Context: Goods and Services Tax (GST) revenues data for the first nine months of 2023-24 reveal weak consumer expenditure because of uneven consumption growth across States.
About National Statistics Office (NSO)
About The Goods and Service Tax Act
|
|---|
Must Read: Resolving Regional Disparities: States in South are more developed than North
News Source: The Hindu
|
Must Read |
|
| NCERT Notes For UPSC | UPSC Daily Current Affairs |
| UPSC Blogs | UPSC Daily Editorials |
Context: Voice clone fraud has been on the rise in India as voice cloning through artificial intelligence is increasingly being used for scams.
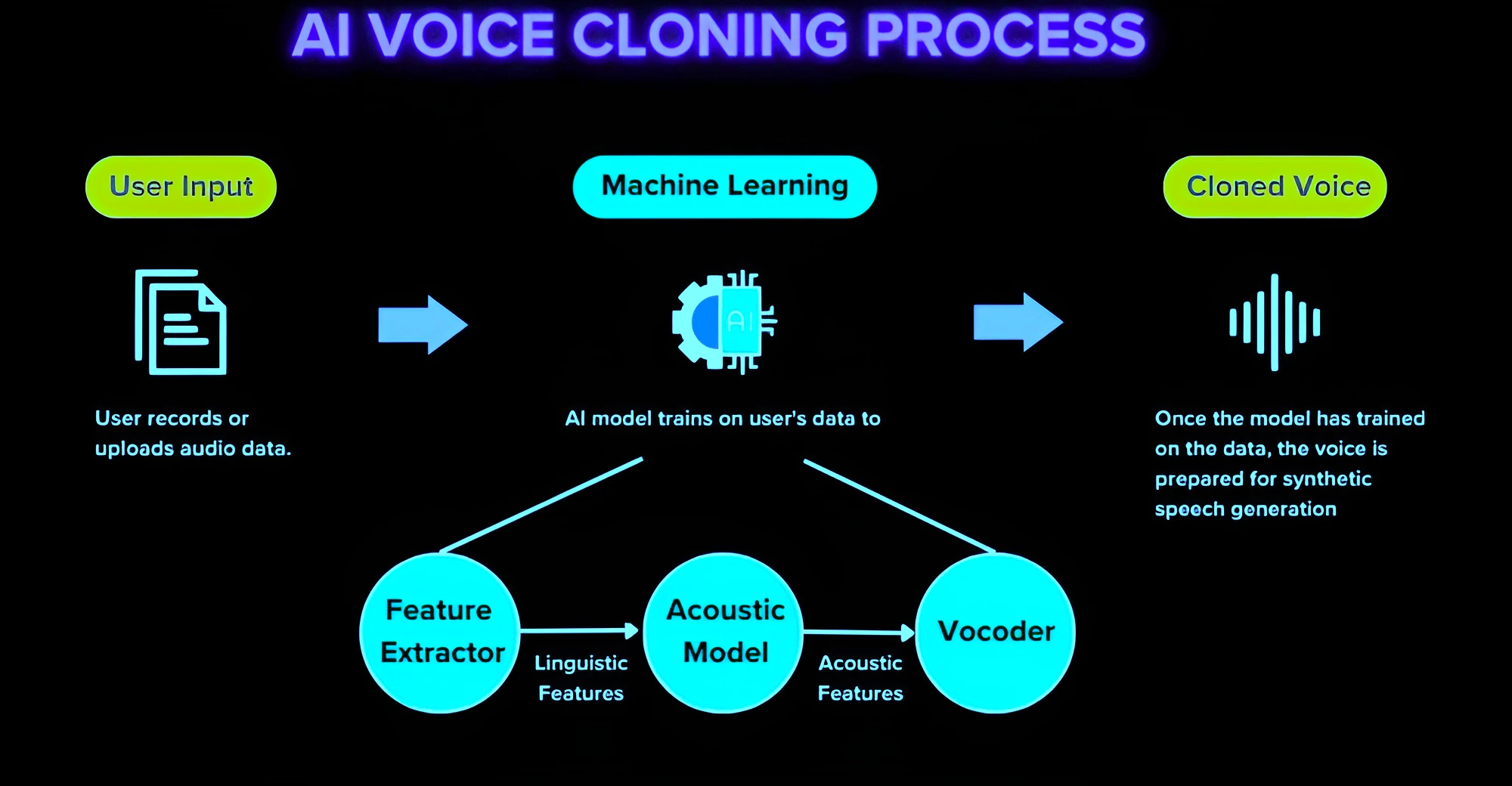 For instance, recently a Lucknow resident fell prey to a cyberattack that used AI to impersonate the voice of the victim’s relative, requesting the person to transfer a substantial amount through UPI.
