The Karnataka Department of Health and Family Welfare has conducted 2,567 testsVto check the prevalence of KFD disease.
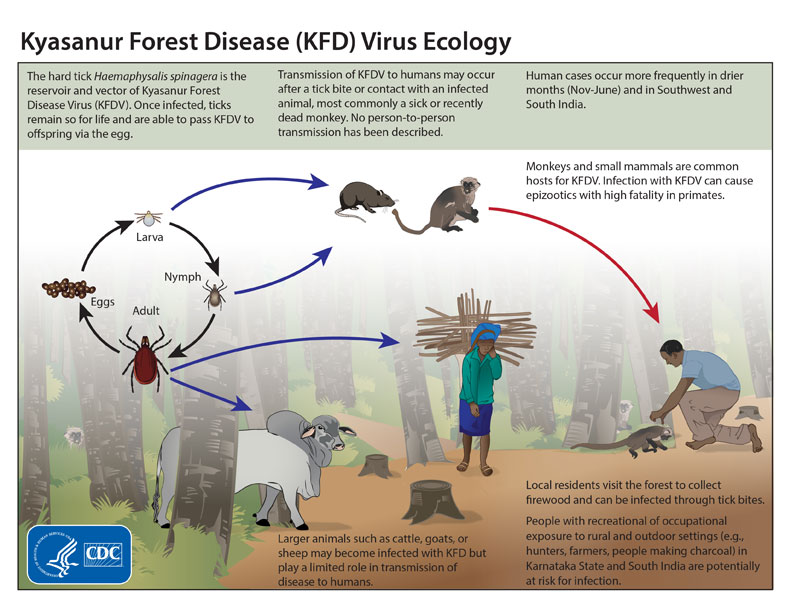
News Source: TheHindu
| Must Read | |
| NCERT Notes For UPSC | UPSC Daily Current Affairs |
| UPSC Blogs | UPSC Daily Editorials |
| Daily Current Affairs Quiz | Daily Main Answer Writing |
| UPSC Mains Previous Year Papers | UPSC Test Series 2024 |
Recently, India has joined the Global Alliance for Circular Economy and Resource Efficiency (GACERE).
What is the Circular Economy?
|
|---|
News Source: PIB
| Must Read | |
| NCERT Notes For UPSC | UPSC Daily Current Affairs |
| UPSC Blogs | UPSC Daily Editorials |
| Daily Current Affairs Quiz | Daily Main Answer Writing |
| UPSC Mains Previous Year Papers | UPSC Test Series 2024 |
Indian Institute of Technology, Kanpur has tested India’s first Hypervelocity Expansion Tunnel Test Facility.
Fund for Improvement of S&T Infrastructure (FIST):
|
|---|
Aerodynamics:
Hypervelocity:
Ionization:
Hypersonic:
|
|---|
News source: PIB
| Must Read | |
| NCERT Notes For UPSC | UPSC Daily Current Affairs |
| UPSC Blogs | UPSC Daily Editorials |
| Daily Current Affairs Quiz | Daily Main Answer Writing |
| UPSC Mains Previous Year Papers | UPSC Test Series 2024 |
A recent report published in Nature Communication highlights the exacerbation of water scarcity worldwide due to declining water quality, particularly attributed to nitrogen pollution in rivers.
The Vital Role of Nitrogen in Earth’s Ecosystems
|
|---|
| At Global Level | At India Level |
International Nitrogen Initiative:
Gothenburg Protocol (1999):
South Asia Nitrogen Hub (SANH):
Colombo Declaration on Sustainable Nitrogen Waste Management:
|
Soil Health Card:
Neem-Coated Urea:
Bharat Stage Norms:
|
Addressing nitrogen pollution through sustainable management is crucial for achieving global sustainable development goals and improving economic efficiency.
