Recently, the capacity building commission has launched the Young Scientists Induction Training programme in collaboration with the office of the principal scientific adviser (Office of PSA) at the Indian Institute of Management Visakhapatnam (IIM-V).
News Source: PIB
| Must Read | |
| NCERT Notes For UPSC | UPSC Daily Current Affairs |
| UPSC Blogs | UPSC Daily Editorials |
| Daily Current Affairs Quiz | Daily Main Answer Writing |
| UPSC Mains Previous Year Papers | UPSC Test Series 2024 |
For the year 2024 -25, the interim union budget has allocated Rs 1 crore to encourage the private sector to scale up research and innovation in sunrise industries.
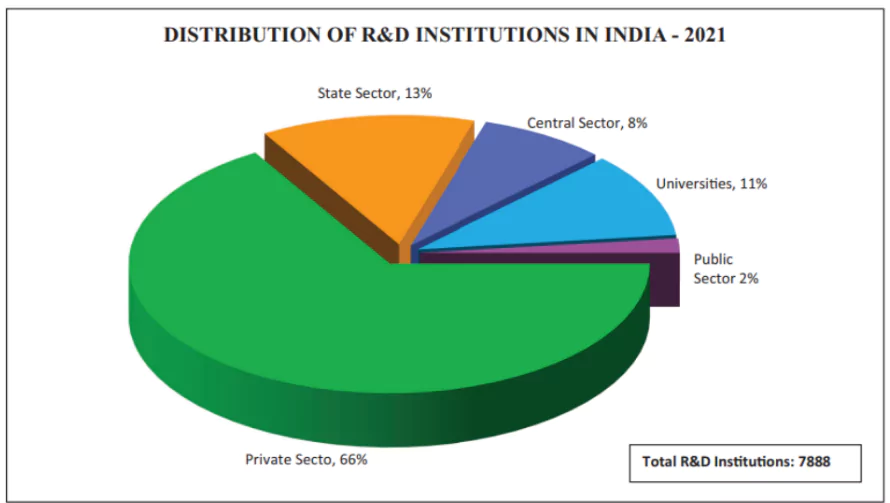 Information Technology: These companies are focused on developing innovative solutions and are investing in AI, data analytics, etc.
Information Technology: These companies are focused on developing innovative solutions and are investing in AI, data analytics, etc.
National Research Foundation (NRF)
Key Objectives Of National Research Foundation
|
|---|
News Source: Downtoearth
| Must Read | |
| NCERT Notes For UPSC | UPSC Daily Current Affairs |
| UPSC Blogs | UPSC Daily Editorials |
| Daily Current Affairs Quiz | Daily Main Answer Writing |
| UPSC Mains Previous Year Papers | UPSC Test Series 2024 |
The foundation stone of Talabira Thermal Power Project of Neyveli Lignite Corporation India Limited was laid by the Prime Minister in Sambalpur, Odisha
News source: news on Air
| Must Read | |
| NCERT Notes For UPSC | UPSC Daily Current Affairs |
| UPSC Blogs | UPSC Daily Editorials |
| Daily Current Affairs Quiz | Daily Main Answer Writing |
| UPSC Mains Previous Year Papers | UPSC Test Series 2024 |
Recently, the Interim Budget 2024-25 presented by the Union Finance Minister announced the expansion of the application of Nano DAP on various crops in all agro climatic zones.
About DAP or Di-Ammonium Phosphate
Indian Farmers Fertiliser Cooperative Limited (IFFCO)
|
|---|

The various significant benefits of Nano DAP underscores the necessity for its more adoption and expansion. The expansion of the application of Nano DAP on various crops in all agro climatic zones is a right and required step, however the need to strike a balance between technological advancements and environmental sustainability is must.
Also Read:
News Source: The Indian Express
| Must Read | |
| NCERT Notes For UPSC | UPSC Daily Current Affairs |
| UPSC Blogs | UPSC Daily Editorials |
| Daily Current Affairs Quiz | Daily Main Answer Writing |
| UPSC Mains Previous Year Papers | UPSC Test Series 2024 |
Recently, the Indian Navy thwarted two piracy attempts off the Somali coast within a span of 36 hours.
News Source: The Indian Express
| Must Read | |
| NCERT Notes For UPSC | UPSC Daily Current Affairs |
| UPSC Blogs | UPSC Daily Editorials |
| Daily Current Affairs Quiz | Daily Main Answer Writing |
| UPSC Mains Previous Year Papers | UPSC Test Series 2024 |
Department for Promotion of Industry and Internal Trade (DPIIT) organizes nationwide ‘One District One Product Sampark’ events.