For instance, recently a Lucknow resident fell prey to a cyberattack that used AI to impersonate the voice of the victim’s relative, requesting the person to transfer a substantial amount through UPI. Must Read: NCRB Data On Cyber Crime In India
Some Examples of Voice Cloning Scams
|
|---|
News Source: TH
|
Must Read |
|
| NCERT Notes For UPSC | UPSC Daily Current Affairs |
| UPSC Blogs | UPSC Daily Editorials |
Context: The Union Health Minister launched India’s first health food street, Prasadam in Ujjain Madhya Pradesh.
About Food Safety Standards Authority of India (FSSAI)
About National Health Mission (NHM)
|
|---|
News Source: Indian Express
|
Must Read |
|
| NCERT Notes For UPSC | UPSC Daily Current Affairs |
| UPSC Blogs | UPSC Daily Editorials |
Context: 1,75,025 pilgrims from India have been finalized for Haj Pilgrimage 2024.
About Haj Committee of India
|
|---|
News Source: PIB
|
Must Read |
|
| NCERT Notes For UPSC | UPSC Daily Current Affairs |
| UPSC Blogs | UPSC Daily Editorials |
Context: Shri Ram Janmabhoomi Mandir or Ayodhya Ram Mandir will be inaugurated on January 22.
About Pran Pratishtha (Consecration Ceremony)
|
|---|
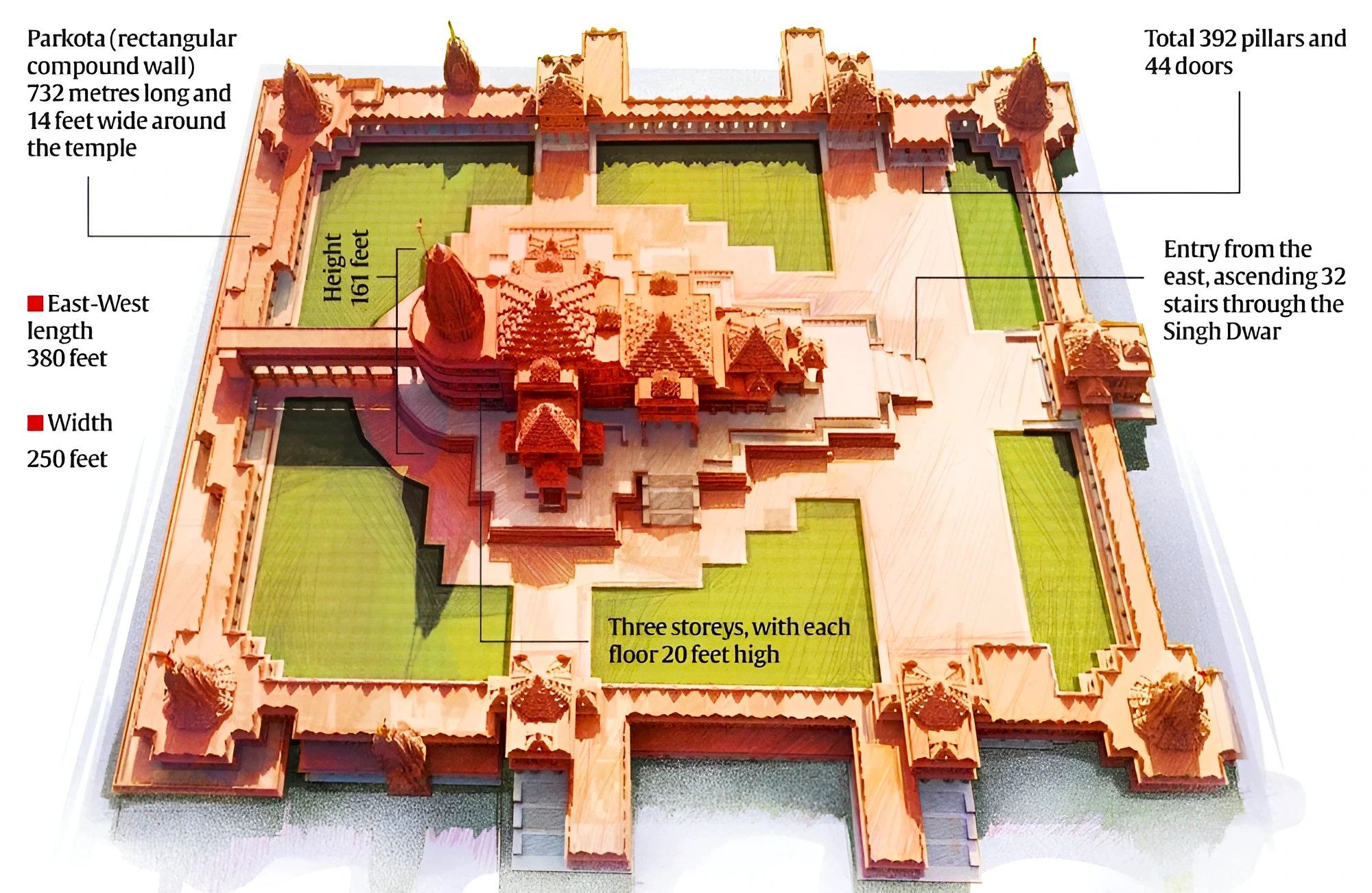 Foundation of the temple: It is built of a 14-metre-thick layer of roller-compacted concrete. And a 21-foot-high granite plinth has been placed to protect against ground moisture.
