Kuttanad, Kerala, known for idyllic backwaters, rivers, canals, and vast paddy fields, faces the alarming consequences of changing weather patterns.
|
|---|
About Globally Important Agricultural Heritage Systems (GIAHS)
About Ramsar Sites
|
|---|
| Must Read | |
| NCERT Notes For UPSC | UPSC Daily Current Affairs |
| UPSC Blogs | UPSC Daily Editorials |
| Daily Current Affairs Quiz | Daily Main Answer Writing |
| UPSC Mains Previous Year Papers | UPSC Test Series 2024 |
Recently, a new study suggested that Luna Crater (1.8-kilometre-wide) in Gujarat may have been caused by the largest meteorite to strike the planet in the last 50,000 years.
About Meteorite
Difference between Meteor, Meteorite and Meteoroid
|
|---|
| Must Read | |
| NCERT Notes For UPSC | UPSC Daily Current Affairs |
| UPSC Blogs | UPSC Daily Editorials |
| Daily Current Affairs Quiz | Daily Main Answer Writing |
| UPSC Mains Previous Year Papers | UPSC Test Series 2024 |
India is witnessing an unprecedented construction boom, with over 3,00,000 housing units manufactured annually that poses significant environmental challenges.

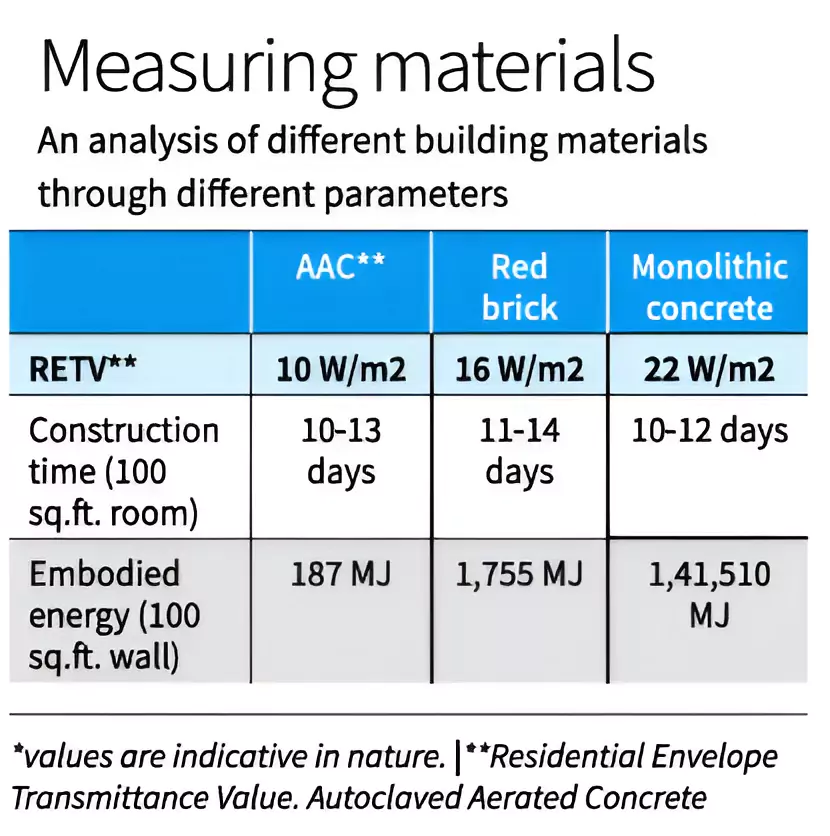
The journey toward sustainable construction is challenging but essential for a greener future. The goal can be achieved by re-imagining construction design and practices, manufacturing innovative walling materials, and fostering a culture of sustainability, resilient and energy-efficient structures that align with environmental goals and significantly improve the quality of life for the masses.
