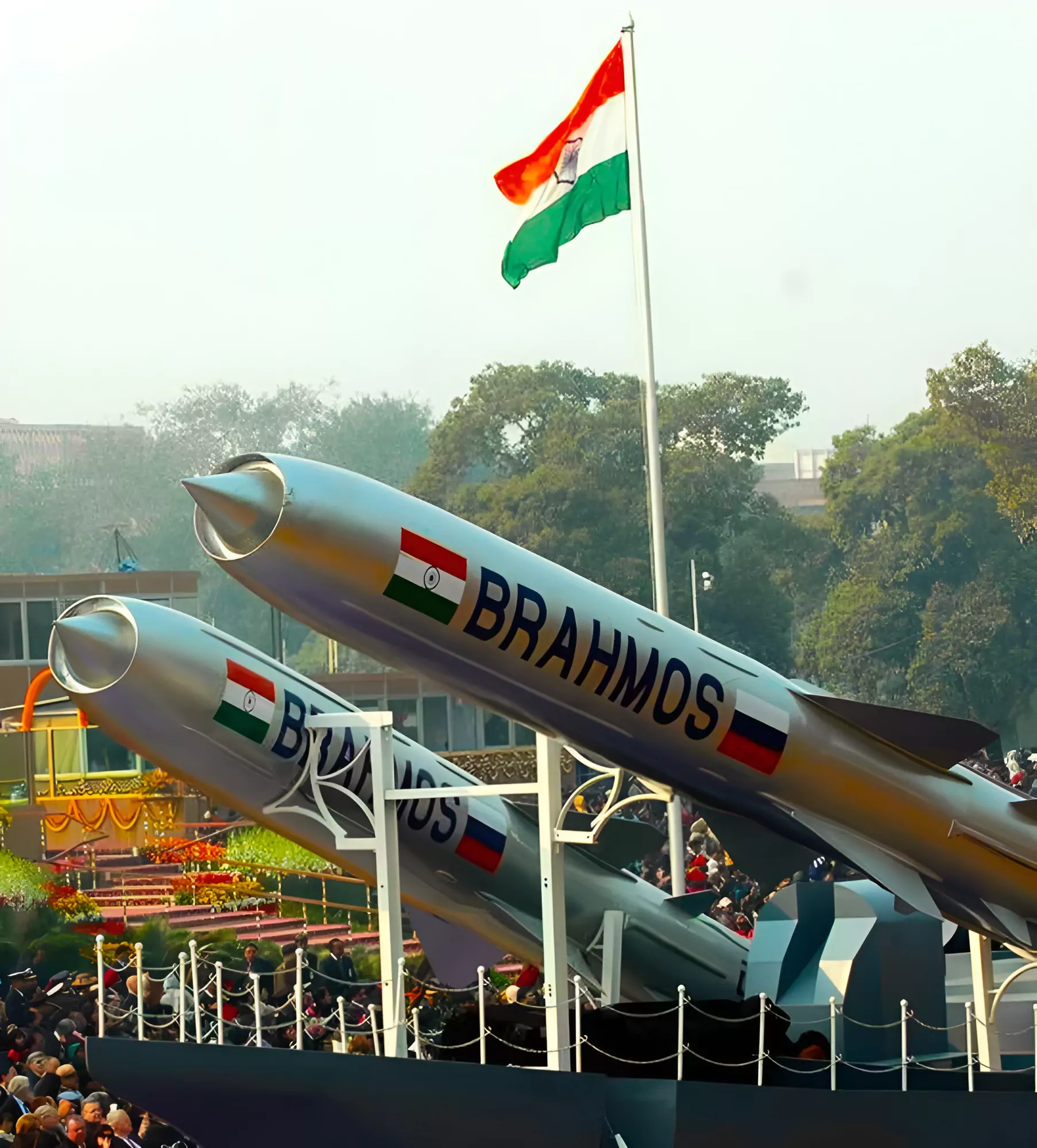
The Cabinet Committee on Security has cleared Indian Navy’s proposals to buy 220 BrahMos extended-range missiles for its warships worth around Rs 20,000 crore.