Foundation of the temple: It is built of a 14-metre-thick layer of roller-compacted concrete. And a 21-foot-high granite plinth has been placed to protect against ground moisture.
About Nagara Style of Temple Architecture
|
|---|
Also Read: Jagannath Temple Beautification Project
News source: Indian Express
|
Must Read |
|
| NCERT Notes For UPSC | UPSC Daily Current Affairs |
| UPSC Blogs | UPSC Daily Editorials |
Context: The criticisms are faced by the recently notified Post-Graduate Medical Education Regulations, 2023 (PGMER 2023 Regulations) in India.
News Source: The Hindu
|
Must Read |
|
| NCERT Notes For UPSC | UPSC Daily Current Affairs |
| UPSC Blogs | UPSC Daily Editorials |
Context: With the expansion of Janaushadhi Kendra to more than 10,000 centers the pharma companies are facing losses.
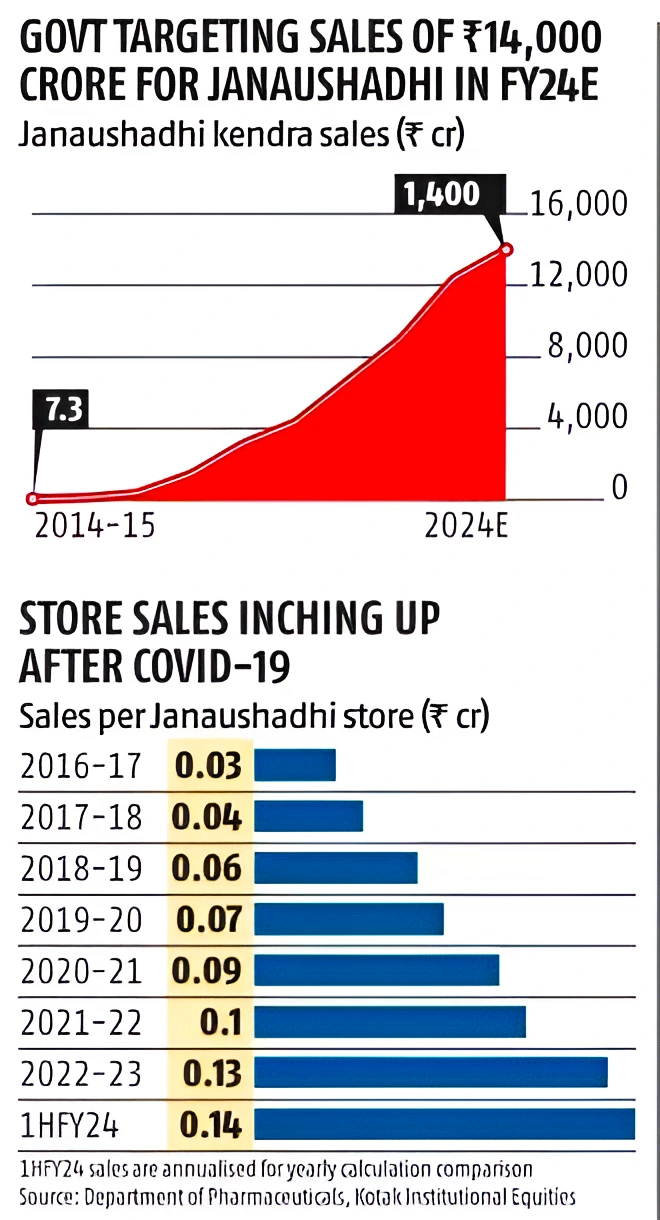
About Generic Drugs
Continue To Read: Generic Medicines |
|---|
News Source: BS
|
Must Read |
|
| NCERT Notes For UPSC | UPSC Daily Current Affairs |
| UPSC Blogs | UPSC Daily Editorials |
Context: Recently, seven products from Odisha, have been added to the list of GI tags.
