The Reserve Bank of India (RBI) has asked Visa and Mastercard to stop commercial card transactions under the Business Payment Solution Providers (BPSP) business.
| Feature | BPSP | RTGS | NEFT |
| Payment Mechanism | No need of mechanism to accept credit payments | Real Time Gross Settlement. | National Electronic Funds Transfer. |
| Settlement of time | Immediate | Real-time | Near real-time |
| Unique feature | Through BPSP, businesses can trade and pay supplier with reduced fees | This system requires a high fee for transactions compared to NEFT. | This system is not suitable for real-time or urgent fund transfers. |
| Transaction | The BPSP facility allows corporate credit card players to enable large payments directly to vendors or merchants’ bank accounts. | This system involves large amounts of cash transactions | This fund transfer system is generally for smaller value transactions. |
News Source: Thehindubusinessline
| Must Read | |
| NCERT Notes For UPSC | UPSC Daily Current Affairs |
| UPSC Blogs | UPSC Daily Editorials |
| Daily Current Affairs Quiz | Daily Main Answer Writing |
| UPSC Mains Previous Year Papers | UPSC Test Series 2024 |
Recently the Prime Minister of India participated in the World Governments Summit 2024 in Dubai as Guest of Honour.
News Source: PIB
| Must Read | |
| NCERT Notes For UPSC | UPSC Daily Current Affairs |
| UPSC Blogs | UPSC Daily Editorials |
| Daily Current Affairs Quiz | Daily Main Answer Writing |
| UPSC Mains Previous Year Papers | UPSC Test Series 2024 |
Recently,Environmental groups petitioned the U.S. government seeking protection for the American horseshoe crab, a “living fossil”.

Concerns with their Medical Use :
|
|---|
What are Living Fossils ?
Other Examples of Living Fossils
|
|---|
News Source: The Hindu
| Must Read | |
| NCERT Notes For UPSC | UPSC Daily Current Affairs |
| UPSC Blogs | UPSC Daily Editorials |
| Daily Current Affairs Quiz | Daily Main Answer Writing |
| UPSC Mains Previous Year Papers | UPSC Test Series 2024 |
Recently, the Indian Prime Minister met the President of the Republic of Madagascar on the sidelines of the World Governments Summit in Dubai.
News Source: PIB
| Must Read | |
| NCERT Notes For UPSC | UPSC Daily Current Affairs |
| UPSC Blogs | UPSC Daily Editorials |
| Daily Current Affairs Quiz | Daily Main Answer Writing |
| UPSC Mains Previous Year Papers | UPSC Test Series 2024 |
Recently, Indian Coast Guard Offshore Patrol Vessel (OPV) ICGS Varaha (indigenously built) made a significant port call at Maputo Port, Mozambique.
News Source: IBG News
| Must Read | |
| NCERT Notes For UPSC | UPSC Daily Current Affairs |
| UPSC Blogs | UPSC Daily Editorials |
| Daily Current Affairs Quiz | Daily Main Answer Writing |
| UPSC Mains Previous Year Papers | UPSC Test Series 2024 |
The Odisha government added Gupteshwar forest division to the Biodiversity Heritage Site making it fourth in the biodiversity heritage site from the state.
The state govt has asked the Odisha Biodiversity Board to prepare a long-term plan for intensive conservation and development of the forest.
Gupteshwar Forest
|
|---|
Biological Diversity Act 2002
|
|---|
News Source: Onmanorama and Indian Express
| Must Read | |
| NCERT Notes For UPSC | UPSC Daily Current Affairs |
| UPSC Blogs | UPSC Daily Editorials |
| Daily Current Affairs Quiz | Daily Main Answer Writing |
| UPSC Mains Previous Year Papers | UPSC Test Series 2024 |
The ‘Scheme Guidelines for Implementation of Pilot Projects for Use of Green Hydrogen in the Transport Sector‘ have been issued by the Ministry of New and Renewable Energy (MNRE).
