Context: Seychelles recently declared a state of emergency in response to a blast at an explosives stockpile triggered due to flooding.
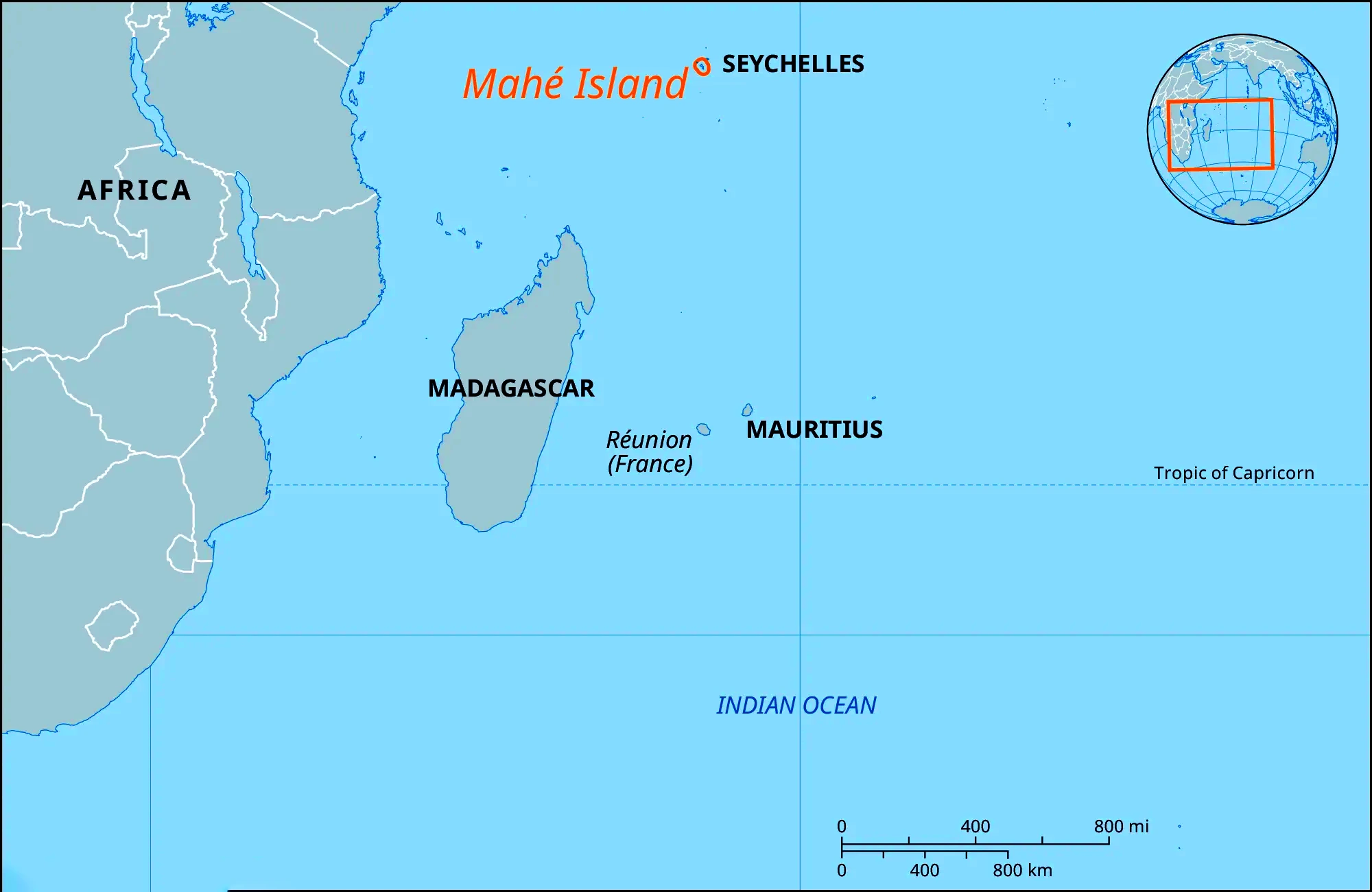 UNESCO World Heritage Sites in Seychelles:
UNESCO World Heritage Sites in Seychelles:
News Source: Financial Express
Context: The central government banned the use of sugarcane juice and sugar syrup for ethanol production in the 2023-24 supply year to ensure adequate sugar availability and control prices.