News Source: The Hindu
| Must Read | |
| NCERT Notes For UPSC | UPSC Daily Current Affairs |
| UPSC Blogs | UPSC Daily Editorials |
| Daily Current Affairs Quiz | Daily Main Answer Writing |
| UPSC Mains Previous Year Papers | UPSC Test Series 2024 |
A Memorandum of Understanding was signed between IIT Kanpur and Conlis Global (Canada based- biotech company) for the licensing of the new technology that facilitates bone regeneration.
| Osteoinduction is the process that triggers the formation of new bone tissue. |
|---|
News Source: Hindustan Times
| Must Read | |
| NCERT Notes For UPSC | UPSC Daily Current Affairs |
| UPSC Blogs | UPSC Daily Editorials |
| Daily Current Affairs Quiz | Daily Main Answer Writing |
| UPSC Mains Previous Year Papers | UPSC Test Series 2024 |
The Climate and Clean Air Conference 2024 emphasized global cooperation to eliminate short lived climate pollutants, such as methane, black carbon, and hydrofluorocarbons.
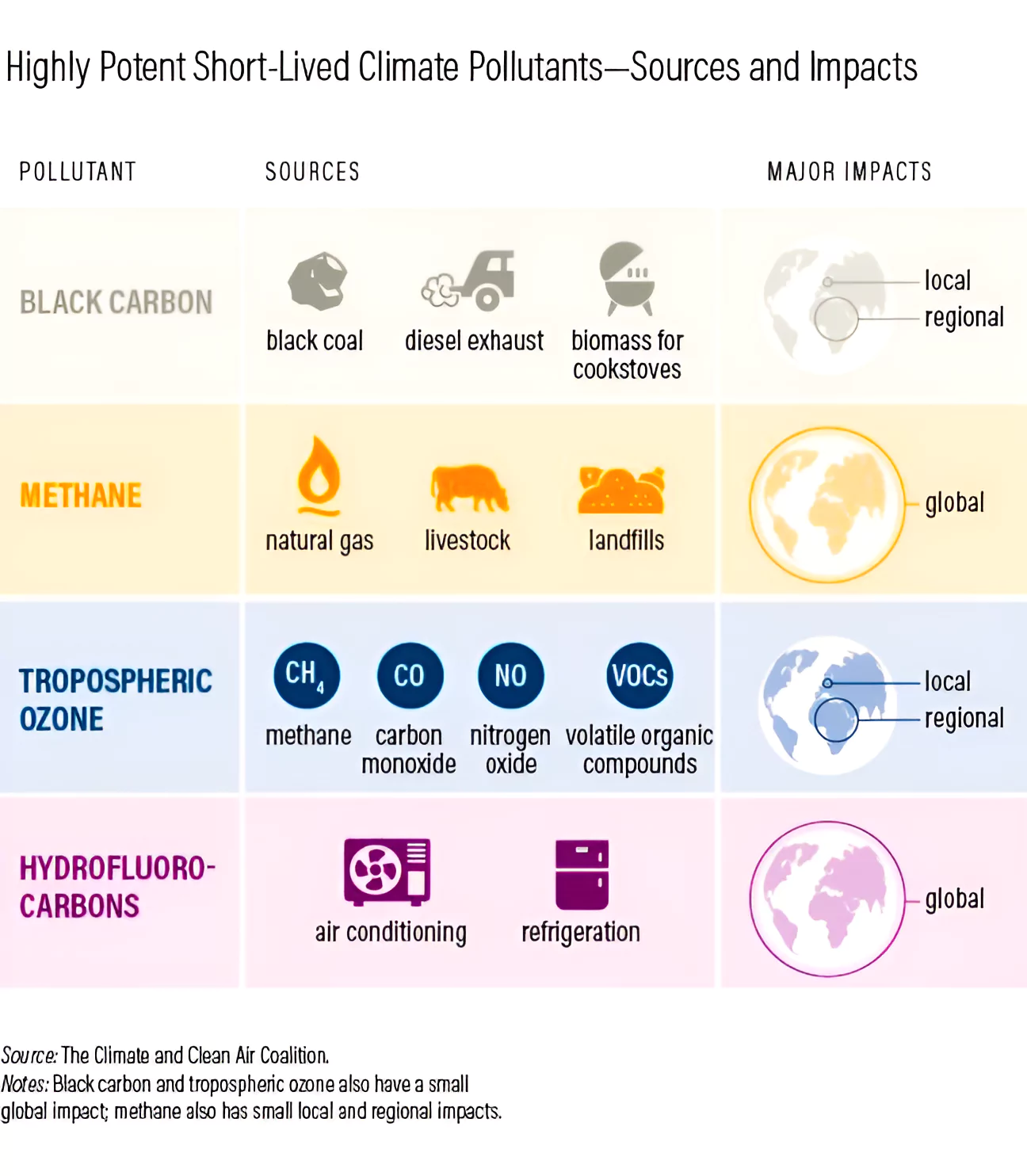
While addressing short-lived climate pollutants (SLCPs) has significant benefits, there are also some drawbacks and challenges associated with taking action on them:
Cooling and warming aerosols
Cooling Aerosols:
Warming Aerosols:
|
|---|
News Source: Down to Earth
| Must Read | |
| NCERT Notes For UPSC | UPSC Daily Current Affairs |
| UPSC Blogs | UPSC Daily Editorials |
| Daily Current Affairs Quiz | Daily Main Answer Writing |
| UPSC Mains Previous Year Papers | UPSC Test Series 2024 |