| Kapdaganda shawl | It is an embroidered shawl on an off-white coarse cloth with red, yellow and green colored threads by women of the Dongria Kondh tribe |
| Lanjia Saura Painting | It is a painting art that belongs to the Lanjia Saura community, paintings are in the form of exterior murals |
| Koraput Kala Jeera Rice | It is a black-colored rice variety, famous for its aroma, taste, texture and nutritional value. |
| Similipal Kai chutney | It is a chutney made with red weaver ants by the tribals in Odisha’s Mayurbhanj district. Chutney is a good source of protein, calcium, zinc etc. |
| Nayagarh Kanteimundi Brinjal | They are known for the prickly thorns on the stems and whole plant. The green and round fruits contain more seeds as compared to other genotypes. |
| Odisha Khajuri Guda | It is a natural sweetener extracted from date palm trees and has its origin in the Gajapati district. |
| Dhenkanal Magji | It is a sweet made from buffalo milk cheese, with a distinct appearance, taste, flavor, shape, and size. |
| Product | Category | State |
| Mahoba Gaura Patthar Hastashlip | Handicraft | Uttar Pradesh |
| Mainpuri Tarkashi | Handicraft | Uttar Pradesh |
| Sambhal Horn Craft | Handicraft | Uttar Pradesh |
| Amroha Dholak | Handicraft | Uttar Pradesh |
| Baghpat Home Furnishings | Handicraft | Uttar Pradesh |
| Barabanki Handloom Product | Handicraft | Uttar Pradesh |
| Kalpi Handmade Paper | Handicraft | Uttar Pradesh |
| Atreyapuram Pootharekulu | Food Stuff | Andhra Pradesh |
| Ladakh Seabuckthorn | Agricultural | Ladakh (UT) |
| Bhandara Chinoor Rice | Agricultural | Maharashtra |
| Jaderi Namakatti | Handicraft | Tamil Nadu |
| Agra Leather Footwear | Manufactured | Uttar Pradesh |
| Nathdwara Pichhwai Painting | Handicraft | Rajasthan |
| Kanyakumari Matti Banana | Agricultural | Tamil Nadu |
| Mushqbudji Rice | Agricultural | Jammu & Kashmir |
| Chedibutta Saree | Handicraft | Tamil Nadu |
| Agsechi Vayingim (Agassaim Brinjal) | Agricultural | Goa |
| Rajouri Chikri Wood Craft | Handicraft | Jammu & Kashmir |
| Sat Shiro Bheno (Sat Shirancho Bhendo) | Agricultural | Goa |
| Marcha Rice | Agricultural | Bihar |
| Jalesar Dhatu Shilp (Metal Craft) | Handicraft | Uttar Pradesh |
| Goa Mankurad Mango | Agricultural | Goa |
| Goan Bebinca | Food Stuff | Goa |
| Udaipur Koftgari Metal Craft | Handicraft | Rajasthan |
| Bikaner Kashidakari Craft | Handicraft | Rajasthan |
| Jodhpur Bandhej Craft | Handicraft | Rajasthan |
| Bikaner Usta Kala Craft | Handicraft | Rajasthan |
| Bhaderwah Rajmash | Agricultural | Jammu & Kashmir |
| Ramban Sulai Honey | Food Stuff | Jammu & Kashmir |
| Udangudi Panangkarupatti | Food Stuff | Tamil Nadu |
| Goa Cashew (Kaju Or Caju) | Agricultural | Goa |
| Basohli Pashmina Woolen Products | Handicraft | Jammu & Kashmir |
| Kendrapara Rasabali | Food Stuff | Odisha |
| Arunachal Pradesh Khaw Tai” (Khamti Rice) | Agricultural | Arunachal Pradesh |
| Udhampur Kaladi | Food Stuff | Jammu & Kashmir |
| Arunachal Pradesh Yak Churpi | Food Stuff | Arunachal Pradesh |
| Arunachal Pradesh Tangsa Textile Product | Handicraft | Arunachal Pradesh |
| Uttarakhand Berinag Tea | Agricultural | Uttarakhand |
| Uttarakhand Bichhu Buti (Nettle) Fabrics | Handicraft | Uttarakhand |
| Uttarakhand Mandua | Agricultural | Uttarakhand |
| Uttarakhand Jhangora | Agricultural | Uttarakhand |
| Uttarakhand Gahat | Agricultural | Uttarakhand |
| Uttarakhand Lal Chawal (Red Rice) | Agricultural | Uttarakhand |
| Uttarakhand Kala Bhat | Agricultural | Uttarakhand |
| Uttarakhand Malta Fruit | Agricultural | Uttarakhand |
| Uttarakhand Chaulai (Ramdana) | Agricultural | Uttarakhand |
| Almora Lakhori Mirchi | Agricultural | Uttarakhand |
| Uttarakhand Buransh | Food Stuff | Uttarakhand |
| Uttarakhand Pahari Toor Dal | Agricultural | Uttarakhand |
| Nainital Mombatti (Candle) | Manufactured | Uttarakhand |
| Rangwali Pichhoda of Kumaon | Handicraft | Uttarakhand |
| Ramnagar Nainital Litchi | Agricultural | Uttarakhand |
| Ramgarh Nainital Aadu (Peach) | Agricultural | Uttarakhand |
| Chamoli Wooden Ramman Mask | Handicraft | Uttarakhand |
| Uttarakhand Likhai (Wood Carving) | Handicraft | Uttarakhand |
Read More on GI Tag, here.