| Must Read | |
| NCERT Notes For UPSC | UPSC Daily Current Affairs |
| UPSC Blogs | UPSC Daily Editorials |
| Daily Current Affairs Quiz | Daily Main Answer Writing |
| UPSC Mains Previous Year Papers | UPSC Test Series 2024 |
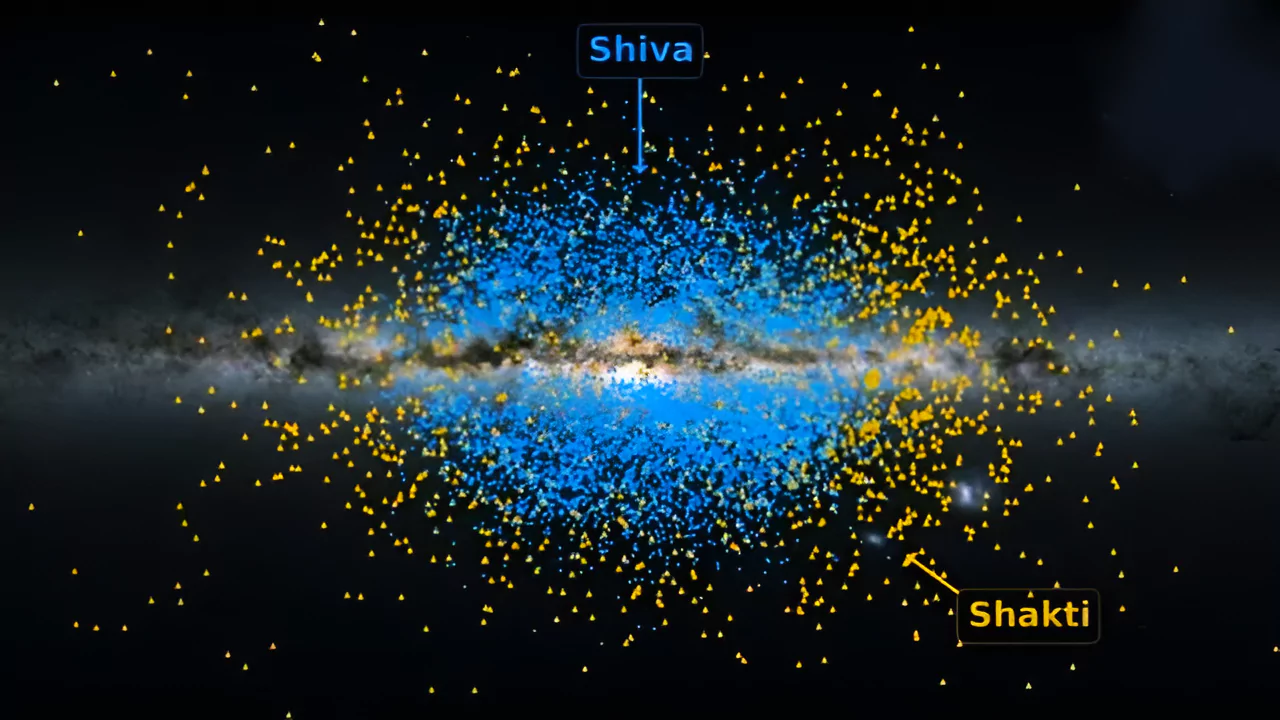
Recently astronauts has discovered to ancient streams of stars Shiva and Shakti which are among the earliest building blocks of Milky way galaxy.
| Must Read | |
| NCERT Notes For UPSC | UPSC Daily Current Affairs |
| UPSC Blogs | UPSC Daily Editorials |
| Daily Current Affairs Quiz | Daily Main Answer Writing |