In the Raisina Dialogue 2024, the Chief of Defense staff Of India discussed the emergence of Grey Zone warfare in modern warfare.
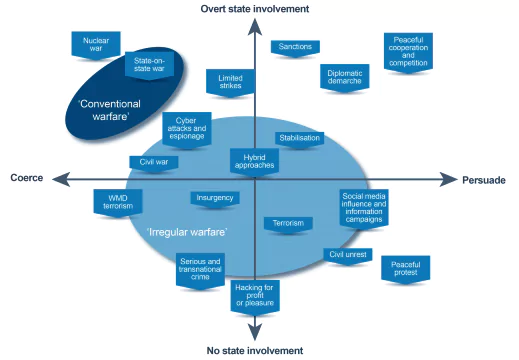
News Source: The Hindu
| Must Read | |
| NCERT Notes For UPSC | UPSC Daily Current Affairs |
| UPSC Blogs | UPSC Daily Editorials |
| Daily Current Affairs Quiz | Daily Main Answer Writing |
| UPSC Mains Previous Year Papers | UPSC Test Series 2024 |
Recently, India’s Defence Minister held a bilateral meeting with his counterpart on the sidelines of the Raisina Dialogue in New Delhi.
The Raisina Dialogue
|
|---|
News Source: PIB
| Must Read | |
| NCERT Notes For UPSC | UPSC Daily Current Affairs |
| UPSC Blogs | UPSC Daily Editorials |
| Daily Current Affairs Quiz | Daily Main Answer Writing |
| UPSC Mains Previous Year Papers | UPSC Test Series 2024 |
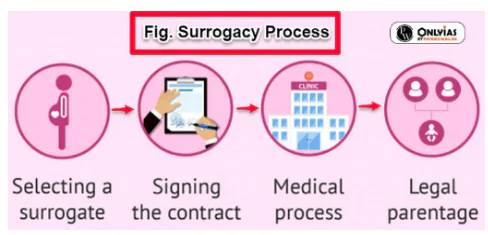
The Central government ammended Surrogacy Rules 2022 and allowed couples with medical conditions to use donor gametes for surrogacy.
What Are the Surrogacy Rules 2022?
|
|---|
Surrogacy in India: Assisted Reproductive Technology (Regulation) Act, 2021
|
|---|
News Source: The Hindu
| Must Read | |
| NCERT Notes For UPSC | UPSC Daily Current Affairs |
| UPSC Blogs | UPSC Daily Editorials |
| Daily Current Affairs Quiz | Daily Main Answer Writing |
| UPSC Mains Previous Year Papers | UPSC Test Series 2024 |
Recently, the Plasma Analyser Package for Aditya (PAPA) payload onboard the Aditya-L1 detected solar wind impact of Coronal Mass Ejections.