Source: Indian Express
|
Must Read |
|
| NCERT Notes For UPSC | UPSC Daily Current Affairs |
| UPSC Blogs | UPSC Daily Editorials |
Context: The First Advance Estimates (FAEs) released by the National Statistical Office (NSO), Ministry of Statistics and Programme Implementation (MoS&PI) showed that India’s GDP will grow by 7.3% in the current financial year (2023-24).
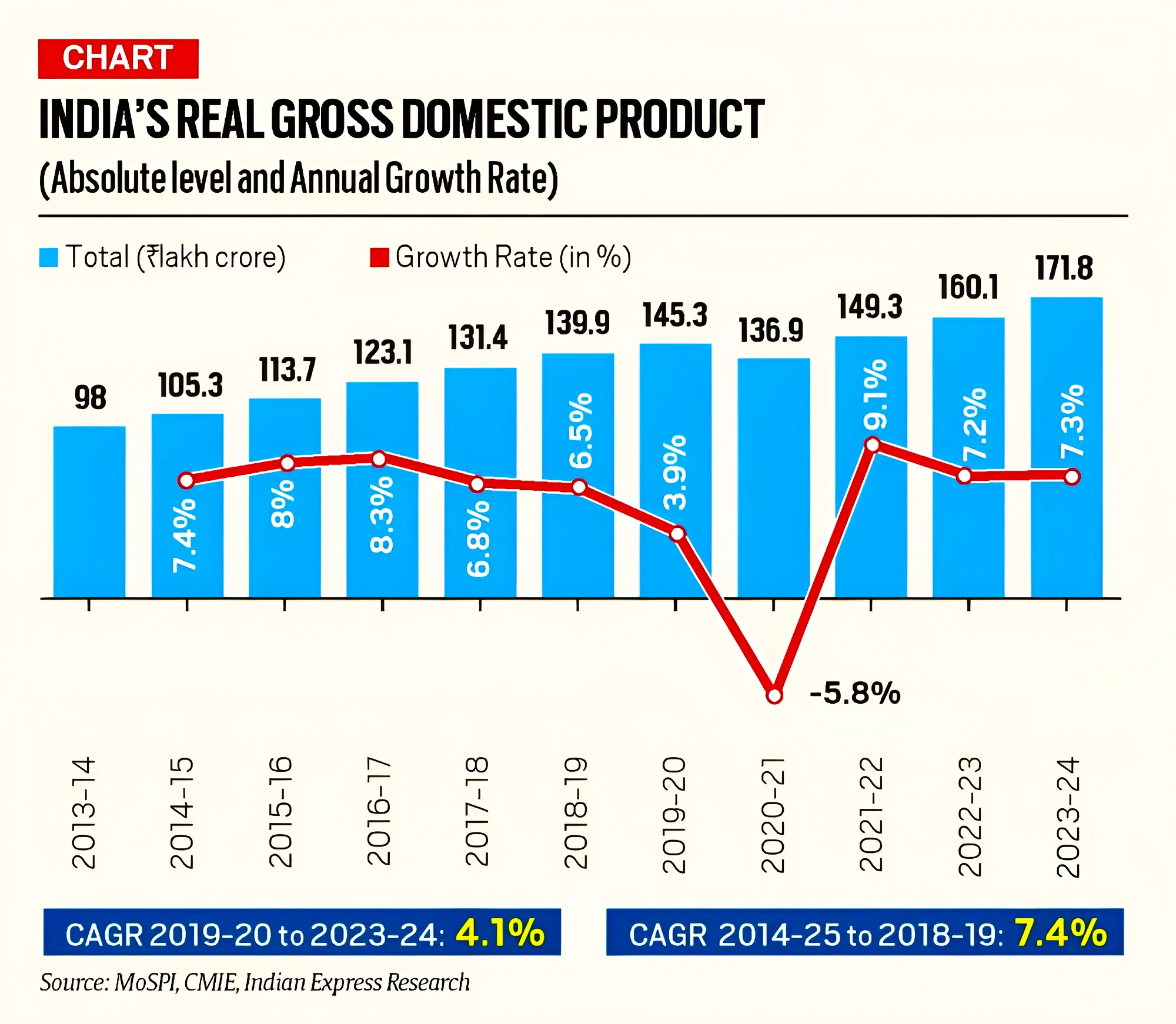
|
|---|
Expenditure Method
|
|---|
Must Read: India To Be A $ 7 Trillion Economy By 2030: CEA
News Source: Indian Express
|
Must Read |
|
| NCERT Notes For UPSC | UPSC Daily Current Affairs |
| UPSC Blogs | UPSC Daily Editorials |
Context: As per the Union Health Ministry, 75% of new infectious diseases that have emerged over the past three decades have been zoonotic, and the Ministry is increasing its focus on zoonotic diseases.
| Zoonoses | Associated Diseases |
| Bacterial Zoonoses | Anthrax, Tuberculosis, Brucellosis, Plague, Leptospirosis, Salmonellosis, Lyme Disease, Leprosy |
| Viral Zoonoses | Rabies, Hantavirus, Arbovirus Infections, Yellow Fever, Influenza, Acquired Immune Deficiency Syndrome- AIDS, Ebola, Chikungunya Fever, Dengue Fever, Zika Fever, Severe acute respiratory syndrome (SARS), Monkeypox, Coronavirus Disease 2019 (COVID-19) |