| UPSC Mains Previous Year Papers | UPSC Test Series 2024 |
Scientists are advocating for the adoption of Quantum Cryptography as a cutting-edge technology to safeguard sensitive communications.
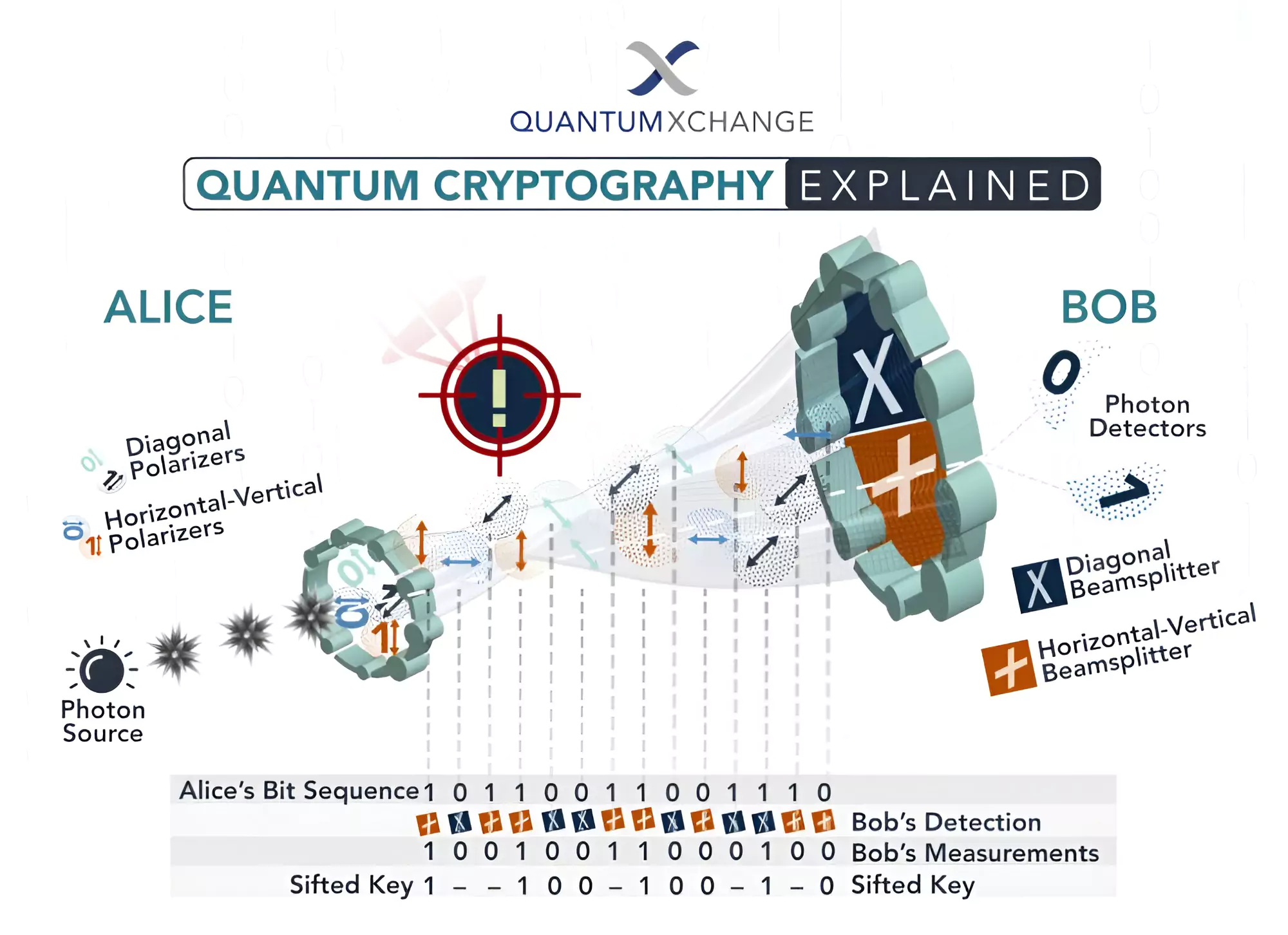 In this process, the sender transmits photons through a polarizer with four potential polarizations and bit designations: Vertical (One bit), Horizontal (Zero bit), 45 degrees right (One bit), or 45 degrees left (Zero bit).
In this process, the sender transmits photons through a polarizer with four potential polarizations and bit designations: Vertical (One bit), Horizontal (Zero bit), 45 degrees right (One bit), or 45 degrees left (Zero bit). 