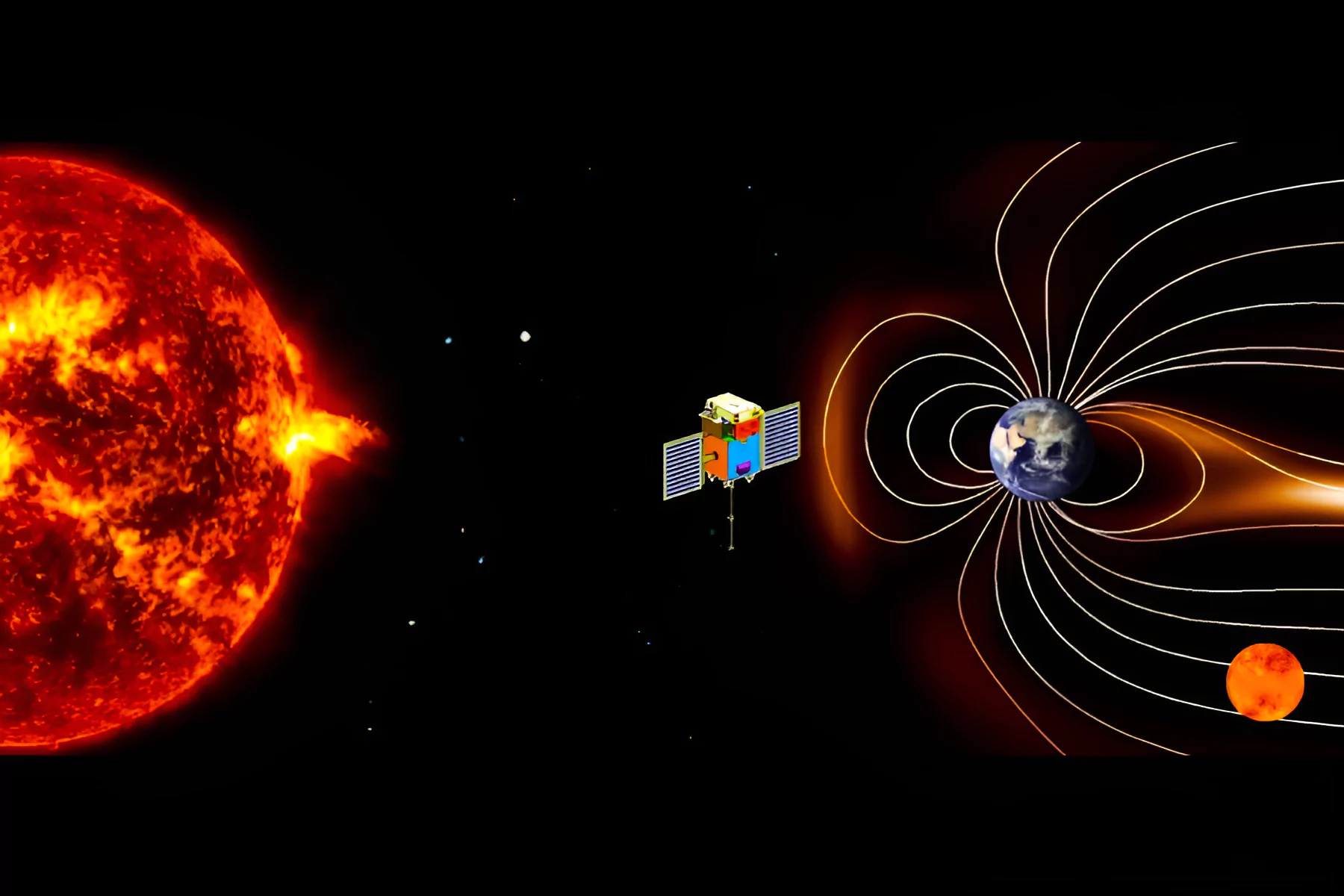
Aditya L-1 Mission |
| Mission Objective: Aditya-L1 endeavours to conduct a comprehensive solar study, encompassing the corona, photosphere, chromosphere, solar emissions, solar winds, flares, and Coronal Mass Ejections (CMEs). |
| Launch Vehicle: Polar Satellite Launch Vehicle (PSLV C-57) |
| Primary Payload: Visible Emission Line Coronagraph (VELC) |
| Secondary Payload: Solar Ultraviolet Imaging Telescope (SUIT), Solar Low Energy X-ray Spectrometer (SoLEXS), High Energy L1 Orbiting X-ray Spectrometer (HEL1OS), Aditya Solar wind Particle EXperiment (ASPEX), Plasma Analyser Package for Aditya (PAPA) |
Purpose:
|
L 1 Point/ Lagrange Point 1:
|
News Source: The Hindu
| Must Read | |
| NCERT Notes For UPSC | UPSC Daily Current Affairs |
| UPSC Blogs | UPSC Daily Editorials |
| Daily Current Affairs Quiz | Daily Main Answer Writing |
| UPSC Mains Previous Year Papers | UPSC Test Series 2024 |
Armenia has suspended its participation in a Russia-led security bloc, CSTO, due to differences with other member states.