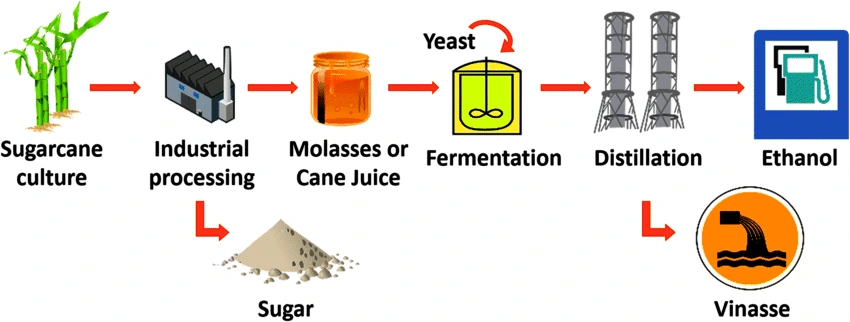
| Sugar sector in India:
Regional Production: Uttar Pradesh and Maharashtra, the primary sugarcane-growing states, contribute to approximately 65 percent of the total sugarcane cultivation area. Key sugarcane-producing states: Uttar Pradesh (225.2 million tonnes), Maharashtra (123.9 million tonnes), Karnataka (62.5 million tonnes), Tamil Nadu (16.9 million tonnes) and Bihar (12.1 million tonnes). Export share: India stands as the second-largest sugar exporter worldwide. By Product of Sugar Industry: Bagasse, Molasses and filter muds. Read more about Sugarcane Production In India here. |
|---|
Must Read: Global Biofuel Alliance: Advancing Sustainable Energy
Source: Indian Express
Context: The Indian Pharmacopoeia Commission (IPC) issued a drug safety alert regarding the common painkiller, Meftal.
The Indian Pharmacopoeia Commission (IPC)
Chairperson: The Secretary, Ministry of Health and Family Welfare. Mandate:
Pharmacovigilance Programme of India:
|
|---|
Source: Livemint
Context: United Nations Secretary-General Antonio Guterres has invoked Article 99 of the UN Charter in a bid to establish a ceasefire amid Israel’s ongoing military attacks on the Gaza Strip, particularly in its southern region.
UNSC:
UN- Secretary General:
|
|---|
Must Read: UNSC Reforms For A New Era; What The World Thinks
| How does a Humanitarian ceasefire different from Humanitarian Pause ?
Humanitarian Pause: The United Nations defines a “humanitarian pause” as a “temporary cessation of hostilities purely for humanitarian purposes”.
Humanitarian Ceasefire: The UN defines it as a “suspension of fighting agreed upon by the parties to a conflict, typically as part of a political process”, with the goal being to “allow parties to engage in dialogue, including the possibility of reaching a permanent political settlement”. |
|---|
Source: Indian Express
Context: Recently, Google has launched a project “Gemini,” a new multimodal general artificial intelligence (AI) to exhibit human-like behavior.
News Source: The Indian Express
Context: Recently, the Union Minister of Earth Sciences has informed Lok Sabha that the earthquake activity in the year 2023 increased and it was mainly attributed to the activation of the Almora fault in Western Nepal.