Additional Reading: Different types of Hydrogen Production:
|
News Source: Livemint
| Must Read | |
| NCERT Notes For UPSC | UPSC Daily Current Affairs |
| UPSC Blogs | UPSC Daily Editorials |
| Daily Current Affairs Quiz | Daily Main Answer Writing |
| UPSC Mains Previous Year Papers | UPSC Test Series 2024 |
Ministry of Social Justice and Empowerment, to spread awareness, launches Nasha Mukh Bharat Abhiyan (NMBA) Vehicle for Delhi NCR.
News Source: PIB
| Must Read | |
| NCERT Notes For UPSC | UPSC Daily Current Affairs |
| UPSC Blogs | UPSC Daily Editorials |
| Daily Current Affairs Quiz | Daily Main Answer Writing |
| UPSC Mains Previous Year Papers | UPSC Test Series 2024 |
This article is based on the news “Education Minister says APAAR to be aspirational and global document for students in India” which was published in the All India Radio. At the national conference on ‘APAAR ID: One Nation One Student ID Card’, it was revealed that about 25 crore Automated Permanent Academic Account Registry (APAAR) have been created.

Academic Bank of Credits (ABC)It is envisaged as per the National Education Policy 2020. It facilitates the academic mobility of students with the freedom to study across the Higher Education Institutions in the country with an appropriate “credit transfer” mechanism from one programme to another, leading to attain a Degree/ Diploma/PG-diploma, etc. Features:
Also Read: More Subjects, Credit System |
|---|
| Must Read | |
| NCERT Notes For UPSC | UPSC Daily Current Affairs |
| UPSC Blogs | UPSC Daily Editorials |
| Daily Current Affairs Quiz | Daily Main Answer Writing |
| UPSC Mains Previous Year Papers | UPSC Test Series 2024 |
The health officials in Alaska have identified the first known death linked to a virus called Alaska Pox.


News Source: Livemint
| Must Read | |
| NCERT Notes For UPSC | UPSC Daily Current Affairs |
| UPSC Blogs | UPSC Daily Editorials |
| Daily Current Affairs Quiz | Daily Main Answer Writing |
| UPSC Mains Previous Year Papers | UPSC Test Series 2024 |
