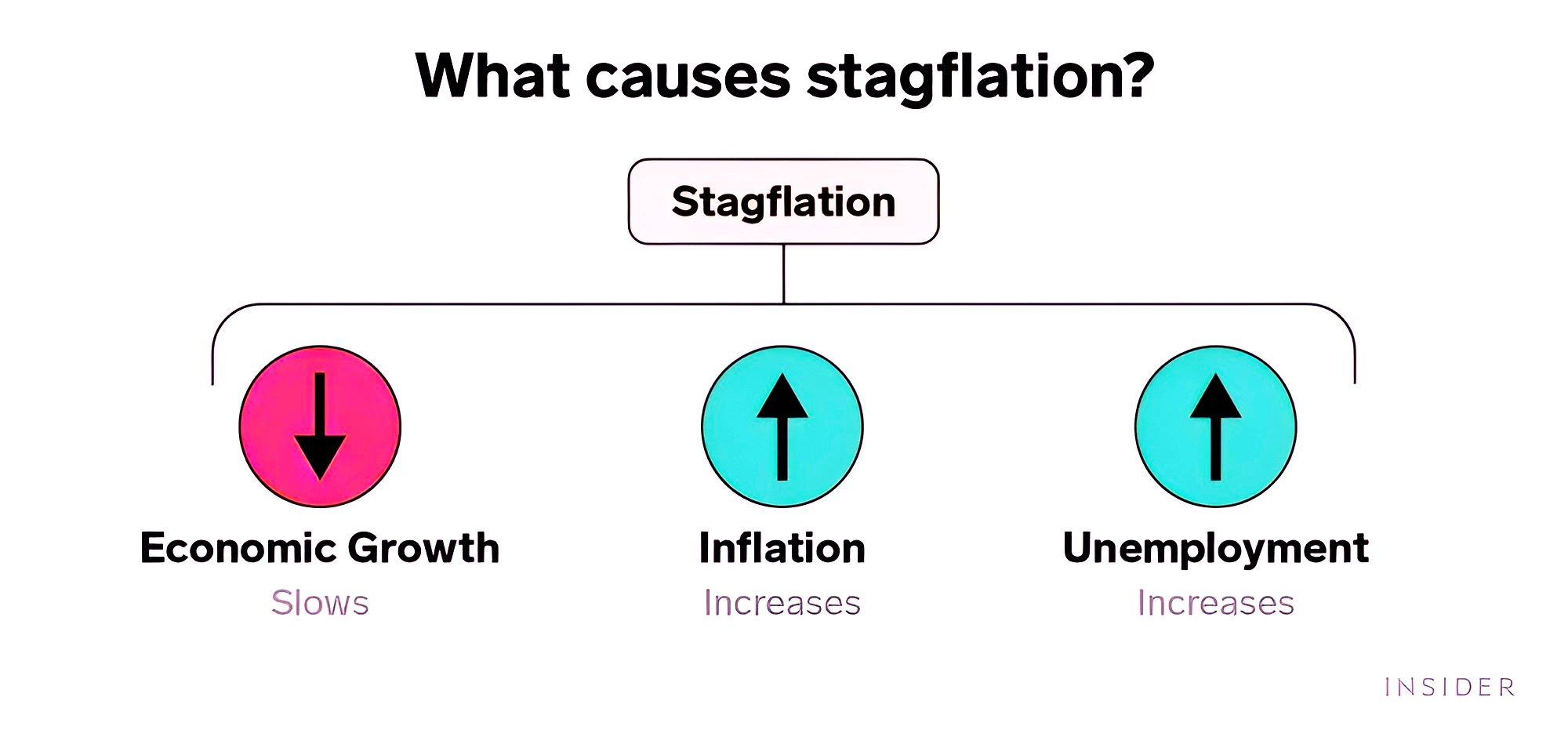
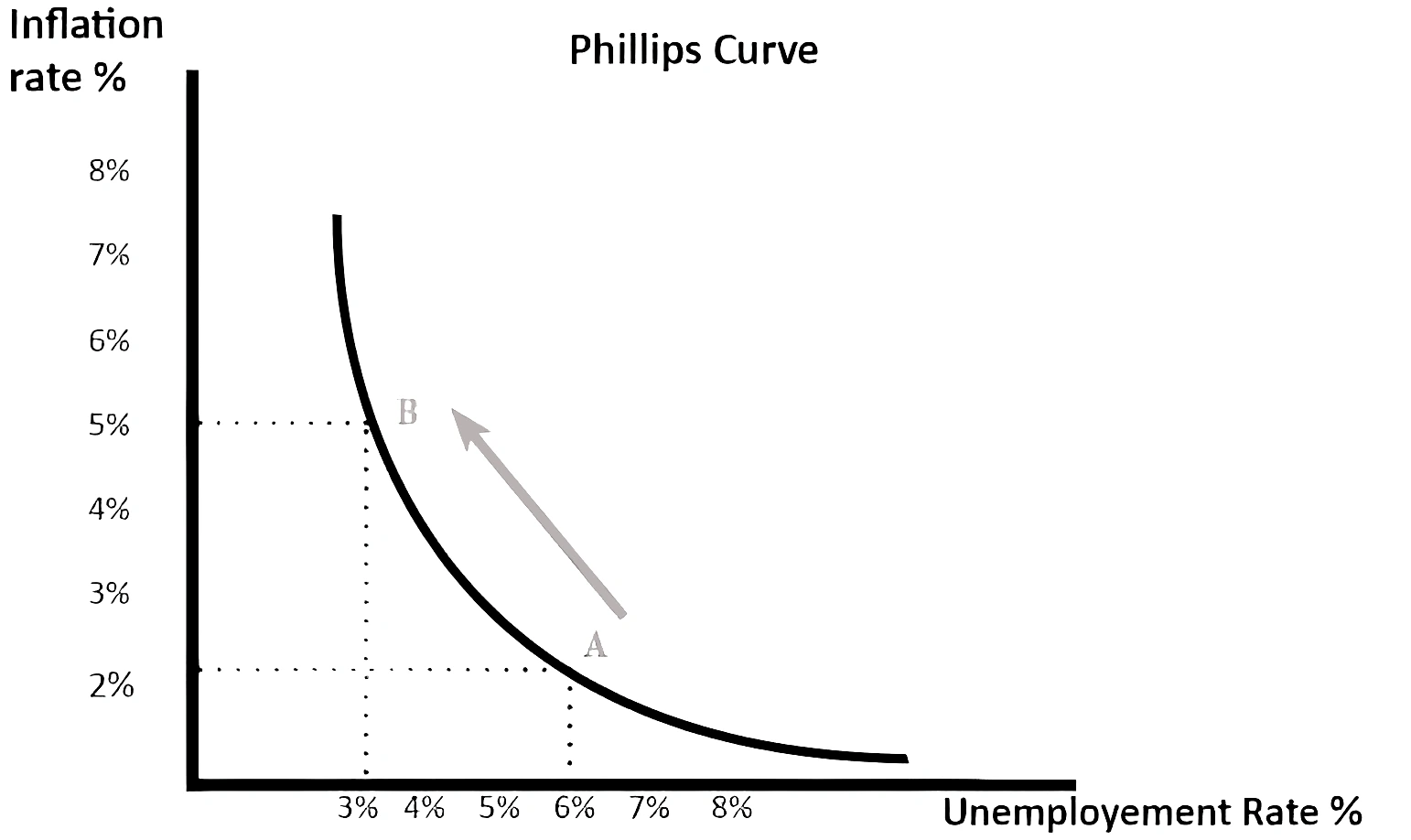 Causes:
Causes: Must Read: RBI Monetary Policy Committee’s Status Quo on Repo Rates and Policy Stance
Source: The Hindu
Context: Tiger Deaths in India 2023: According to the National Tiger Conservation Authority (NTCA), 168 tigers died in India in 2023, till December 15, 2023.
