GoI has Extended the Sugar subsidy scheme for Antyodaya Anna Yojna (AAY) families distributed through the Public Distribution Scheme (PDS) until 31 March 2026.
Also Read: Pradhan Mantri Garib Kalyan Anna Yojana
News Source: PIB
| Must Read | |
| NCERT Notes For UPSC | UPSC Daily Current Affairs |
| UPSC Blogs | UPSC Daily Editorials |
| Daily Current Affairs Quiz | Daily Main Answer Writing |
| UPSC Mains Previous Year Papers | UPSC Test Series 2024 |
The US State Department has approved the sale of MQ-9B remotely piloted aircraft to India under the foreign military sales program.

What Are UAVs ?
|
|---|

Also Read:
News Source: The Hindu
| Must Read | |
| NCERT Notes For UPSC | UPSC Daily Current Affairs |
| UPSC Blogs | UPSC Daily Editorials |
| Daily Current Affairs Quiz | Daily Main Answer Writing |
| UPSC Mains Previous Year Papers | UPSC Test Series 2024 |
Indian Coast Guard celebrated its 48th Raising Day in New Delhi on 1st February.
About Indian Coast Guard
|
Also Read: The Challenge Of Maritime Security In The Global South
News Source: News on Air
|
Must Read |
|
| NCERT Notes For UPSC | UPSC Daily Current Affairs |
| UPSC Blogs | UPSC Daily Editorials |
| Daily Current Affairs Quiz | Daily Main Answer Writing |
| UPSC Mains Previous Year Papers | UPSC Test Series 2024 |
Recently, the Union Cabinet approved the continuation of Animal Husbandry Infrastructure Development Fund (AHIDF), launched in 2020-21, to be implemented under Infrastructure Development Fund (IDF) with an outlay of Rs.29,610.25 crore for another three years up to 2025-26.
Establishment: It has been announced under Atma Nirbhar Bharat Abhiyan stimulus package as a Central Sector Scheme for ensuring growth in infrastructure of Animal Husbandry.
Also Read: Rashtriya Gokul Mission
News Source: PIB
|
Must Read |
|
| NCERT Notes For UPSC | UPSC Daily Current Affairs |
| UPSC Blogs | UPSC Daily Editorials |
| Daily Current Affairs Quiz | Daily Main Answer Writing |
| UPSC Mains Previous Year Papers | UPSC Test Series 2024 |
Context:
The Union Cabinet has ratified the Bilateral Investment Treaty between India and the United Arab Emirates.
As per The Standing Committee on External Affairs report 2021 recommendations on the subject ‘India and Bilateral Investment Treaties’
Also Read: INDIA-UAE Relations
News Source: PIB
|
Must Read |
|
| NCERT Notes For UPSC | UPSC Daily Current Affairs |
| UPSC Blogs | UPSC Daily Editorials |
| Daily Current Affairs Quiz | Daily Main Answer Writing |
| UPSC Mains Previous Year Papers | UPSC Test Series 2024 |
A Green Propulsion System, developed under the Technology Development Fund (TDF) scheme of the Defence Research and Development Organisation (DRDO), has successfully demonstrated in-orbit functionality on a payload launched by PSLV C-58 mission.
What is Propulsion Technology?
The PSLV C-58 Mission:
|
|---|
News Source: PIB
| Must Read | |
| NCERT Notes For UPSC | UPSC Daily Current Affairs |
| UPSC Blogs | UPSC Daily Editorials |
| Daily Current Affairs Quiz | Daily Main Answer Writing |
| UPSC Mains Previous Year Papers | UPSC Test Series 2024 |
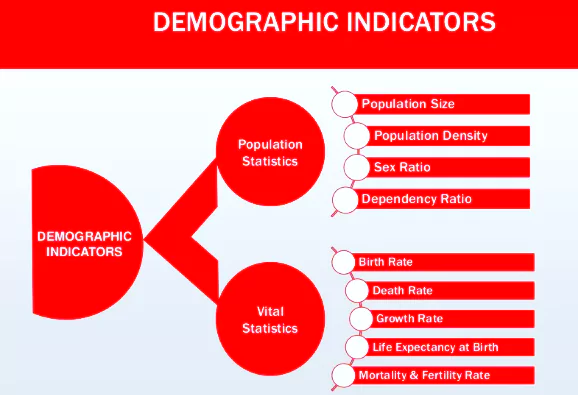
This article is based on the news “Budget: Govt panel to look into India’s demographic challenges” which was published in the Economic Times. While presenting the Interim Budget 2024, the Finance Minister said that a high-powered committee will be constituted to consider the challenges arising from “fast population growth and demographic changes”.
| Relevancy for Prelims: NITI Aayog, National Family Health Survey (NFHS), United Nations, UNDP, Parliament Budget Session 2024 Live Updates, Union Budget 2024-25, Interim Budget 2024-2025.