One District One Product: It is an initiative launched with the aim of unlocking the full potential of districts, fostering economic and socio-cultural growth, and generating employment, particularly in rural areas.
In the era of globalization, initiatives such as One District One Product prove beneficial for local sectors grappling with challenges like credit access, high institutional credit costs, technology gaps, supply chain integration issues, and safety compliance. Reinforcing these aspects through One District One Product not only minimizes waste and generates employment but also aligns with the government’s objective of doubling income for farmers and local artisans.
News Source: PIB
| Must Read | |
| NCERT Notes For UPSC | UPSC Daily Current Affairs |
| UPSC Blogs | UPSC Daily Editorials |
| Daily Current Affairs Quiz | Daily Main Answer Writing |
| UPSC Mains Previous Year Papers | UPSC Test Series 2024 |
According to the latest global burden estimates by the World Health Organization (WHO), in 2022, India witnessed over 14.1 lakh new cancer cases and recorded more than 9.1 lakh deaths attributed to the disease.
Universal Health Coverage (UHC)
|
|---|
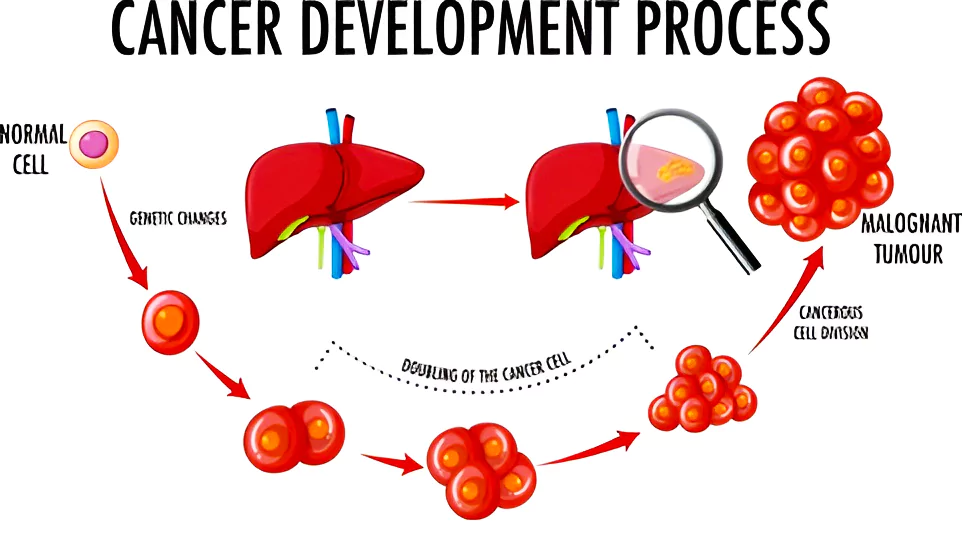