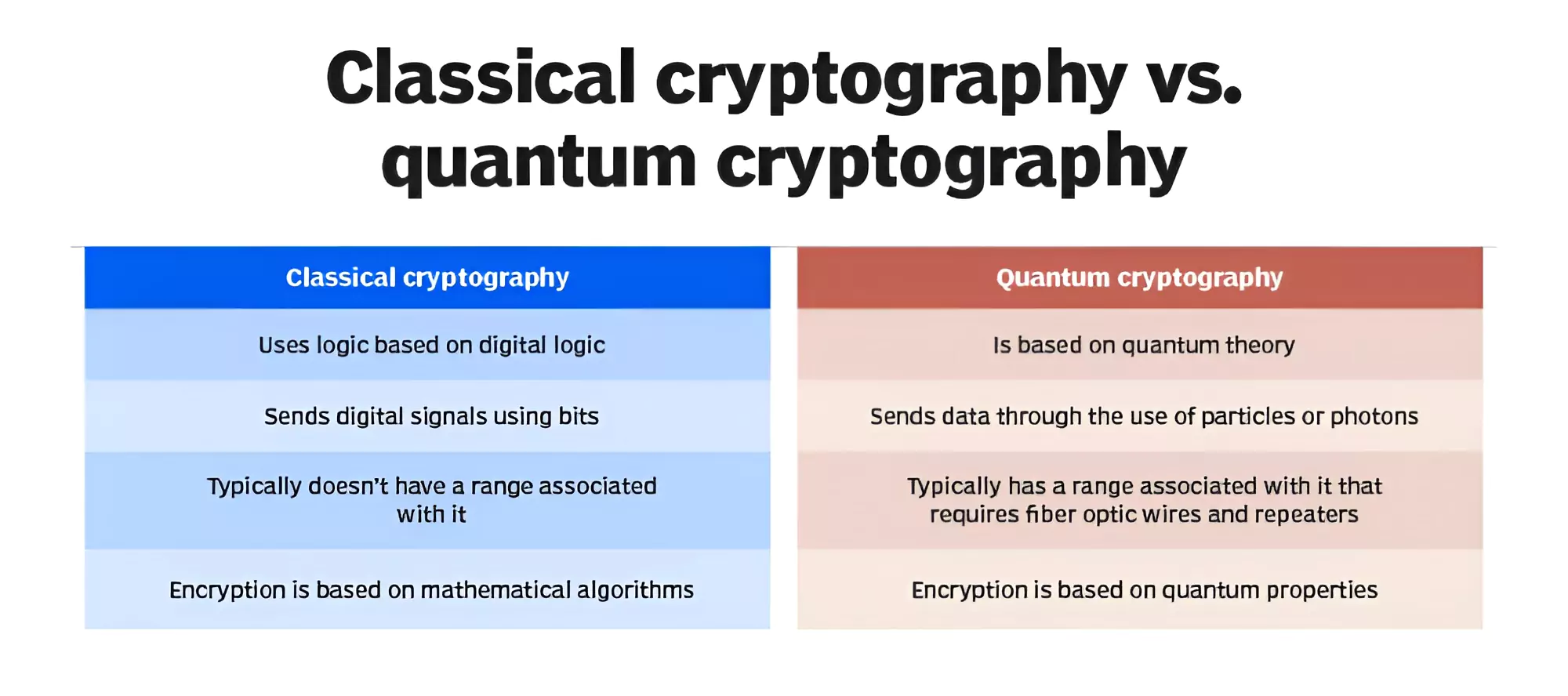
| Must Read | |
| NCERT Notes For UPSC | UPSC Daily Current Affairs |
| UPSC Blogs | UPSC Daily Editorials |
| Daily Current Affairs Quiz | Daily Main Answer Writing |
| UPSC Mains Previous Year Papers | UPSC Test Series 2024 |
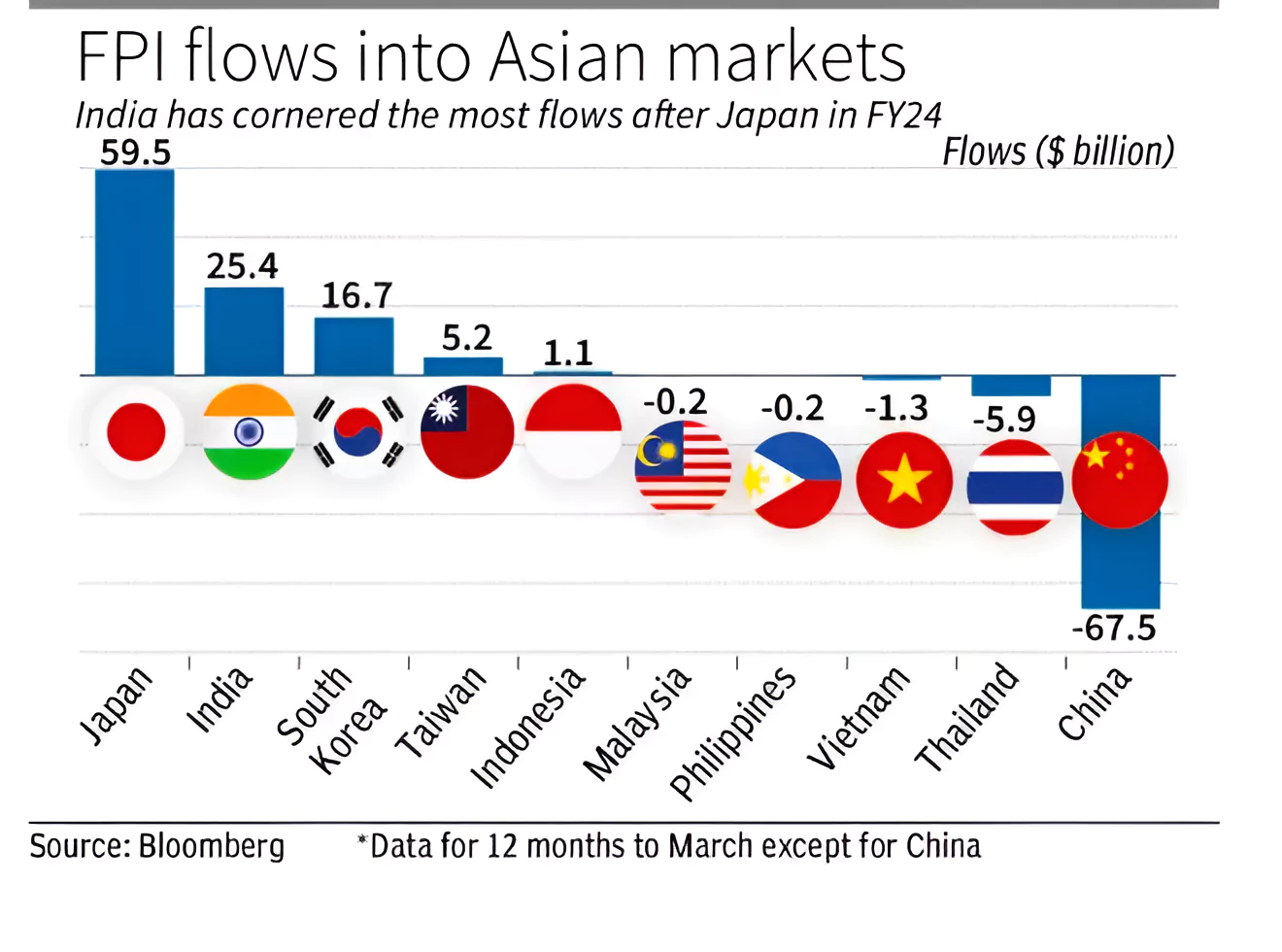
India received overseas inflows totaling ₹3.33 lakh crore, equivalent to $40.4 billion, in equities, debt, and hybrid instruments combined during the current financial year, marking a record high.