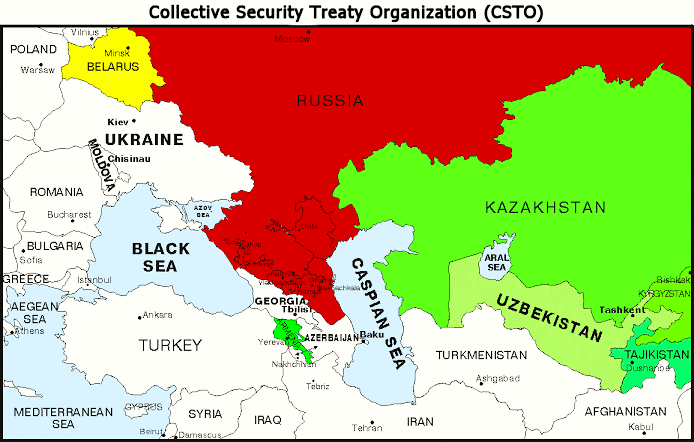
News Source: The Hindu
| Must Read | |
| NCERT Notes For UPSC | UPSC Daily Current Affairs |
| UPSC Blogs | UPSC Daily Editorials |
| Daily Current Affairs Quiz | Daily Main Answer Writing |
| UPSC Mains Previous Year Papers | UPSC Test Series 2024 |
This article is based on the news “Two years on, global support for Ukraine won’t falter” which was published in the Indian Express. Two years into the Russia Ukraine War, there appears little signs of de-escalations and ceasefire.
| Relevancy for Prelims: Ukraine War, NATO, United Nations, Israel-Hamas Conflict, and European Union (EU).
Relevancy for Mains: Two Years of Russia Ukraine War: Current Status, Impact On World and India, and Future. |
|---|
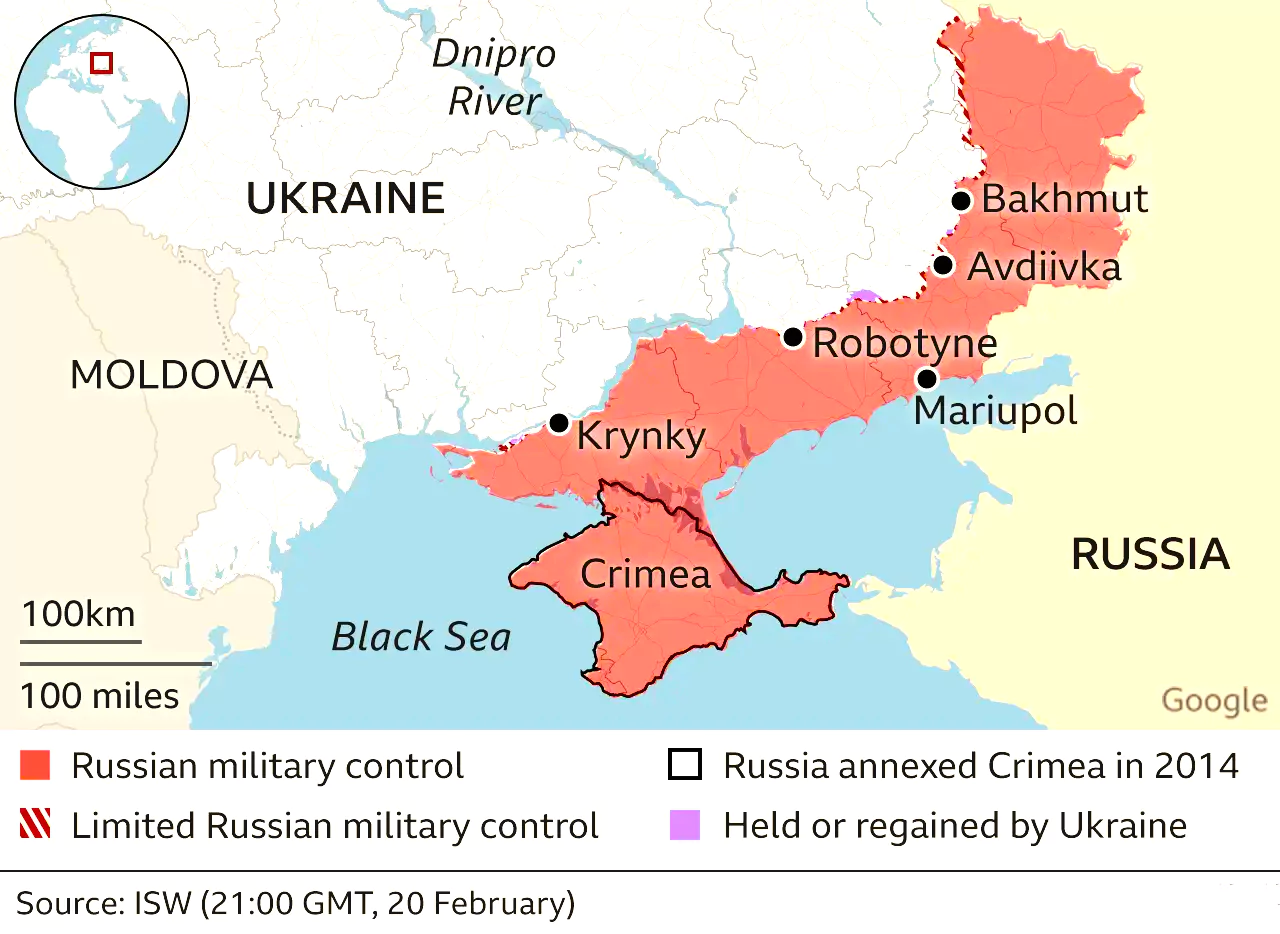
It is imperative for all stakeholders to prioritize dialogue and return to the negotiation table. The escalation of hostilities and violence serves no one’s interests and only exacerbates suffering and instability.
| Prelims PYQ (2019):