News Source : DTE
| Must Read | |
| NCERT Notes For UPSC | UPSC Daily Current Affairs |
| UPSC Blogs | UPSC Daily Editorials |
| Daily Current Affairs Quiz | Daily Main Answer Writing |
| UPSC Mains Previous Year Papers | UPSC Test Series 2024 |
To formalize and support the Indian Fishery Sector, recently the Union Cabinet approved the PM MKSSY (Pradhan Mantri Matsya Kisan Samridhi Sah-Yojana).
Fisheries Infrastructure Development Fund (FIDF)
|
|---|
News Source: PIB
| Must Read | |
| NCERT Notes For UPSC | UPSC Daily Current Affairs |
| UPSC Blogs | UPSC Daily Editorials |
| Daily Current Affairs Quiz | Daily Main Answer Writing |
| UPSC Mains Previous Year Papers | UPSC Test Series 2024 |
Casgevy and Lyfgenia, the first CRISPR-based gene therapies have received approval from the Food and Drug Administration (FDA) for sickle cell anemia and beta-thalassemia treatment.
Gene Therapy
Gene Editing
Germline Editing
|
|---|
Sickle Cell Disease
Thalassaemia
|
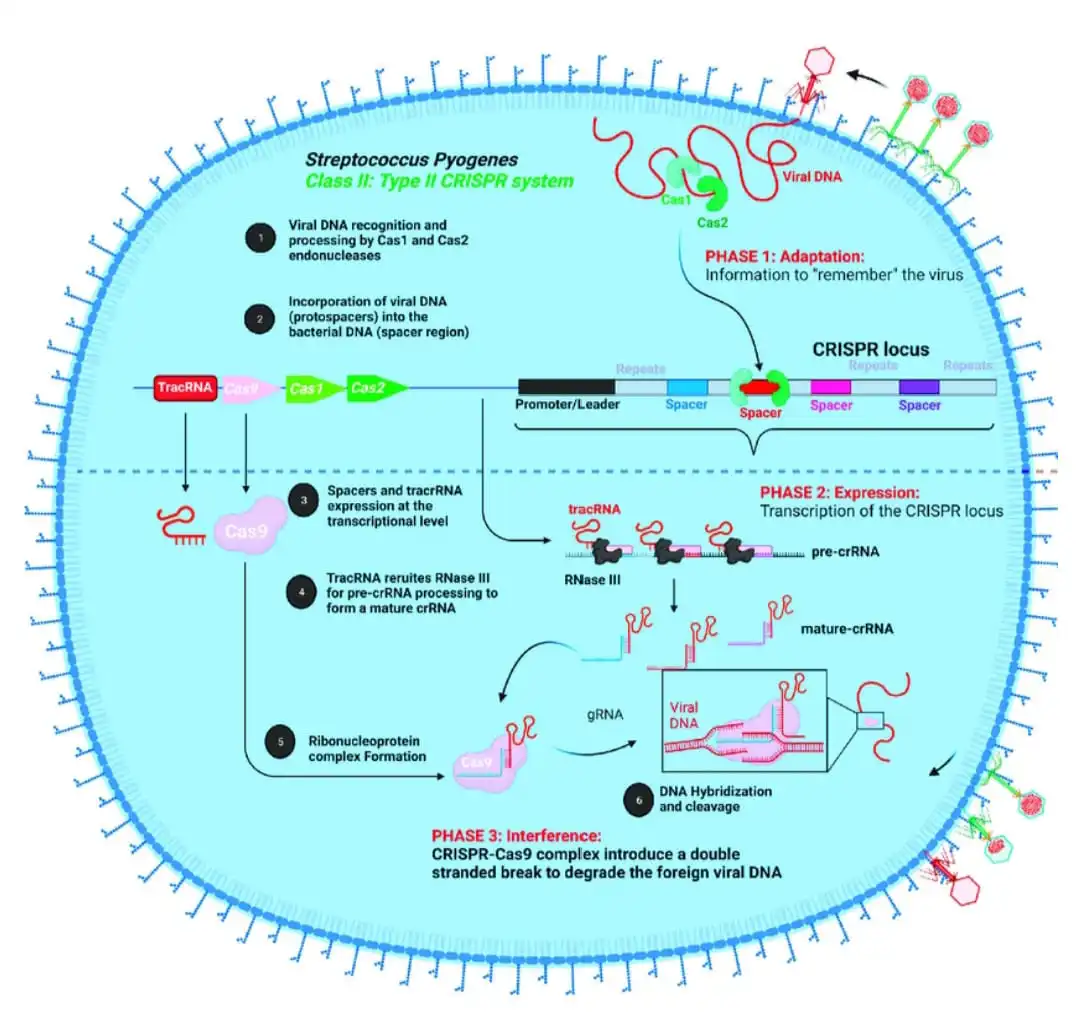
News Source: The Hindu
| Must Read | |
| NCERT Notes For UPSC | UPSC Daily Current Affairs |
| UPSC Blogs | UPSC Daily Editorials |
| Daily Current Affairs Quiz | Daily Main Answer Writing |
| UPSC Mains Previous Year Papers | UPSC Test Series 2024 |
Recently, the Himachal Pradesh government started a pilot program to connect Fair Price Shops to the Open Network for Digital Commerce (ONDC) platform.