About National Tiger Conservation Authority (NTCA):
About Wildlife Protection Society of India (WPSI):
|
|---|
Must Read: 50th Anniversary Of Project Tiger
About Jim Corbett National Park:
|
|---|
To Read more about Aftermath of Cheetah Relocation, here.
News Source: Live Mint
Context: Recently, the Chief Minister of Himachal Pradesh inaugurated the newly-constructed Sanjauli-Dhalli tunnel.

Also Read: Analysis Of The Uttarakhand Silkyara Tunnel Collapse
News Source: Pioneer
Context: This article is based on the news “Govt suspends new wrestling panel: Being run from Brij Bhushan’s premises” which was published in the Indian Express. The Union Sports Ministry suspended the newly-elected committee of the Wrestling Federation of India (WFI).
| Relevancy for Prelims: Wrestling Federation of India (WFI), Indian Olympic Association (IOA), Sports Authority of India (SAI), and Prevention of Sexual Harassment at Workplace (POSH) Act 2013,
Relevancy for Mains: Sports Governance in India: Challenges, Government Initiatives, and Way Forward. |
|---|
Must Read: National Sports Awards 2023
|
|---|
Prevention of Sexual Harassment at Workplace (POSH) Act 2013
Mary Kom Committee
|
|---|
Also Read: Doping In Indian Sports: NADA’s Ineffectiveness Exposed
Government Initiatives to Promote Sports
|
|---|
Respecting sports governance standards is essential to guaranteeing accountability, openness, and fair play. Building trust with athletes, stakeholders, and the general public depends on them. Thus, immediate and stringent corrective measures are needed to uphold the principles of good governance in sports organisations.
Context: This article is based on the news “Global equations have a symbolic role in building a developed India by 2047” which was published in the Live Mint. In early 2024, the Indian Prime Minister is expected to unveil the Vision India@2047 document to transform India into a developed nation with a $30 trillion economy by 2047.