| Rickettsial Zoonoses | Murine Typhus, Tick Typhus, Scrub Typhus, Q-fever, Epidemic Typhus, Rocky Mountain Spotted Fever, Queensland Tick Typhus |
| Protozoan Zoonoses | Toxoplasmosis, Trypanosomiasis, Leishmaniasis, African Sleeping Sickness, Chagas Disease, |
| Helminthic Zoonoses | Echinococcosis (hydatid disease), Taeniasis |
| Fungal Zoonoses | Deep Mycosis – Histoplasmosis, Cryptococcosis |
| Ectoparasites | Scabies, Myiasis |
| Acellular non-viral Pathogens | Mad Cow Disease, also known as Bovine Spongiform Encephalopathy. In human known as Creutzfeldt–Jakob disease (CJD) |
Must Read: New Class Of Antibiotic Against A Drug-Resistant Bacterium
News Source: Livemint
Context: This article is based on the news “52% drop in toy imports in 8 years, 239% jump in exports: Commerce Ministry” which was published in the Business Standard. The Indian Institute of Management (IIM) Lucknow recently conducted a case study on the “Success Story of Made in India Toys.”
| Relevancy for Prelims: Indian Toys, Market Size of Indian Toys, National Action Plan for Toys (NAPT), MSMEs (Micro, Small, and Medium Enterprises), and Production-linked incentive (PLI) Scheme for Toy industry.