What is a Fair Price Shop?
|
|---|
| Feature | E-commerce Platforms | Open Network Digital Commerce (ONDC) |
| App Download | Required to purchase online | Not required: Buyers can shop online |
| Model | Platform-centric: Buyer & seller use same platform | Open-network: Works across multiple platforms & apps |
| Hyper-local Focus | Limited | Encourages local business discovery & connection |
| Product Categories | Wide variety | Currently limited to F&B, groceries, home decor |
| Ownership | Private companies | Decentralized, no single entity owns |
| Onboarding Fee | High | Lower and market-driven |
| Options for Buyers/Sellers | Limited (dominated by few sellers) | More diverse, seller filterable by buyers |
| Transferable Reviews | No, restart required on new platform | Yes, reviews transferable across ONDC platforms |
News Source: PIB
| Must Read | |
| NCERT Notes For UPSC | UPSC Daily Current Affairs |
| UPSC Blogs | UPSC Daily Editorials |
| Daily Current Affairs Quiz | Daily Main Answer Writing |
| UPSC Mains Previous Year Papers | UPSC Test Series 2024 |
The Union Agriculture Minister has recently unveiled new inititives under the Pradhan Mantri Fasal Bima Yojana (PMFBY).
News Source: PIB
| Must Read | |
| NCERT Notes For UPSC | UPSC Daily Current Affairs |
| UPSC Blogs | UPSC Daily Editorials |
| Daily Current Affairs Quiz | Daily Main Answer Writing |
| UPSC Mains Previous Year Papers | UPSC Test Series 2024 |
The protection of sacred groves is a part of the Community Reserve done by state governments.
Kadalundi-Vallikkunnu Community Reserve
|
|---|
What Is a Community Reserve?
|
|---|

Different Names for Sacred Groves
|
|---|
Sacred groves in India are being gradually altered due to ever-expanding human populations, pollution and removal of biomass; effective conservation is the need of the hour to maintain their functional values.
News Source: Scientific American and PIB
| Must Read | |
| NCERT Notes For UPSC | UPSC Daily Current Affairs |
| UPSC Blogs | UPSC Daily Editorials |
| Daily Current Affairs Quiz | Daily Main Answer Writing |
| UPSC Mains Previous Year Papers | UPSC Test Series 2024 |
This article is based on the news “Kaladan project of India ‘almost dead’ after Paletwa fell to Arakan Army: senior Myanmar Opposition leader” which was published in the Hindu. The Arakan Army, a rebel group in Myanmar, captured Paletwa (an important site in the Kaladan project) near the Mizoram border in January 2024, making the Kaladan project almost dead.
| Relevancy for Prelims: Kaladan Multi-Modal Transit Transport Project (KMTTP), Rakhine State, Myanmar Crisis, Myanmar Refugees, India-Myanmar Relation, ASEAN, and Act East Policy.