Consider the following pairs: Sea Bordering country 1. Adriatic Sea : Albania 2. Black Sea : Croatia 3. Caspian Sea : Kazakhstan 4. Mediterranean Sea : Morocco 5. Red Sea : Syria Which of the pairs given above are correctly matched? (a) 1, 2 and 4 only (b) 1, 3 and 4 only (c) 2 and 5 only (d) 1, 2, 3, 4 and 5 Ans: (b) |
|---|
| Mains Question: What is the significance of Indo- US defence deals over Indo-Russian defence deals? Discuss with reference to stability in the Indo- Pacific region. [250 Words, 15 Marks] |
|---|
| Must Read | |
| NCERT Notes For UPSC | UPSC Daily Current Affairs |
| UPSC Blogs | UPSC Daily Editorials |
| Daily Current Affairs Quiz | Daily Main Answer Writing |
| UPSC Mains Previous Year Papers | UPSC Test Series 2024 |
SC Verdict on Newsclick Shows Adherence to Due Pro...
Stay Invested: On Chabahar and India-Iran Relation...
Credit Rating Agencies, Impact on India’s De...
Catapulting Indian Biopharma Industry
Globalisation Under Threat, US Import Tariffs Have...
Global Report on Hypertension, Global Insights and...
<div class="new-fform">
</div>