Relevancy for Mains: Toy Industry in India: Current Status, Significance, Potential, Challenges, and Way Forward. |
|---|
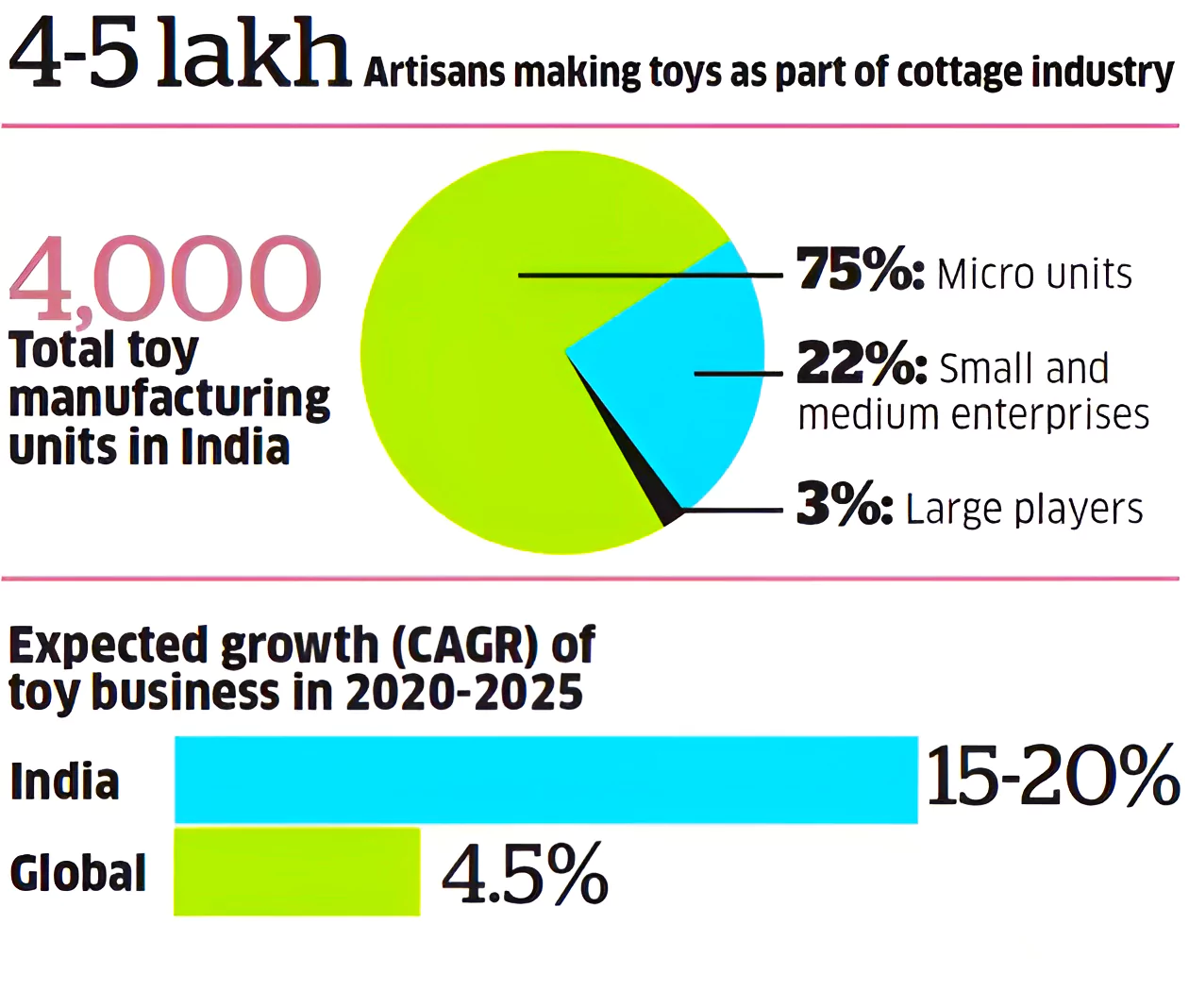 India doubled the number of manufacturing units.
India doubled the number of manufacturing units.Continue To Read: Indian Toy Industry: Exports Witnessed Significant Growth


 Strengthening Education and Skill Development: Toys serve as entertainment and educational resources.
Strengthening Education and Skill Development: Toys serve as entertainment and educational resources.
Indian Toy Industry: Current Status
|
|---|
What are the Government Initiatives for the Toy Industry?
|
|---|
Toy manufacturing is an ideal sector to boost a sluggish economy. Resolution of quality, skilling, and supply chain challenges will pave the way for the anticipated growth of the Indian toy industry.
|
Must Read |
|
| NCERT Notes For UPSC | UPSC Daily Current Affairs |
| UPSC Blogs | UPSC Daily Editorials |
Context: This article is based on the news “IIT Delhi team makes first hi-res landslide risk map for India” which was published in the Hindu. Indian Institute of Technology Delhi has made the first high-resolution landslide susceptibility map for India and the map data is available for free.
| Relevancy for Prelims: National Landslide Susceptibility Map, Landslide Atlas of India, Landslide Early Warning System, Indian Space Research Organisation (ISRO), Indian Meteorological Department (IMD), and Disaster Management In India.