Cancer arises from the transformation of normal cells into tumor cells in a multi-stage process which are the result of the interaction between a person’s genetic factors and three categories of external agents, including:
WHO Global NCD Action Plan 2013–2020
|
|---|
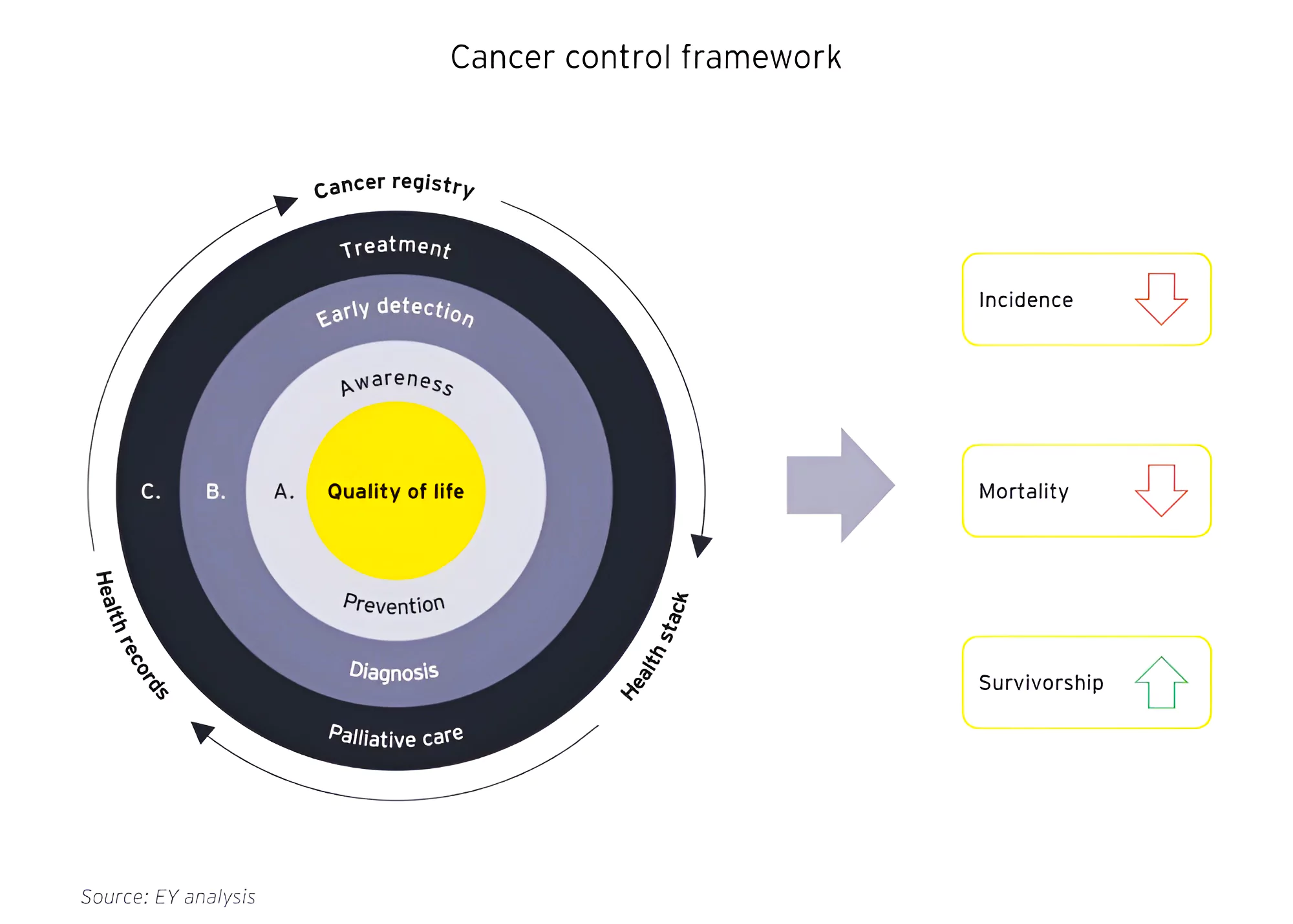
WHO Global Action Plan for the Prevention and Control of NCDs 2013–2020 provides a road map.
Observance of World Cancer Day on 4th February.
Focusing on Scientific Research for the treatment of various types of cancer.
Also Read:
News Source: ET
| Must Read | |
| NCERT Notes For UPSC | UPSC Daily Current Affairs |
| UPSC Blogs | UPSC Daily Editorials |
| Daily Current Affairs Quiz | Daily Main Answer Writing |
| UPSC Mains Previous Year Papers | UPSC Test Series 2024 |
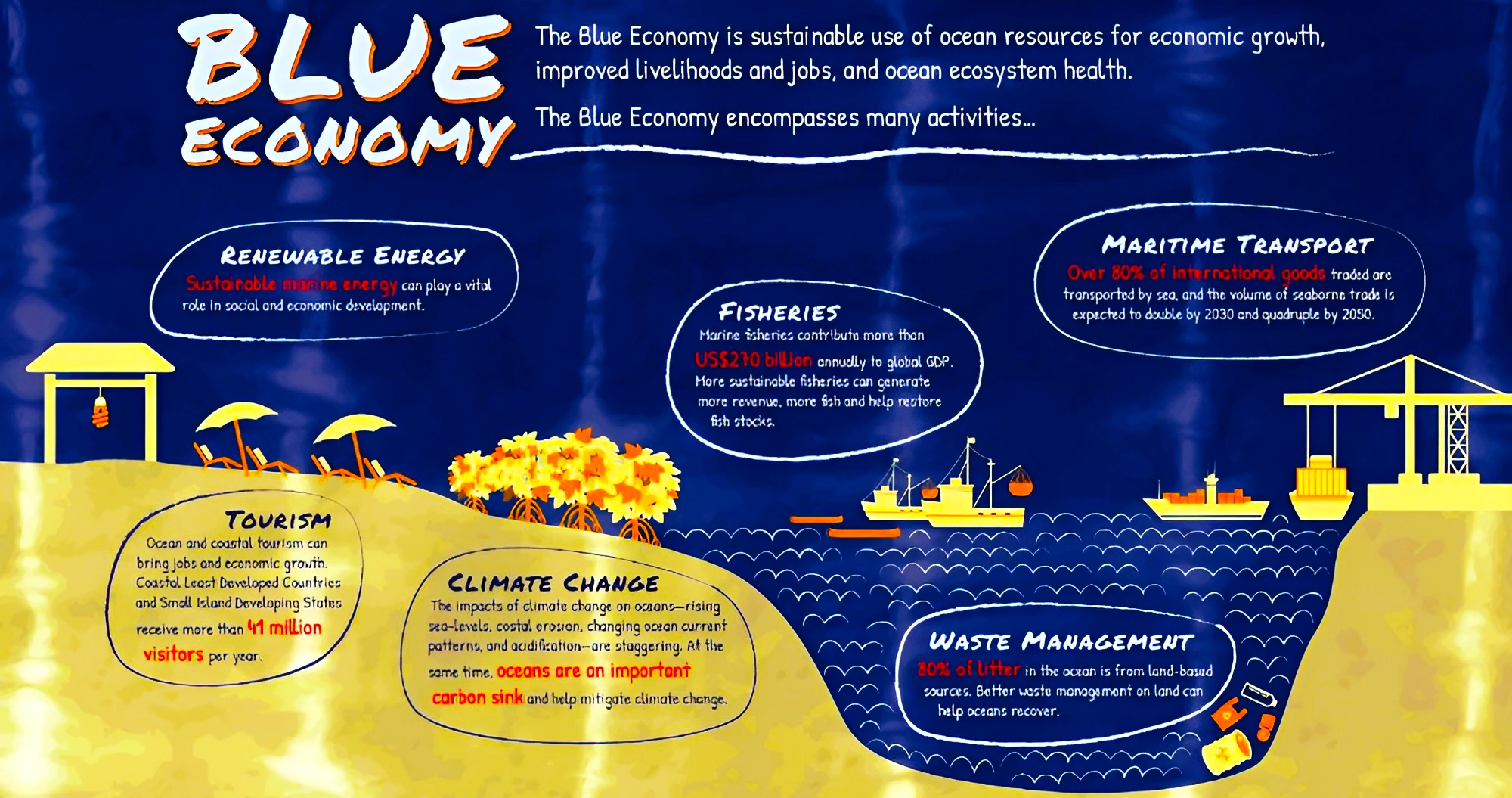
This article is based on the news “Interim budget mentions blue economy 2.0: What this means” which was published in the Indian Express. Recently, the Interim Budget 2024-25 presented by the Union Finance Minister stressed on environment-friendly development through the promotion of “blue economy 2.0”.
| Relevancy for Prelims: Parliament Budget Session 2024 Live Updates, Union Budget 2024-25, Interim Budget 2024-2025, Ocean Resources, Blueprint For Maritime Blue Economy, Global Maritime India Summit 2023 and G20 Summit.
Relevancy for Mains: Interim Budget: Blue Economy 2.0: Status, Policies, Significance, Challenges, and Way Forward. |
|---|
|
|---|
With India’s vast maritime interests, the blue economy holds a significant position in India’s economic growth, employment generation, equity and protection of environment. It is the right time to achieve the best of its potential while maintaining the sustainability of the marine environment.
| Mains Question: Defining Blue Revolution. Explain the problem and strategies for pisciculture development in India. [250 Words, 15 Marks] |
|---|
| Must Read | |
| NCERT Notes For UPSC | UPSC Daily Current Affairs |
| UPSC Blogs | UPSC Daily Editorials |
| Daily Current Affairs Quiz | Daily Main Answer Writing |
| UPSC Mains Previous Year Papers | UPSC Test Series 2024 |
This article is based on the news “Law Commission recommends retaining criminal defamation ‘within the scheme of criminal laws” which was published in the Hindu. Recently, the 22nd Law Commission of India has submitted its report number 285 titled “The Law of Criminal Defamation” to the Government of India.
| Relevancy for Prelims: Recent Criminal Law Reforms, Parliament Passes Three Criminal Law Reform Bills, Law Commission Of India, Information Technology (IT) Act, and Fundamental Rights.