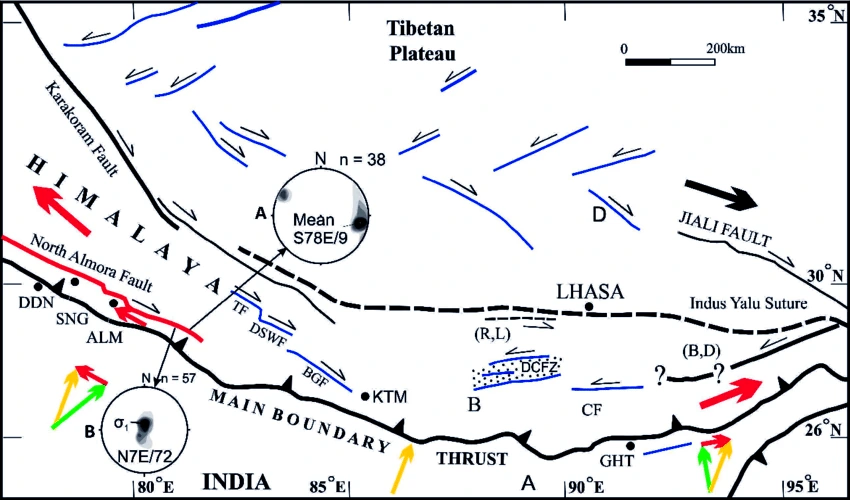
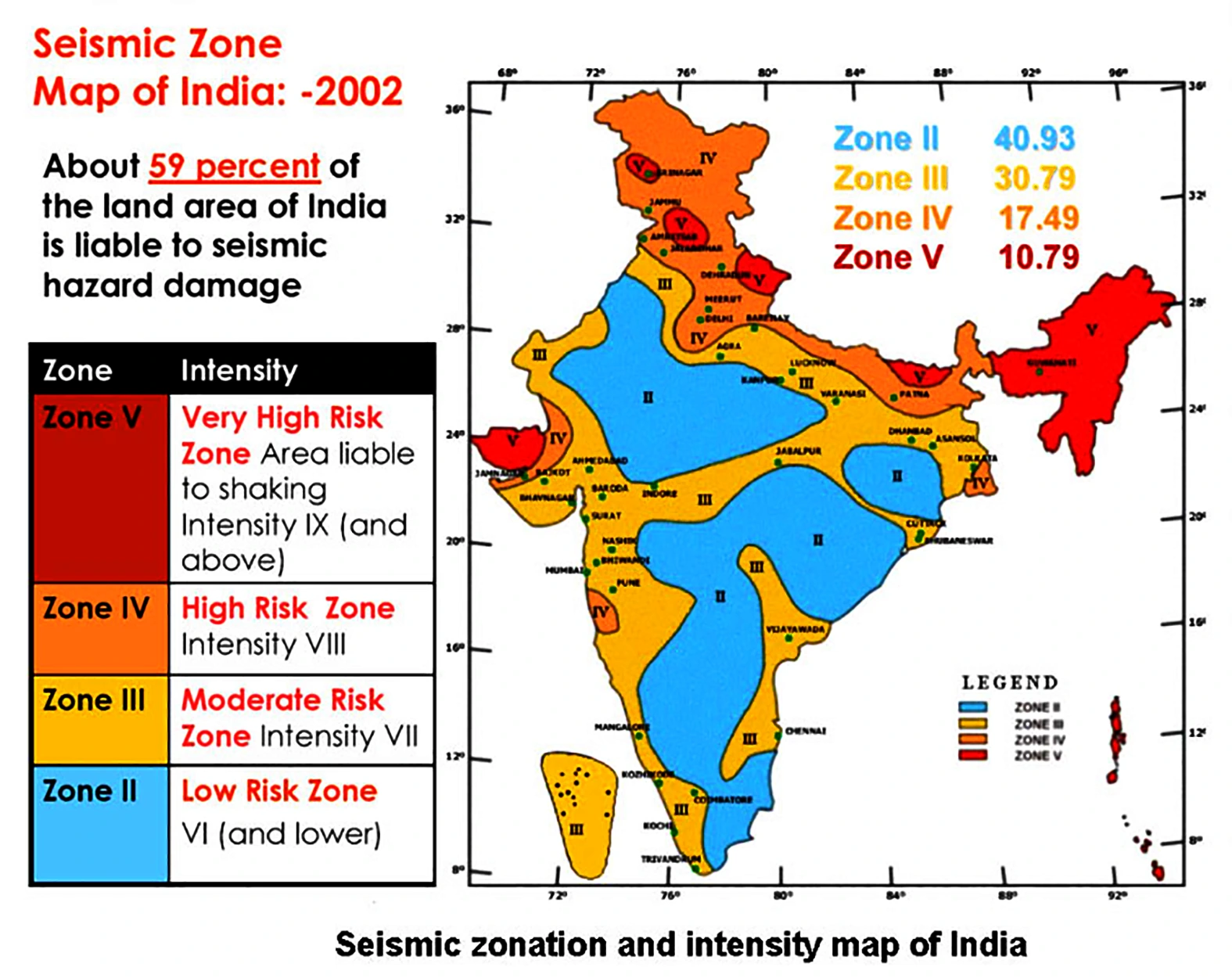
News Source: Livemint
Context: Recently, India’s first Pompe disease patient passed away after battling the disease.