Relevancy for Mains: Landslides in India: Overview, Causes, Types, Case Study, and Way Forward. |
|---|
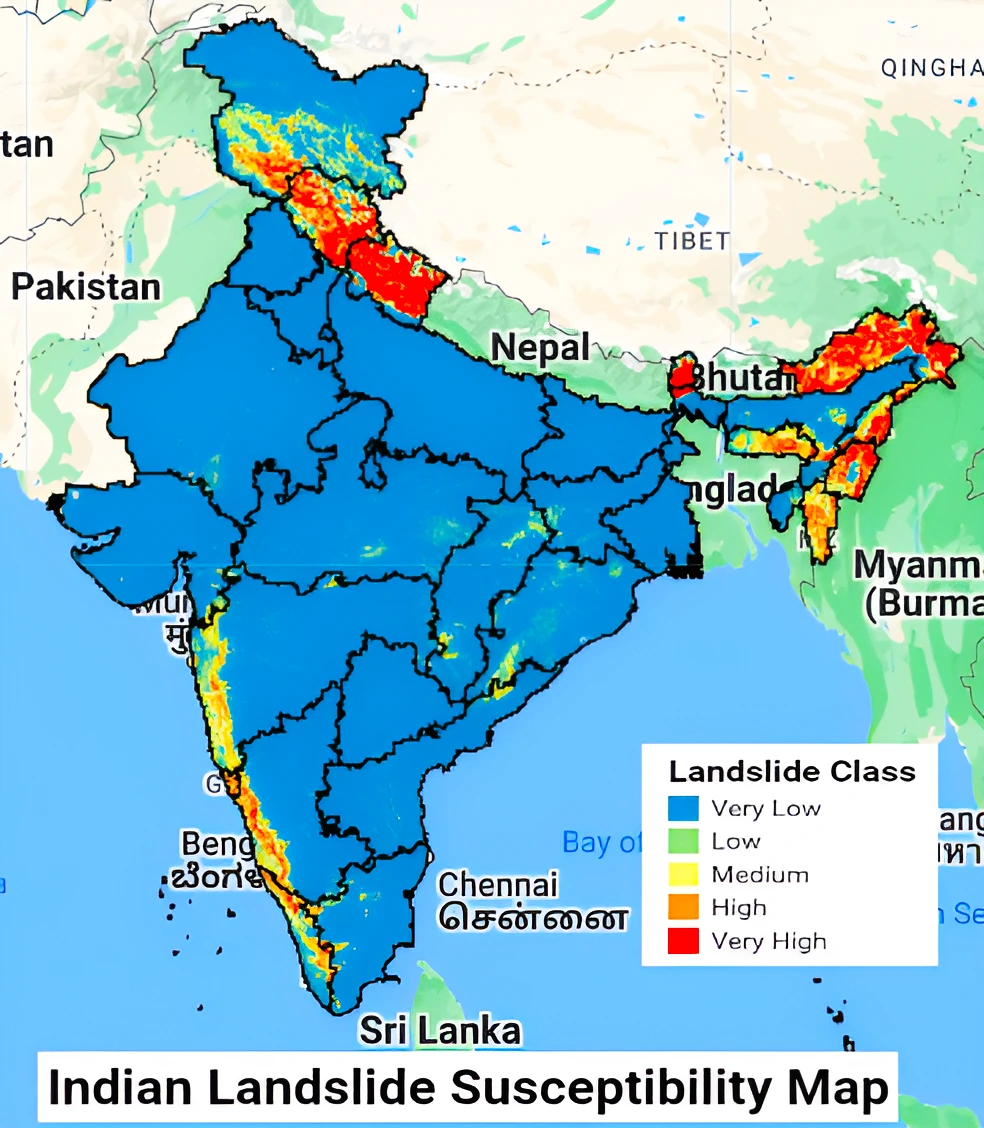
Ensemble learning: It is a machine learning technique that enhances accuracy and resilience in forecasting by merging predictions from multiple models.
|
|---|
Must Read: Interconnected Disaster Risks Report 2023 – UNU-EHS
About Landslide Atlas of India
|
|---|
Case Study: Joshimath Sinking
Reasons for Joshimath Sinking
|
|---|
About National Disaster Management Authority (NDMA)
National Disaster Management Guideline on Management of Landslides and Snow Avalanches.
|
|---|
| Mains Question: Bring Out the causes for more frequent landslides in the Himalayas than in western Ghat. [100 Words, 5 Marks] |
|---|
|
Must Read |
|
| NCERT Notes For UPSC | UPSC Daily Current Affairs |
| UPSC Blogs | UPSC Daily Editorials |
SC Verdict on Newsclick Shows Adherence to Due Pro...
Stay Invested: On Chabahar and India-Iran Relation...
Credit Rating Agencies, Impact on India’s De...
Catapulting Indian Biopharma Industry
Globalisation Under Threat, US Import Tariffs Have...
Global Report on Hypertension, Global Insights and...
<div class="new-fform">
</div>
