Context:
India is quickly emerging as one of the leading players in the global e-commerce industry. E-commerce is dramatically opening up the global market for Indian entrepreneurs at scale and this has changed the fate of ‘Made in India’ products.
What is the State of Exports from India?
Manufacturing:
Other categories:
What are the Challenges with E-Commerce Exports in India?
What are the Related Steps taken?
How India can Lead the E-commerce Export Market?
News Source: The Hindu
Context:
Even though it has been more than two months since the elections to the Delhi Municipal Corporation were held, the city still does not have a Mayor.
Supreme Court Oral Observation:
Issues:
Provisions on Voting Rights of Nominated Members in Municipal Corporations:
Union Government’s Attempts to Control Delhi’s Governance:
Factors Stifling the Authority of Municipal Governments:
Way Forward:
News Source: The Hindu
Context: Recently, Tipu Sultan was in the news because of controversial remarks made by a few political leaders.

Image Source: The Indian Express
Who was Tipu Sultan?
Tipu Sultan’s Reforms:
Context:
The Union Health Ministry has removed the age limit of 65 years for patients registering for organ transplant as part of the National Organ and Tissue Transplant Organization’s guidelines.
National Organ and Tissue Transplant Organization’s guidelines:
| Earlier | Now |
| A patient could register for a transplant only in the domicile state. | A patient irrespective of domicile state can register in any other state for a transplant. |
| Patients above the age of 65 were not eligible for organ donation. | People beyond 65 in need of an organ donation will also be eligible to get one. |
| The patient was not allotted a unique ID, and the registration was valid only in the domicile state. | The patient will be allotted a unique ID by NOTTO on registering which will get carried forward even if the patient changes multiple hospitals in different States. |
| The registration fee was charged from patients. | Health Ministry has intimated states to stop charging registration fees from patients. |
| The domicile policy was in place. | The domicile policy has been removed. All states have been intimated about this decision. |
About NOTTO
Function/Activities
| Additional Information:
Transplantation of Human Organs Act, 1994
Main Provisions:
|
Source: The Hindu, notto.gov.in
Context:
The Union Health Ministry has devised a strategic road map for achieving zero cases of Leprosy by 2030.
Status of Leprosy in India:
About Leprosy:
Steps Taken:
Context:
India’s exports and imports decreased by 6.59% and 3.63% in January, but there are signs that the current account deficit (CAD) will moderate, despite the global slowdown caused by inflation and interest rates.
What is CAD?
What does CAD include?
How did CAD Moderate?
Significance of CAD:
How will moderating CAD impact the market?
Context:
The Supreme Court of India has given permission to fishermen using purse seine fishing gear to fish beyond territorial waters (12 nautical miles) and within the Exclusive Economic Zone (EEZ) (200 nautical miles) of Tamil Nadu, with restrictions.
| Probable Question:
Q. Discuss the significance of the Supreme Court’s decision and its potential implications on the fishing industry and the marine ecosystem of India. |
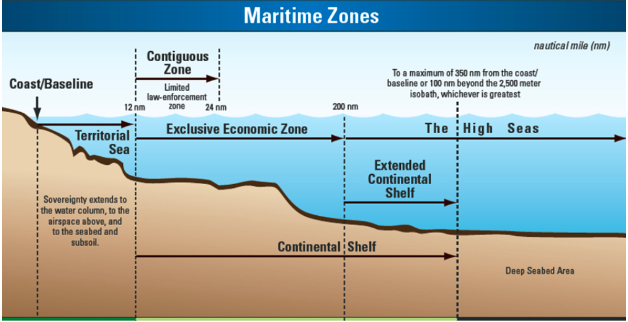
Image Source: usgs.gov
About Exclusive Economic Zone(EEZ):
Multilateral and Regional Conventions:
Current Status of Indian Fisheries
Issue with Court’s Recent Order:
Conclusion
About UNCLOS:
|
SC Verdict on Newsclick Shows Adherence to Due Pro...
Stay Invested: On Chabahar and India-Iran Relation...
Credit Rating Agencies, Impact on India’s De...
Catapulting Indian Biopharma Industry
Globalisation Under Threat, US Import Tariffs Have...
Global Report on Hypertension, Global Insights and...
<div class="new-fform">
</div>