Pompe Disease: Also known as Glycogen Storage Disease Type II, is a rare genetic disorder caused by a deficiency of the enzyme Acid alpha-glucosidase (GAA).
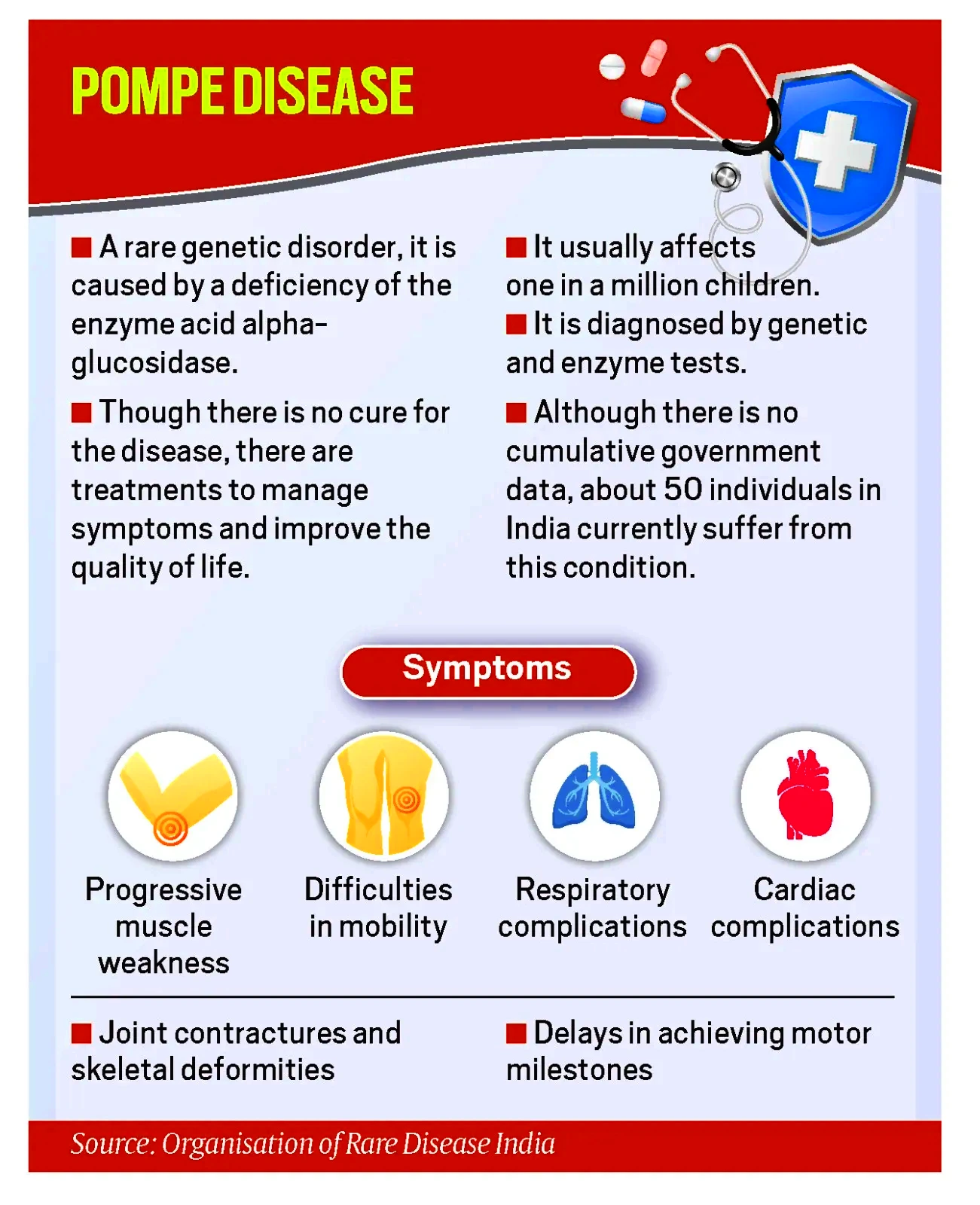
About Rare Diseases:
Must Read: Production Of Drugs To Counter Rare Diseases |
|---|
News Source: IE
Context: The draft text on the Santiago Network has been adopted by the Parties and sent to the Conference of the Parties and Conference of the Parties serving as the meeting of the Parties to the Paris Agreement (COP/CMA).
COP (Conference of Parties):
Must Read: COP28 Climate Summit In Dubai |
|---|
Also Read: Loss And Damage Fund Approved At COP28 Summit
News Source: DTE