| Relevancy for Prelims: Vision India@2047 document, Amrit Kaal, NITI Aayog, and 2024 Asia-Pacific Human Development Report.
Relevancy for Mains: Vision India@2047: India’s Economic Aspirations for 2047: Challenges, and Way Forward. |
|---|
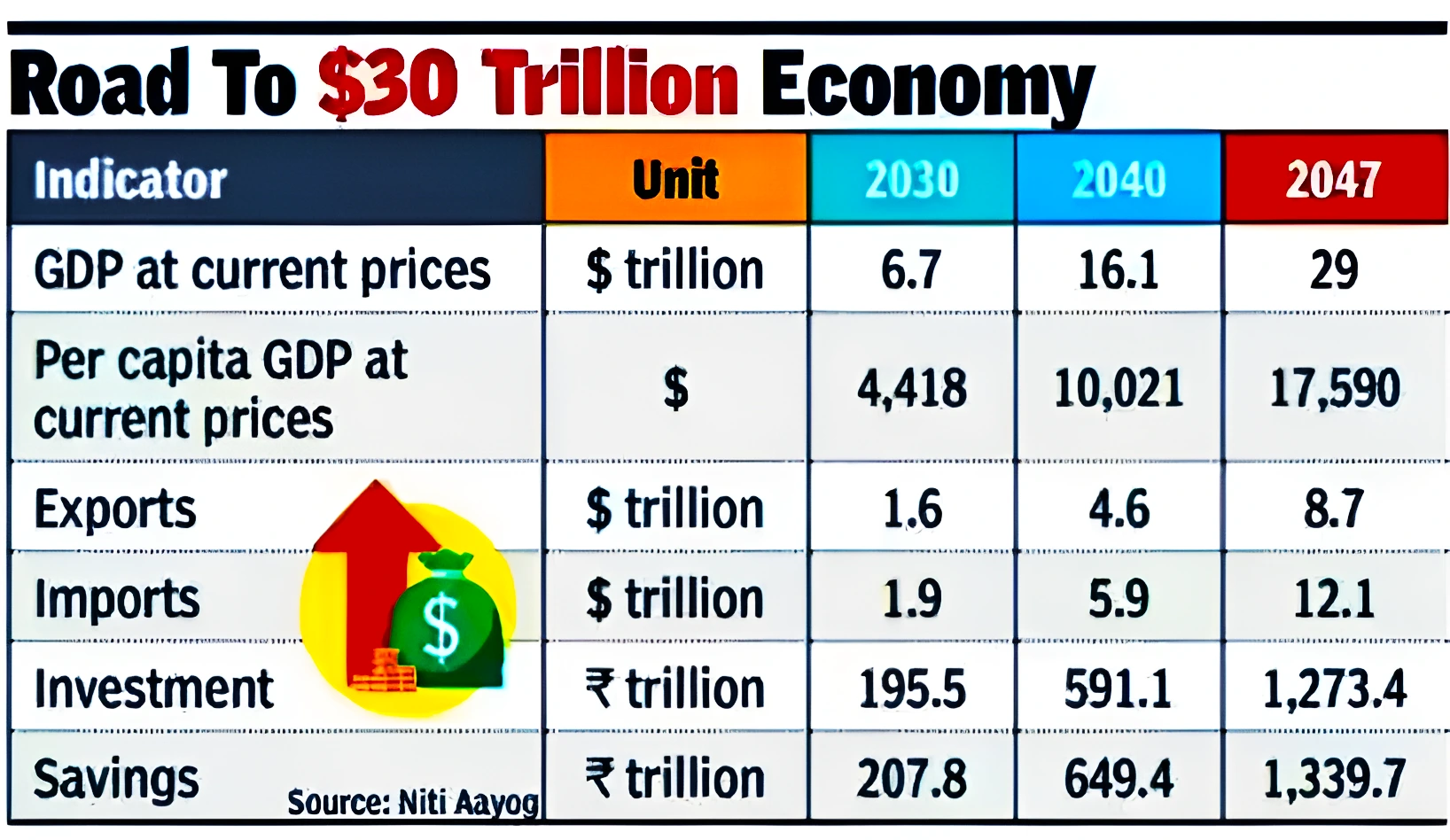 Major Themes for 2047: These include infrastructure, welfare, commerce and industry, technology, and governance.
Major Themes for 2047: These include infrastructure, welfare, commerce and industry, technology, and governance.Continue Reading: Viksit Bharat @2047: Voice Of Youth Workshop
About Amrit Kaal
|
|---|
Must Read: Periodic Labour Force Survey (PLFS) Annual Report 2022
Vision India@2047 presents a comprehensive roadmap for transforming India into a developed nation with a $30 trillion economy, addressing challenges through strategic planning, inclusive growth, and harnessing the nation’s strengths for a prosperous future.
Context: The Veerashaiva Mahasabha has urged the community members not to describe themselves as Hindu in the forthcoming population census.
About Veerashaivas
Also Read: Sister City Relationship Between Janakpur And Ayodhya
News Source: The Hindu
Context: In the first evidence of rapid evolution, scientists have discovered a flower growing in Paris, France, is producing less nectar and smaller flowers to attract fewer pollinators.
Study: Flowers are Starting to Self Pollination Due to Fewer Insects
What is the resurrection approach in ecology?
About Evolution:
|
About Pollination
Also Read: Plants Can Listen Damage To Other Plants
News Source: DTE
SC Verdict on Newsclick Shows Adherence to Due Pro...
Stay Invested: On Chabahar and India-Iran Relation...
Credit Rating Agencies, Impact on India’s De...
Catapulting Indian Biopharma Industry
Globalisation Under Threat, US Import Tariffs Have...
Global Report on Hypertension, Global Insights and...
<div class="new-fform">
</div>