Relevancy for Mains: Defamation Laws in India: Need, Significance, Challenges and Law Commission Report. |
|---|
History of Defamation
|
|---|

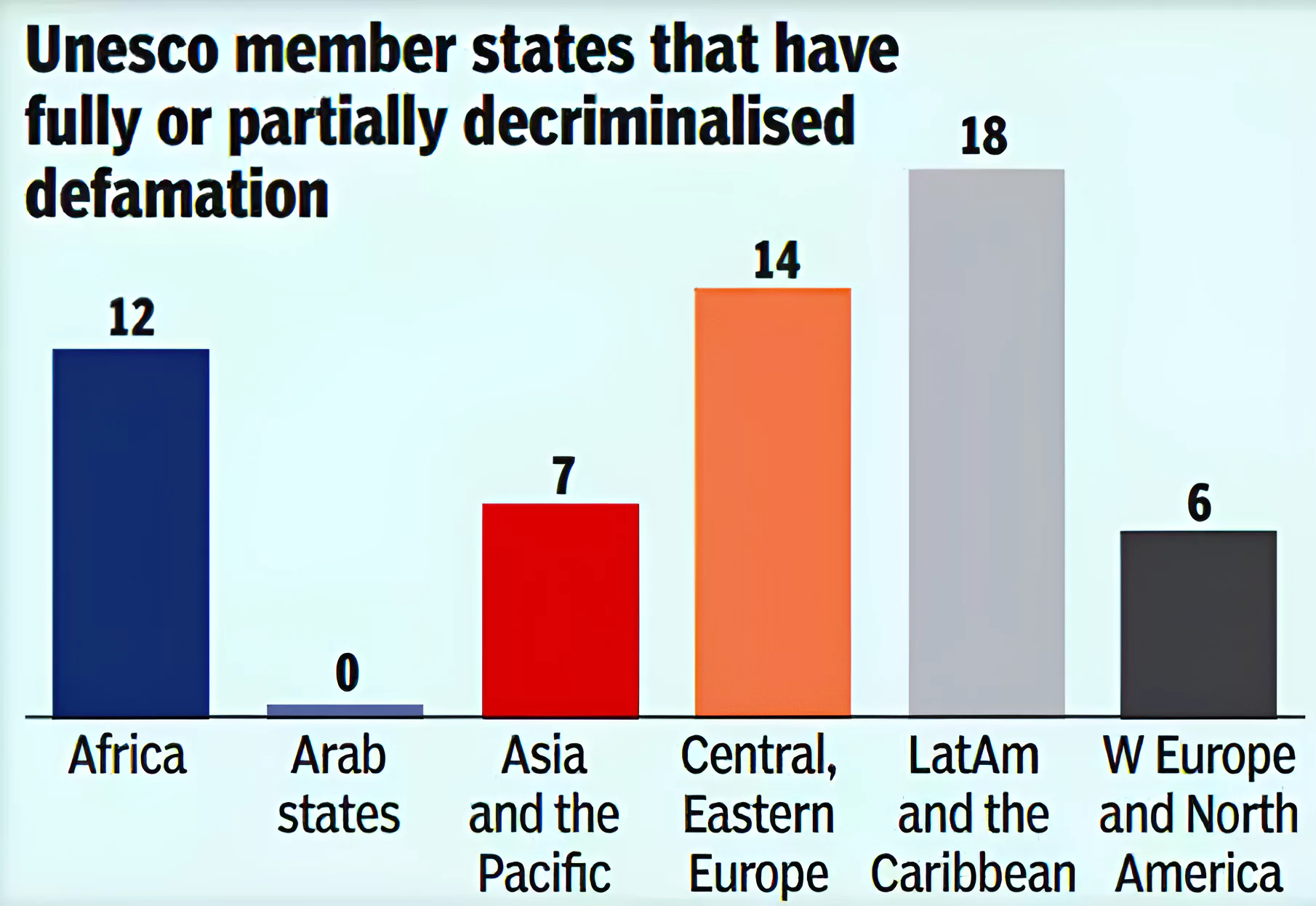 International Practice: The international human rights treaties have emphasised on the right to reputation.
International Practice: The international human rights treaties have emphasised on the right to reputation. Supreme Court’s Verdict on Criminal Defamation Cases
|
|---|
| Mains Question: Discuss Section 66A of IT Act, with reference to its alleged violation of Article 19 of the Constitution. (200 words, 10 marks) |
|---|
| Must Read | |
| NCERT Notes For UPSC | UPSC Daily Current Affairs |
| UPSC Blogs | UPSC Daily Editorials |
| Daily Current Affairs Quiz | Daily Main Answer Writing |
| UPSC Mains Previous Year Papers | UPSC Test Series 2024 |
SC Verdict on Newsclick Shows Adherence to Due Pro...
Stay Invested: On Chabahar and India-Iran Relation...
Credit Rating Agencies, Impact on India’s De...
Catapulting Indian Biopharma Industry
Globalisation Under Threat, US Import Tariffs Have...
Global Report on Hypertension, Global Insights and...
<div class="new-fform">
</div>
