Context: Recently, the Indian Prime Minister arrived in Paris on a two-day official visit.
Significance of France for India

Future Course of Action: France, India, and the world
| Additional Information:
Highlight of Visit
|
News Source: The Indian Express
Context:
ISRO is set to launch the Chandrayaan 3 spacecraft using the LVM3 rocket from Satish Dhawan Space Centre in Sriharikota, India.
About:
Chandrayaan-3’s objectives:
How will Chandrayaan-3 get to the lunar surface?
Advanced technology Equipments on lander to ensure proper soft landing:
Rover Payloads:
Lander payloads:
Key differences between Chandrayaan-2 and Chandrayaan-3:

Image Credits: Indian Express
Relevance of Chandrayaan-3 for India:
Significance of the moon mission:
| Additional Information:
Why hasn’t any spacecraft ever landed near the lunar south pole?
Why do scientists want to explore the lunar south pole?
|
News Source: The Hindu
Context:
India has been experiencing the double burden of two debilitating and severe epidemics – type 2 diabetes (a.k.a. diabetes mellitus, DM) and tuberculosis (TB). The figures for both are staggering.
Current Status:
Link between DM and TB:
| Relationship | Description |
| DM and Respiratory Infections | DM increases the risk of developing respiratory infections. |
| DM as a Risk Factor for TB | DM is a major risk factor that increases the incidence and severity of TB. |
| DM and TB Co-Infections | DM and TB co-infections have an adverse effect on TB treatment outcomes in patients. |
| Prevalence of DM and Pre-Diabetes in TB Patients |
|
Way Forward:
| Additional Information:
About Type 2 Diabetes:
About TB:
|
News Source: The Hindu
Context:
Indian government is looking at resuming operations of state-run ONGC Videsh Ltd’s (OVL) hydrocarbon exploration block in Iraq, which has been under force majeure since 2003.
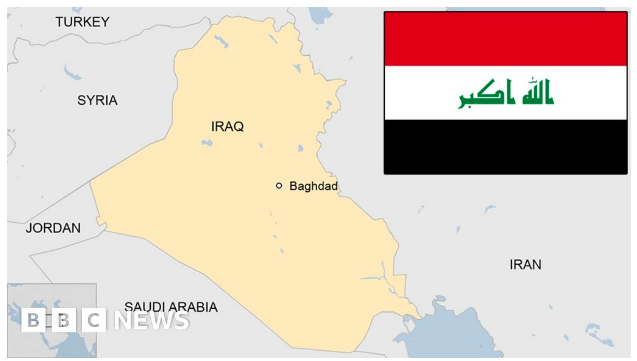
Image Source: BBC
More on News:
About IRAQ:
News Source: Livemint
Context:
The Kanwar yatra begins on the first day of Shravan and finishes on Chaturdashi Tithi, the 14th day during the waning phase of the lunar cycle.
About Kanwar Yatra:
News Source: The Indian Express
Context:
A team of doctors from Tamil Nadu along with scientists from Japan have developed a disease-modifying treatment for Duchenne Muscular Dystrophy (DMD).
About Duchenne Muscular Dystrophy(DMD):
Why are Women affected rarely by DMD?
| Additional Information:
About Dystrophin:
|
News Source : The Hindu
Why in the News?
Key Points:
Aspartame:
News Source: The Hindu
Context: Recently, the Defence Acquisition Council (DAC) approved proposals to procure 26 Rafale Marine aircraft and three additional Scorpene submarines for the Indian Navy.
About Rafale Marine Aircraft
 Their procurement from the French Government is on an Inter-Governmental Agreement (IGA) basis.
Their procurement from the French Government is on an Inter-Governmental Agreement (IGA) basis.About Scorpene submarines
About Defense Acquisition Council (DAC)
|
News Source: HT
Context: Recently, a new study of the sediments from a seasonal lake in the Kaas Plateau has indicated a major shift in the Indian Summer Monsoons towards dry and stressed conditions with low rainfall during the Early-Mid–Holocene, around 8664 years BP.
About Kaas Plateau
Image Source: The Hindu Buisnessline
News Source: The PIB
SC Verdict on Newsclick Shows Adherence to Due Pro...
Stay Invested: On Chabahar and India-Iran Relation...
Credit Rating Agencies, Impact on India’s De...
Catapulting Indian Biopharma Industry
Globalisation Under Threat, US Import Tariffs Have...
Global Report on Hypertension, Global Insights and...
<div class="new-fform">
</div>