Context: Italy has formally withdrawn from China Belt and Road initiative (BRI). Italy, a member of the European Union and NATO, signed up BRI in 2019 under the government of then Prime Minister Giuseppe Conte.
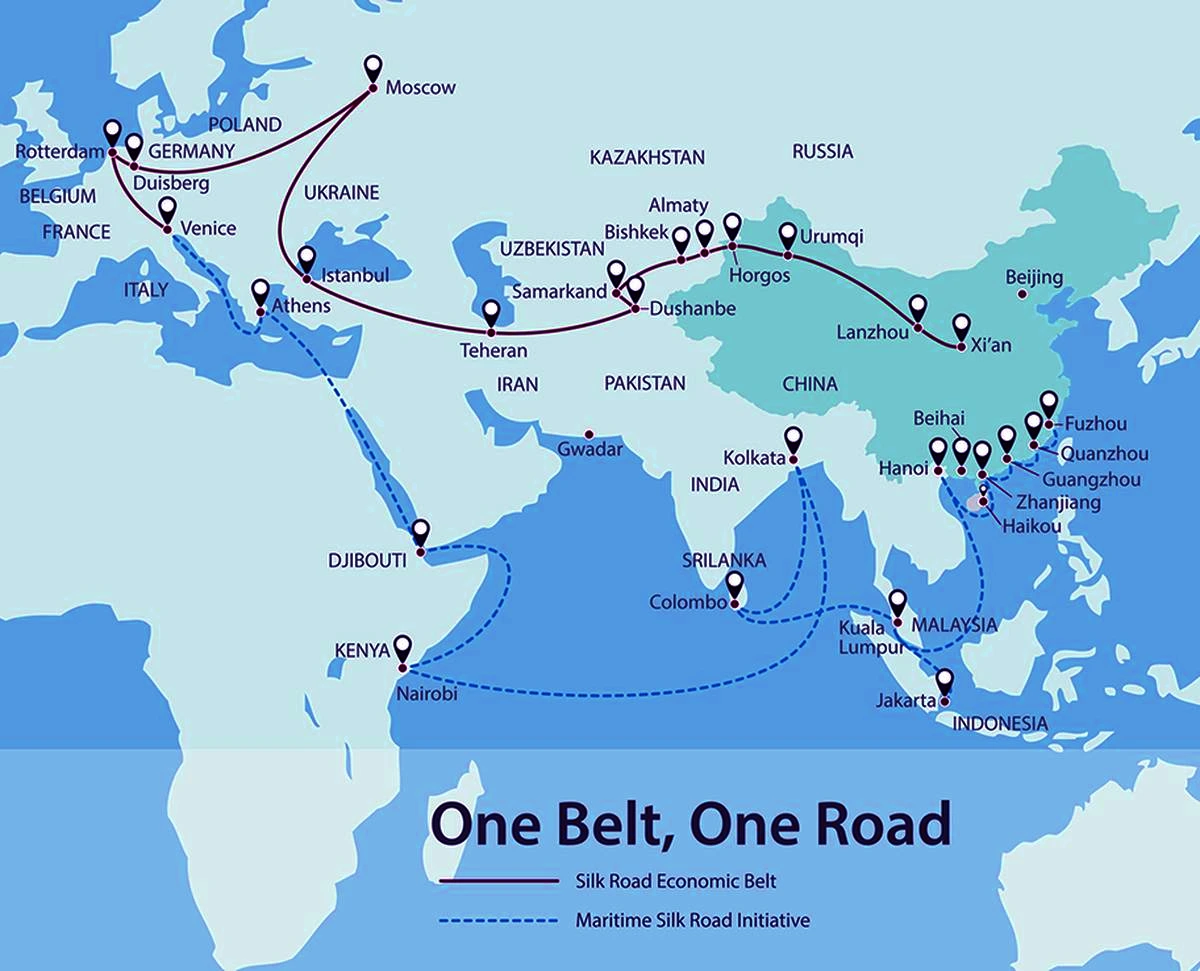
Must read the linked article China Celebrating 10th Anniversary of Belt and Road Initiative here.
Context: The World Meteorological Organization (WMO) recently released the State of Climate Services for health report.
| Relevancy for Prelims: State of Climate Services for Health Report, WMO, Green Climate Fund (GCF), Global Framework for Climate Services (GFCS), UNDP, United Nations Framework Convention on Climate Change (UNFCCC), and National Framework For Climate Services (NFCS).
Relevancy for Mains: Key findings of the State of Climate Services for Health Report, impacts of climate change on