Relevancy for Mains: Kaladan Project: Background, Present Status, Components and Significance |
|---|
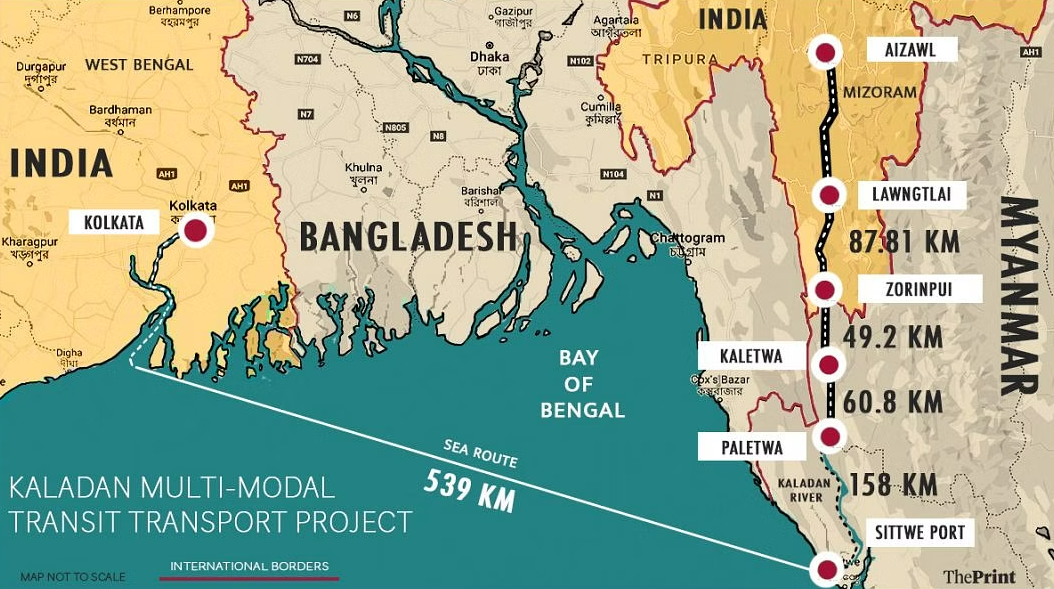
Kaladan Project Map
News Source: The Hindu
| Must Read | |
| NCERT Notes For UPSC | UPSC Daily Current Affairs |
| UPSC Blogs | UPSC Daily Editorials |
| Daily Current Affairs Quiz | Daily Main Answer Writing |
| UPSC Mains Previous Year Papers | UPSC Test Series 2024 |
This article is based on the news “Need to launch next phase of Smart Cities Mission: Parliamentary Committee” which was published in the Hindu. The Standing Committee on Housing and Urban Affairs recently presented a report in the Lok Sabha on “Smart Cities Mission: An Evaluation”.
| Relevancy for Prelims: Interim Budget 2024-2025, Smart Cities Mission, Smart Cities Award, Jamshedpur Model, Urbanization, and Urban Governance Model
Relevancy for Mains: Smart Cities Mission (SCM): Current Progress, Achievements, Challenges, and Way Forward. |
|---|
Smart Cities Mission Success Stories
|
|---|
| Government Programs for Sustainable Urban Development: |
|---|
News Source: The Hindu
| Must Read | |
| NCERT Notes For UPSC | UPSC Daily Current Affairs |
| UPSC Blogs | UPSC Daily Editorials |
| Daily Current Affairs Quiz | Daily Main Answer Writing |
| UPSC Mains Previous Year Papers | UPSC Test Series 2024 |
SC Verdict on Newsclick Shows Adherence to Due Pro...
Stay Invested: On Chabahar and India-Iran Relation...
Credit Rating Agencies, Impact on India’s De...
Catapulting Indian Biopharma Industry
Globalisation Under Threat, US Import Tariffs Have...
Global Report on Hypertension, Global Insights and...
<div class="new-fform">
</div>