Relevancy for Mains: Indian Demography: Current Status, Changes, and Way Forward. |
|---|
| Must Read | |
| NCERT Notes For UPSC | UPSC Daily Current Affairs |
| UPSC Blogs | UPSC Daily Editorials |
| Daily Current Affairs Quiz | Daily Main Answer Writing |
| UPSC Mains Previous Year Papers | UPSC Test Series 2024 |
This article is based on the news “A NEW SCHEME OF BIO-MANUFACTURING & BIO-FOUNDRY TO PROVIDE ENVIRONMENT FRIENDLY ALTERNATIVES” which was published in the Indian Express. Recently, the Finance Minister of India proposed a new scheme of Bio manufacturing and Biofoundry in the Interim Budget 2024-25.
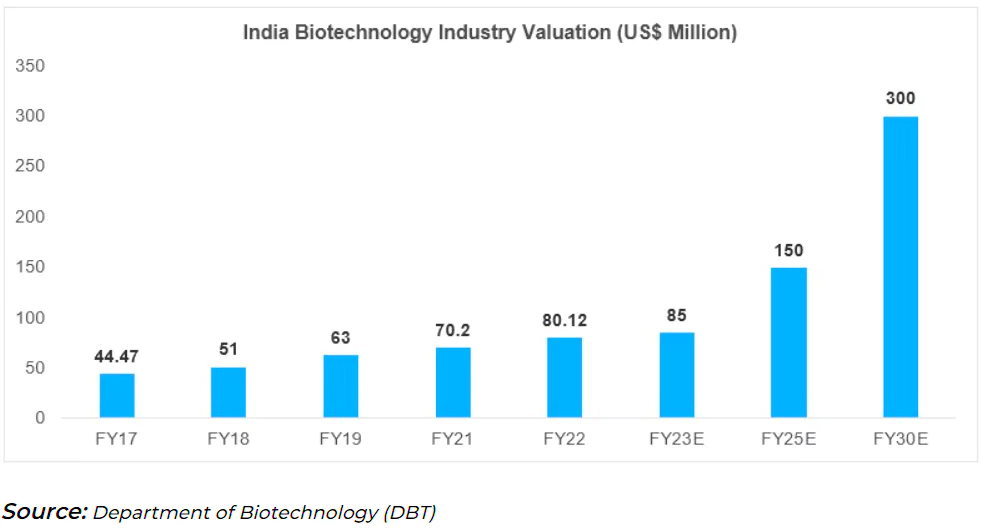
| Relevancy for Prelims: Status of Biotechnology Industry in India, Parliament Budget Session 2024 Live Updates, Union Budget 2024-25, Interim Budget 2024-2025, and Department of Biotechnology (DBT).
Relevancy for Mains: Bio manufacturing and Biofoundry in India: Significance, Challenges, and Way Forward. |
|---|
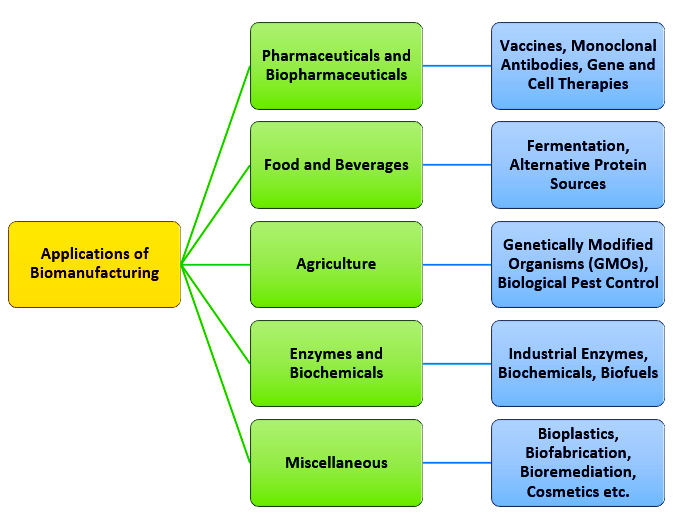
| Bio Economy: It comprises those parts of the economy that use renewable biological resources from land and sea viz. crops, forests, fish, animals and microorganisms, to produce food, products, textiles and energy etc. |
|---|
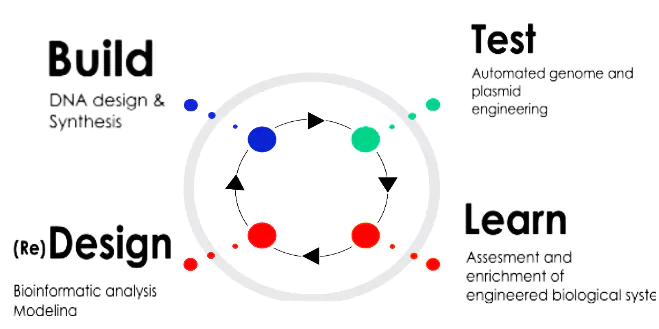 High-throughput (HT) refers to the use of automated equipment to quickly test large numbers of samples for biological activity.