health, Global Climate Policies, Benefits of Climate Services for Health, Challenges and solutions to implementing them. |
|---|
Global Framework for Climate Services (GFCS):
|
|---|
Know more about State Of Climate Services Report 2023 – WMO here.

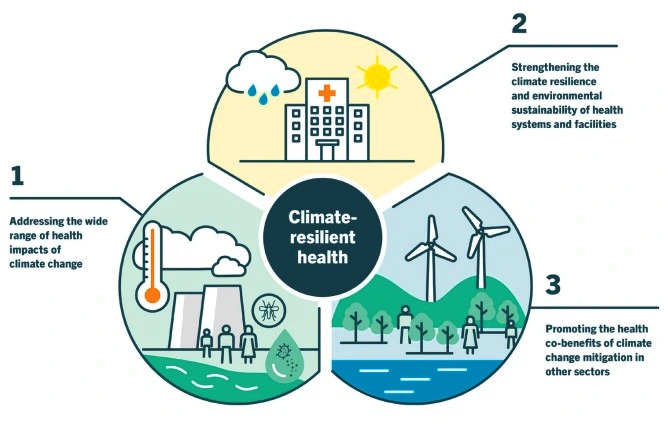
Also Read: NDC Synthesis Report For 2023: UNFCCC
| Case Study:
Social Safety Net System Project (SSNSP) of Mauritania:
|
|---|
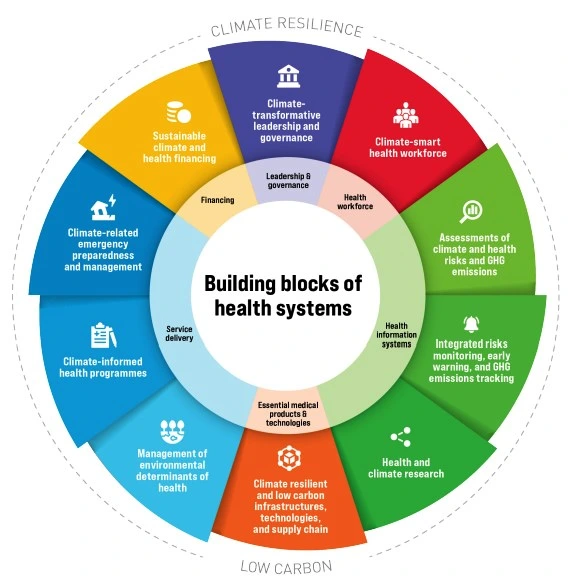
Addressing the impacts of climate change on health requires collaborative efforts, enhanced climate services, and improved integration of climate information into health policies, emphasizing the need for proactive measures and informed decision-making to build climate-resilient and healthier communities globally.