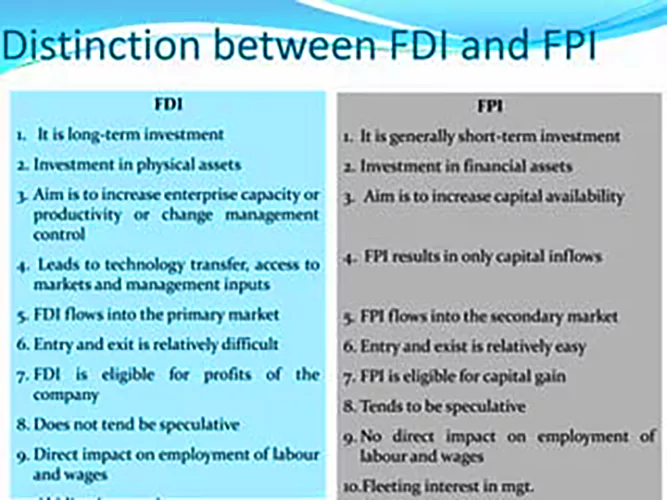
| Must Read | |
| NCERT Notes For UPSC | UPSC Daily Current Affairs |
| UPSC Blogs | UPSC Daily Editorials |
| Daily Current Affairs Quiz | Daily Main Answer Writing |
| UPSC Mains Previous Year Papers | UPSC Test Series 2024 |
The cVIGIL app of Election Commission of India (ECI) received over 99% complaints and close to 89% of these complaints have been resolved within 100 minutes.


| Must Read | |
| NCERT Notes For UPSC | UPSC Daily Current Affairs |
| UPSC Blogs | UPSC Daily Editorials |
| Daily Current Affairs Quiz | Daily Main Answer Writing |
| UPSC Mains Previous Year Papers | UPSC Test Series 2024 |
UNESCO’s Executive Board recently approved the inclusion of 18 new sites into the UNESCO Global Geoparks network.
UNESCO Global Geopark
|
|---|
| Must Read | |
| NCERT Notes For UPSC | UPSC Daily Current Affairs |
| UPSC Blogs | UPSC Daily Editorials |
| Daily Current Affairs Quiz | Daily Main Answer Writing |
| UPSC Mains Previous Year Papers | UPSC Test Series 2024 |
Recently, the Ministry of Home Affairs (MHA) extended the validity of Foreign Contribution (Regulation) Act (FCRA) registration of non-government organizations (NGOs) and associations till June 30.
Foreign Contribution (Regulation) Amendment Act 2020:
|
|---|
| Must Read | |
| NCERT Notes For UPSC | UPSC Daily Current Affairs |
| UPSC Blogs | UPSC Daily Editorials |
| Daily Current Affairs Quiz | Daily Main Answer Writing |
| UPSC Mains Previous Year Papers | UPSC Test Series 2024 |
With the increasingly complex and multifaceted conduct of elections, the District Election Management Plan (DEMP) can be one of the possible solutions to ensure the smooth conduct of elections.
| Must Read | |
| NCERT Notes For UPSC | UPSC Daily Current Affairs |
| UPSC Blogs | UPSC Daily Editorials |
| Daily Current Affairs Quiz | Daily Main Answer Writing |
| UPSC Mains Previous Year Papers | UPSC Test Series 2024 |
A recent study has raised concerns about the alarming rate of soil erosion occurring in the Western Ghats Region (WGR).
| Relevancy for Prelims: Soil Formation, Soil Types In India, Soil Degradation, Soil Conservation, and UNCCD Report On Land Degradation.