High-throughput (HT) refers to the use of automated equipment to quickly test large numbers of samples for biological activity.
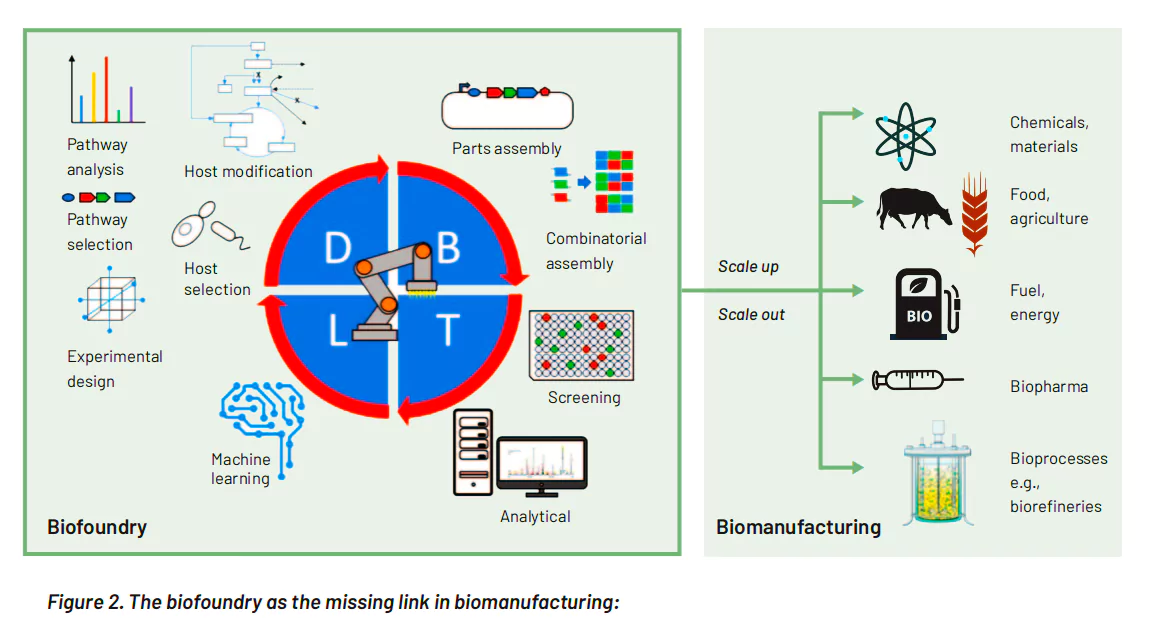
The integration of Bio Manufacturing and Biofoundry in India holds immense potential for driving economic growth, fostering innovation, and addressing global challenges. With strategic investments, regulatory reforms, and capacity building, India can position itself as a leader in Bio Manufacturing, contributing to a sustainable and bio-based future.
| Mains Question: Why is there so much activity in the field of biotechnology in our country? How has this activity benefitted the field of biopharma? (250 words, 15 marks) |
|---|
| Must Read | |
| NCERT Notes For UPSC | UPSC Daily Current Affairs |
| UPSC Blogs | UPSC Daily Editorials |
| Daily Current Affairs Quiz | Daily Main Answer Writing |
| UPSC Mains Previous Year Papers | UPSC Test Series 2024 |
SC Verdict on Newsclick Shows Adherence to Due Pro...
Stay Invested: On Chabahar and India-Iran Relation...
Credit Rating Agencies, Impact on India’s De...
Catapulting Indian Biopharma Industry
Globalisation Under Threat, US Import Tariffs Have...
Global Report on Hypertension, Global Insights and...
<div class="new-fform">
</div>