This article is based on the news “ISRO to launch INSAT-3DS on Feb 17, will improve forecasts” which was published in the Indian Express. ISRO to launch INSAT-3DS on Feb 17 to improve forecasts. It is the third in a series of INSAT-3D satellites.
| Relevancy for Prelims: ISRO, New Targets For ISRO, ISRO Aditya L1 Mission, and ISRO’s Distress Alert Transmitter.
Relevancy for Mains: SPACE & SPACE TECHNOLOGY. |
|---|
|
|---|

Satish Dhawan Space Centre (SDSC)
|
|---|
GSLV-F14
|
Geostationary Transfer Orbit (GTO)
Geostationary Earth Orbit (GEO)
|
|---|
News Source: Indian Express
| Must Read | |
| NCERT Notes For UPSC | UPSC Daily Current Affairs |
| UPSC Blogs | UPSC Daily Editorials |
| Daily Current Affairs Quiz | Daily Main Answer Writing |
| UPSC Mains Previous Year Papers | UPSC Test Series 2024 |
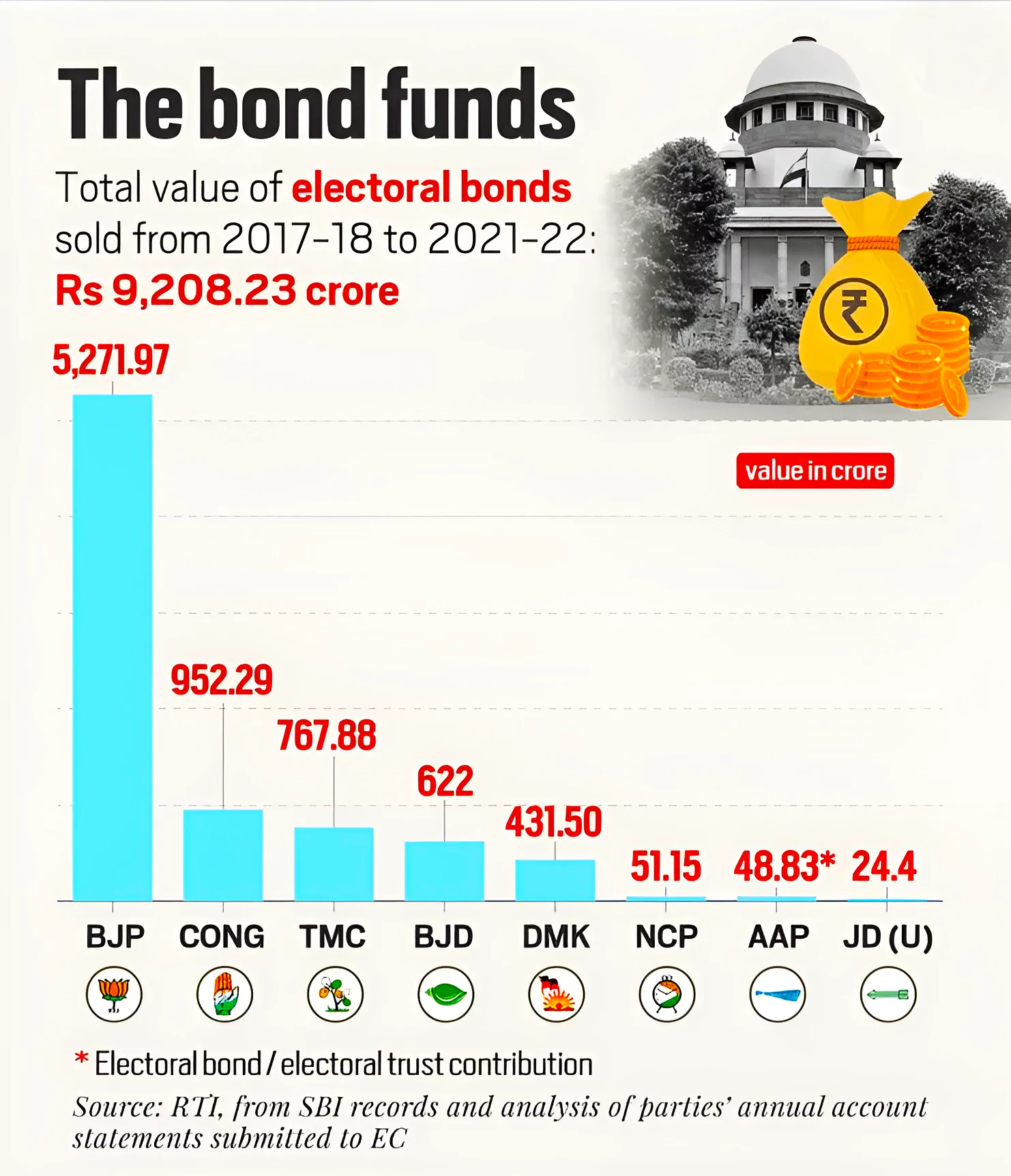
This article is based on the news “Supreme Court strikes down electoral bonds scheme: ‘unconstitutional’, ‘arbitrary and violative of Article 14” which was published in the Indian Express. The Supreme Court struck down the electoral bonds scheme asserting that the scheme violates the right to information under Article 19(1)(a) of the Constitution.
| Relevancy for Prelims: Supreme Court, Political Funding in India, Election Commission Of India and Reserve Bank Of India (RBI), and Fundamental Rights (Article 12-35).
Relevancy for Mains: Electoral Bonds: Background, Legal Timeline, Court Proceedings and Judgments. |
|---|
Legal Framework for Political Funding in India
|
|---|
| Must Read | |
| NCERT Notes For UPSC | UPSC Daily Current Affairs |
| UPSC Blogs | UPSC Daily Editorials |
| Daily Current Affairs Quiz | Daily Main Answer Writing |
| UPSC Mains Previous Year Papers | UPSC Test Series 2024 |
SC Verdict on Newsclick Shows Adherence to Due Pro...
Stay Invested: On Chabahar and India-Iran Relation...
Credit Rating Agencies, Impact on India’s De...
Catapulting Indian Biopharma Industry
Globalisation Under Threat, US Import Tariffs Have...
Global Report on Hypertension, Global Insights and...
<div class="new-fform">
</div>