Relevancy for Mains: Soil Erosion: Reasons, Impacts, Conservation Efforts, and Challenges. |
|---|
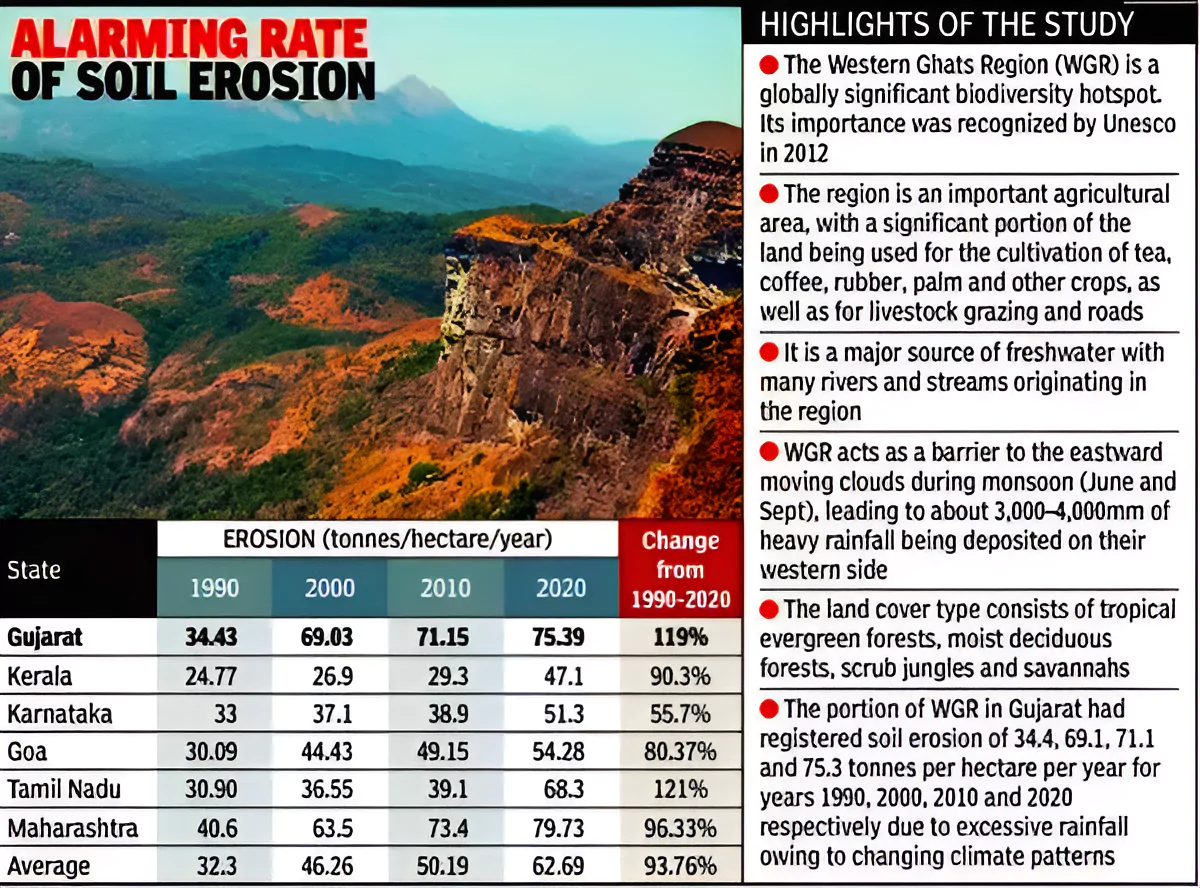
 Kerala and Karnataka: They witnessed a concerning increase of 90% and 56% respectively.
Kerala and Karnataka: They witnessed a concerning increase of 90% and 56% respectively.