| Mains Question: Climate Change has made healthcare a bigger concern for Disadvantaged communities” Comment (150 words, 10 Marks) |
|---|
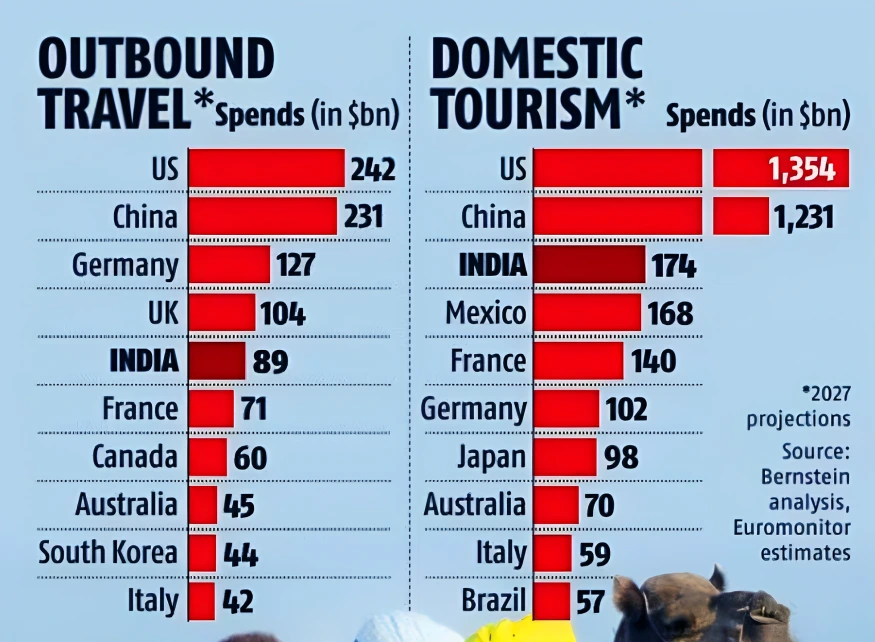
Context: This article is based on the news “India on course to become 5th-largest market for travel and tourism” which was published in the Business Standard. According to a report by Bernstein, India is ready to become the next big travel market in the world, projected to hit the 5th rank in outbound tourism with spends of $89 billion in 2027 as compared with the current 10th position with $38 billion in 2019.
| Relevancy for Prelims: Outbound Tourism, Indian Tourism Industry, World Tourism Organization (WTO), World Travel & Tourism Council (WTTC), G20 summit, and UNESCO World Heritage Sites In India.
Relevancy for Mains: Indian Tourism Industry; Current status, Strengths, Weaknesses, and Way Forward. |
|---|
Also Read: World Tourism Day 2023 – Theme, Significance, and More

Indian tourism industry shows immense potential for growth, with rising outbound tourism, increased domestic spending, and strategic initiatives, yet challenges like infrastructure and safety must be addressed for sustained success.
SC Verdict on Newsclick Shows Adherence to Due Pro...
Stay Invested: On Chabahar and India-Iran Relation...
Credit Rating Agencies, Impact on India’s De...
Catapulting Indian Biopharma Industry
Globalisation Under Threat, US Import Tariffs Have...
Global Report on Hypertension, Global Insights and...
<div class="new-fform">
</div>
