Context:
The recent heavy rainfall across the entire North Indian belt has unleashed mayhem in many states.
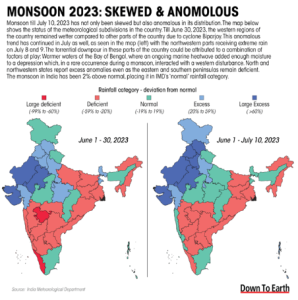
Trend of Monsoon in 2023
Factors for Landslides
Factors Leading to Monsoon Mayhem
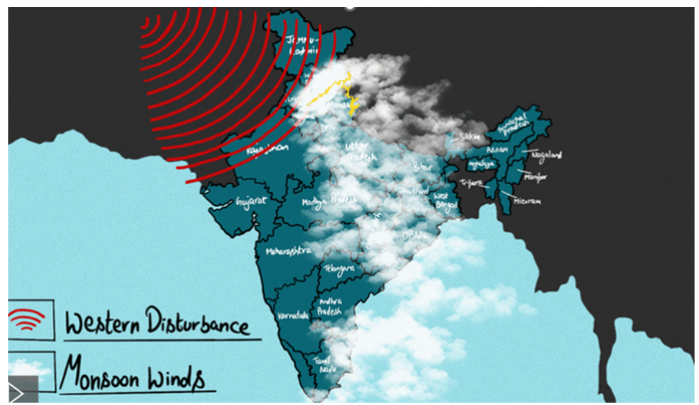
Image Source: India Today
Way Forward
| Terminology Used in Article:
Western Disturbance:
Monsoonal Winds:
Landslide:
|
News Source: The Hindu
Context:
Recently, the Union Government has released the operational guidelines for the management of non-communicable diseases (NCDs), acknowledging the increasing burden of such diseases as the country’s population continues to grow.
About Palliative Care:
Need for Palliative Care In India:
Existing Program for Palliative Care:
Gaps in the Revised NP-NCD Guidelines:
Challenges to Palliative Care:
Way Forward:
| Additional Information:
About Non Communicable Disease (NCD):
Status of NCDs in India:
|
News Source: The Hindu
Context:
Union Home Minister and Minister of Cooperation will inaugurate a day-long mega conclave “Strengthening PACS through FPOs” in New Delhi on July 14, 2023.
More on News:
About Primary Agricultural Credit Societies (PACS):
Functioning of PACS:
Concern:
Significance:
| Additional Information:
About Farmers Producer Organisation (FPO)
|
News Source: PIB
Context:
Leaders of the Solomon Islands and China promised to expand relations that have fuelled unease in the U.S and Australia about China’s influence in the South Pacific.
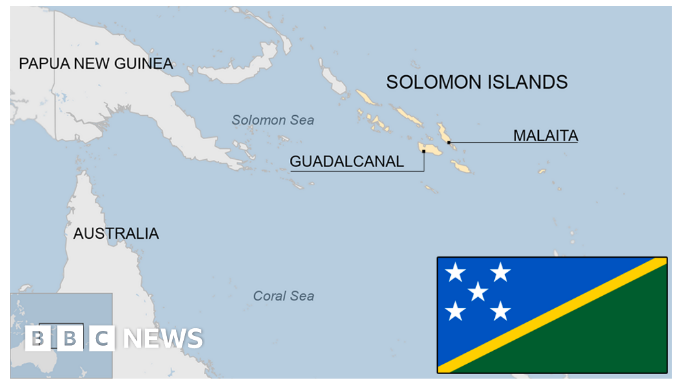
Image Source: BBC
More on News:
Concerns of USA and Australia
Attempt to dominate Pacific Island countries
| Additional Information:
About Solomon Islands:
Pacific Island countries: Fiji, Kiribati, Marshall Islands, Micronesia, Nauru, Palau, Papua New Guinea, Samoa, Solomon Islands, Tonga, Tuvalu, Vanuatu, Cook Islands, and Niue. |
News Source: The Hindu
Context:
Recently, the Prime Minister appreciated the role of Unified Logistics Interface Platform (ULIP) in transforming India’s logistics sector.
About ULIP:
Objectives:
Components
Benefits of ULIP:
A) To Government:
B) To Service Providers, Shippers, Transporters:
News Source: pib
Context:
The unwillingness of many leading countries in Africa, Asia and Latin America to stand with NATO over the war in Ukraine has brought to the fore once again the term “Global South.”
About Global South:
About Global North:
|
Classification of Countries as per the Cold War metrics:
News Source: The Hindu
Context:
Researchers at Microsoft announced that they had figured out a way to create a strange kind of particle called Majorana zero modes, that could potentially revolutionise quantum computing.
About Majorana Zero Mode:
Application of Majorana Zero Mode:
Antiparticle
Fermion
|
News Source: The Hindu
Context:
As part of the third G20 culture working group (CWG) meeting in Hampi, a Guinness world record was created for the largest display of Lambani items titled with ‘Threads of Unity’.
About Lambani Embroidery:
News Source: Indian Express
Context:
Recently, the Urban 20 Mayoral Summit was held in Gandhinagar.
About the Summit:
G20 Communiqué from the Mayors to G20 leaders:
News Source: pib
SC Verdict on Newsclick Shows Adherence to Due Pro...
Stay Invested: On Chabahar and India-Iran Relation...
Credit Rating Agencies, Impact on India’s De...
Catapulting Indian Biopharma Industry
Globalisation Under Threat, US Import Tariffs Have...
Global Report on Hypertension, Global Insights and...
<div class="new-fform">
</div>