Western Ghats Region (WGR)
|
|---|
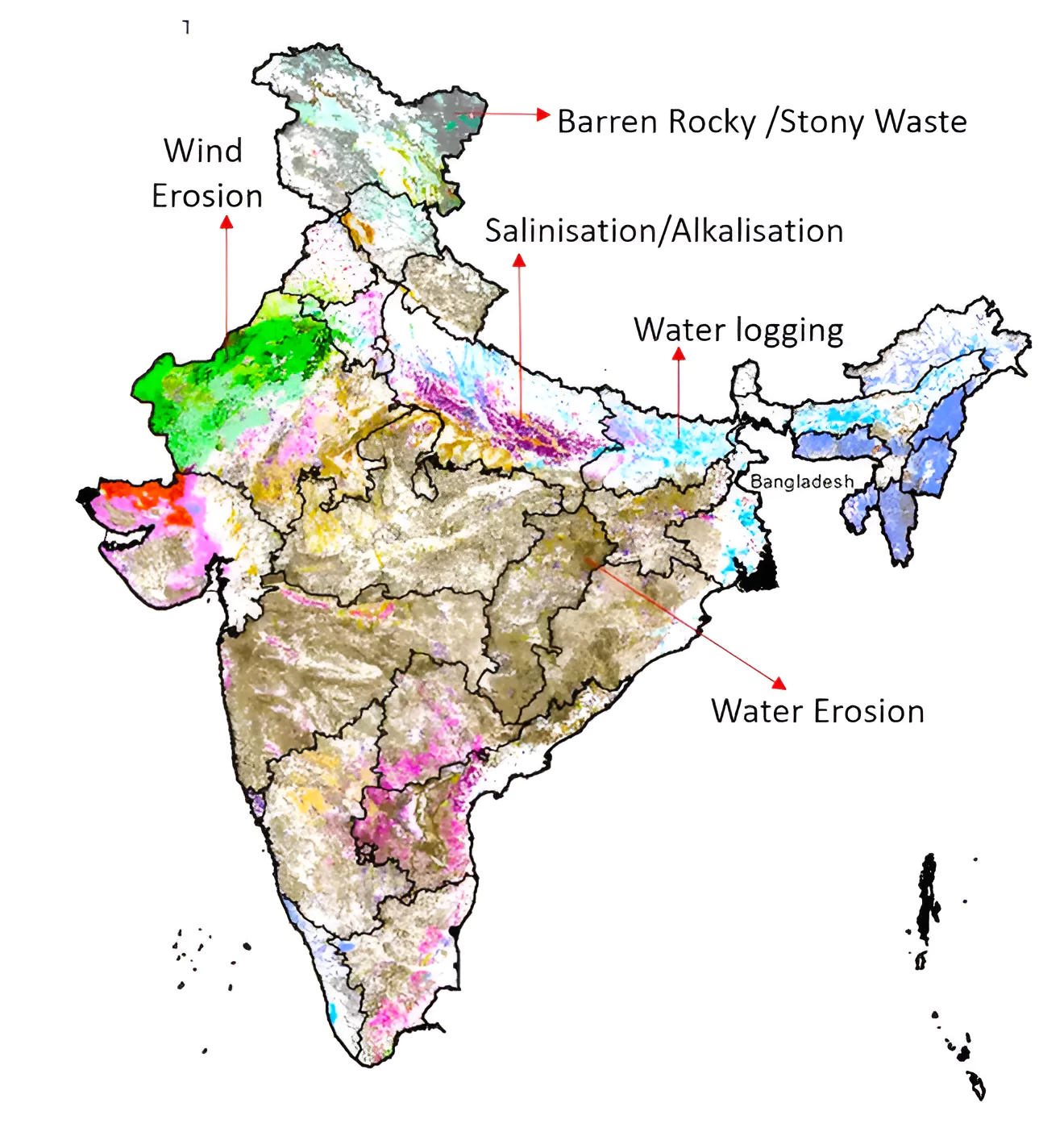
Soil erosion is broadly categorized into different types depending on the agent which triggers the erosion activity.
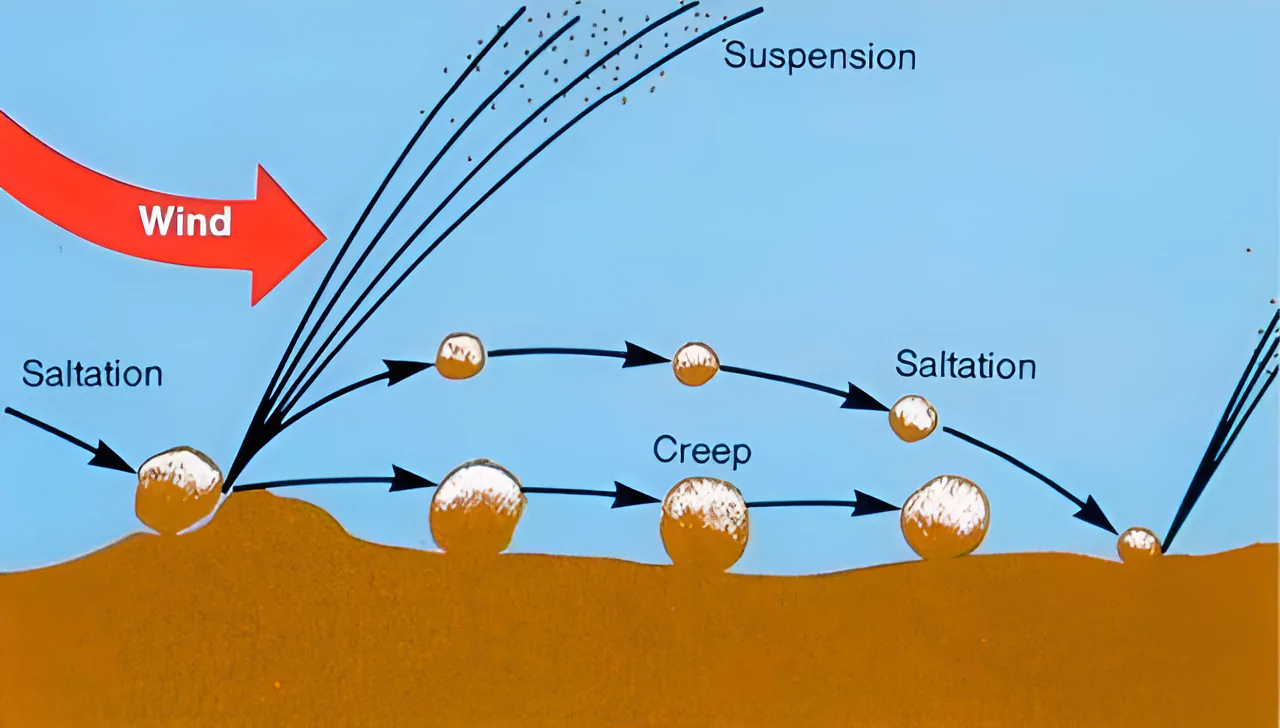
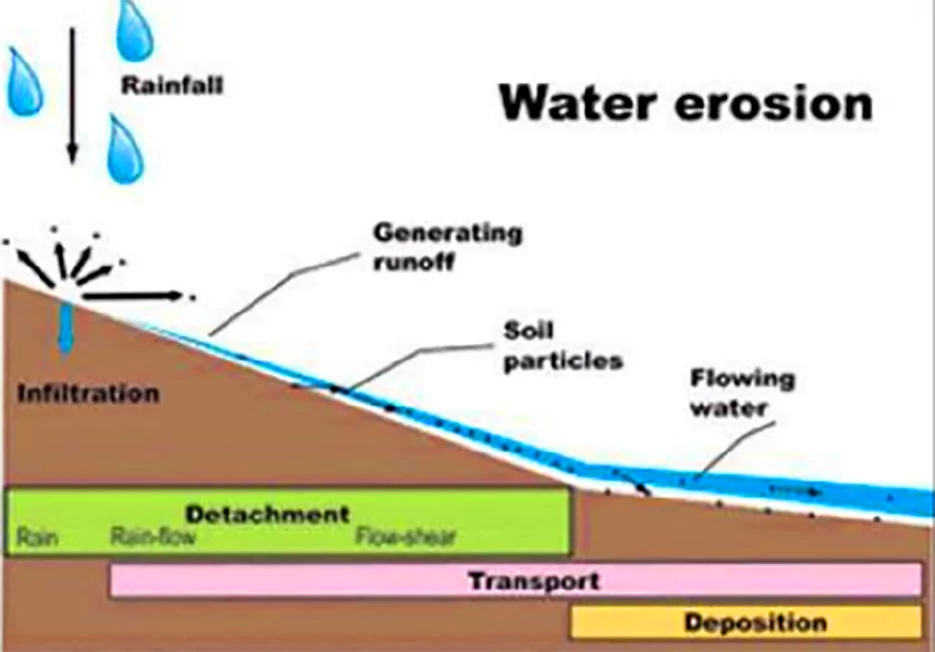
In India almost 130 million hectares of land, i.e. 45 % of total geographical surface area, is affected by serious soil erosion through gorge and gully, , cultivated wastelands, sandy areas, deserts and water logging. Its major impacts include:
Government Initiatives taken to Prevent Soil Erosion in India
|
|---|
| Prelims PYQ (2016):
‘Gadgil Committee Report’ and ‘Kasturirangan Committee Report’, sometimes seen in the news, are related to (a) constitutional reforms (b) Ganga Action Plan (c) linking of rivers (d) protection of Western Ghats Ans: (d) |
|---|
| Must Read | |
| NCERT Notes For UPSC | UPSC Daily Current Affairs |
| UPSC Blogs | UPSC Daily Editorials |
| Daily Current Affairs Quiz | Daily Main Answer Writing |
| UPSC Mains Previous Year Papers | UPSC Test Series 2024 |
<div class="new-fform">
</div>
